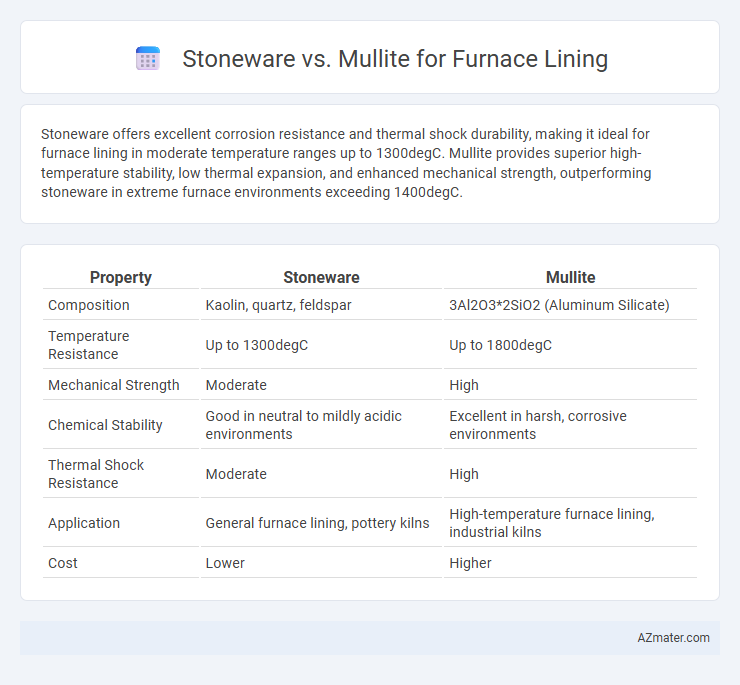
Stoneware offers excellent corrosion resistance and thermal shock durability, making it ideal for furnace lining in moderate temperature ranges up to 1300degC. Mullite provides superior high-temperature stability, low thermal expansion, and enhanced mechanical strength, outperforming stoneware in extreme furnace environments exceeding 1400degC.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stoneware | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, quartz, feldspar | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Aluminum Silicate) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1300degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Stability | Good in neutral to mildly acidic environments | Excellent in harsh, corrosive environments |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Application | General furnace lining, pottery kilns | High-temperature furnace lining, industrial kilns |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Stoneware and mullite are prominent materials used in furnace lining due to their exceptional thermal stability and resistance to corrosive environments. Stoneware, a dense and fine-grained ceramic, offers excellent durability and heat retention, making it suitable for medium-temperature applications. Mullite, containing approximately 72% alumina, excels at higher temperatures with superior thermal shock resistance and low thermal conductivity, enhancing furnace efficiency and lifespan.
Properties of Stoneware Explained
Stoneware offers high durability and excellent thermal shock resistance, making it suitable for furnace linings exposed to rapid temperature changes. Its dense, vitrified structure provides low porosity and strong resistance to chemical corrosion, ensuring longevity in harsh environments. Stoneware also maintains mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, contributing to efficient insulation and structural integrity within industrial furnaces.
Key Characteristics of Mullite
Mullite is a refractory ceramic material prized for its exceptional thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and high resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for furnace linings. Its composition primarily contains alumina and silica, which grants superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to stoneware. Mullite's porous structure allows for efficient insulation while maintaining durability at temperatures exceeding 1,700degC, outperforming traditional stoneware lining in industrial high-temperature applications.
Thermal Resistance: Stoneware vs Mullite
Stoneware exhibits moderate thermal resistance withstanding temperatures up to approximately 1200degC, making it suitable for general furnace lining applications. Mullite offers superior thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1700degC, thus preferred in high-temperature industrial furnaces. The enhanced thermal stability of mullite reduces thermal shock and extends the service life of furnace linings compared to stoneware.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Stoneware exhibits excellent compressive strength, typically ranging between 40 to 60 MPa, making it resistant to mechanical wear and thermal shock in furnace linings. Mullite, with its superior mechanical strength of approximately 100 to 150 MPa, offers enhanced durability and resistance to deformation under high-temperature conditions. The higher flexural strength and fracture toughness of mullite make it a preferred choice for furnace linings subjected to rigorous mechanical stresses and cyclic thermal loads.
Chemical Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Stoneware offers excellent chemical durability and corrosion resistance due to its dense, vitrified structure composed mainly of aluminosilicate compounds, making it suitable for moderate furnace environments. Mullite, with higher alumina content and superior phase stability at elevated temperatures, provides outstanding chemical inertness and resistance to slag attack and acidic gases, extending furnace lining longevity in harsh conditions. The choice between stoneware and mullite hinges on the specific chemical aggressiveness and thermal demands of the furnace atmosphere.
Cost and Availability Factors
Stoneware offers a cost-effective solution for furnace lining due to its widespread availability and lower raw material expenses compared to mullite. Mullite, while providing superior thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures, tends to be more expensive and less readily accessible, impacting overall project budgets. Choosing between stoneware and mullite depends largely on budget constraints and the specific thermal requirements of the furnace application.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Stoneware furnace linings require careful handling during installation due to their brittleness and susceptibility to thermal shock, necessitating precise fitting and gradual heating cycles to prevent cracking. Mullite linings offer superior thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, allowing for more straightforward installation with reduced risk of damage and longer intervals between maintenance. Maintenance for stoneware involves frequent inspections and potential replacements of cracked sections, whereas mullite's durability results in lower maintenance costs and extended furnace operational life.
Common Applications in Industrial Furnaces
Stoneware and mullite are widely used materials for furnace linings due to their high-temperature resistance and durability. Stoneware, composed primarily of aluminosilicate clay, is commonly applied in lower temperature industrial furnaces such as those used in ceramics and glass manufacturing. Mullite, with its superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, is preferred in high-temperature environments including metallurgical furnaces and cement kilns, where resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack is critical.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Furnace Lining
Stoneware offers high mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for general furnace applications with moderate temperatures. Mullite excels with superior thermal stability and chemical resistance at higher temperatures, providing enhanced durability in extreme industrial environments. Selecting the right furnace lining material depends on the operational temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress specific to your furnace conditions.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Mullite for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com