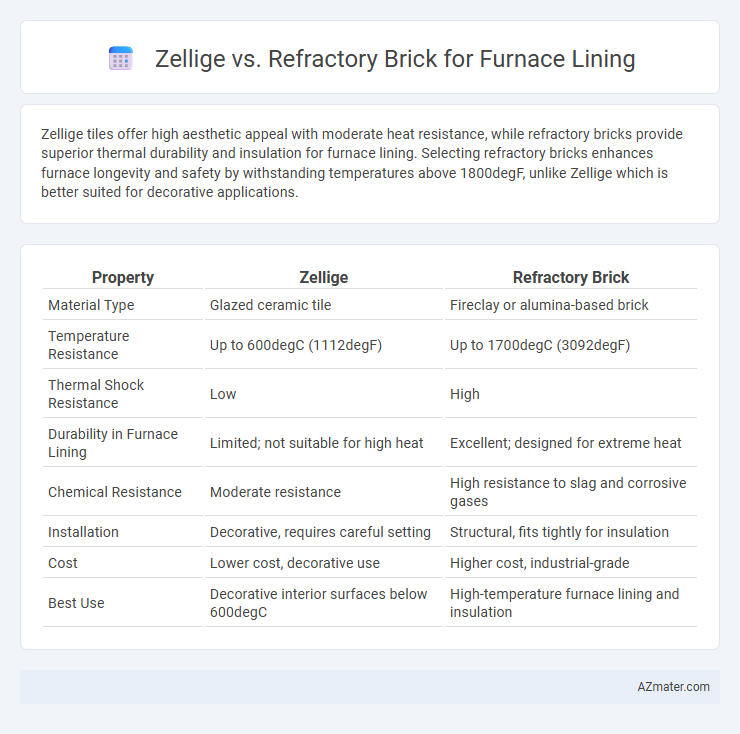
Zellige tiles offer high aesthetic appeal with moderate heat resistance, while refractory bricks provide superior thermal durability and insulation for furnace lining. Selecting refractory bricks enhances furnace longevity and safety by withstanding temperatures above 1800degF, unlike Zellige which is better suited for decorative applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Zellige | Refractory Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic tile | Fireclay or alumina-based brick |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 600degC (1112degF) | Up to 1700degC (3092degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | High |
| Durability in Furnace Lining | Limited; not suitable for high heat | Excellent; designed for extreme heat |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | High resistance to slag and corrosive gases |
| Installation | Decorative, requires careful setting | Structural, fits tightly for insulation |
| Cost | Lower cost, decorative use | Higher cost, industrial-grade |
| Best Use | Decorative interior surfaces below 600degC | High-temperature furnace lining and insulation |
Introduction to Zellige and Refractory Brick
Zellige is a traditional Moroccan ceramic tile known for its glazed, colorful, and handcrafted appearance, primarily used in decorative applications rather than industrial settings. Refractory brick, also called firebrick, is specifically engineered from high-alumina and silica materials to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock, making it ideal for furnace lining. The material properties of refractory brick provide superior heat resistance and structural integrity compared to the decorative and porous nature of Zellige.
Defining Furnace Lining Requirements
Furnace lining requirements prioritize high thermal resistance, durability under extreme temperatures, and chemical stability to protect furnace structure and ensure operational efficiency. Zellige, a handmade glazed terracotta tile, is less suitable for furnace linings due to lower refractory properties and thermal tolerance compared to refractory bricks, which are specifically engineered to withstand intense heat and corrosive environments. Selecting furnace lining material involves assessing thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and resistance to thermal shock to maintain furnace integrity and longevity.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Zellige tiles are handcrafted from natural clay, shaped and glazed through traditional Moroccan artisanal techniques, resulting in a dense, decorative ceramic product with high aesthetic appeal but moderate heat resistance. Refractory bricks consist of fireclay or high alumina materials, produced via pressing and firing at extremely high temperatures to create strong, thermally resistant monolithic blocks designed specifically for furnace lining. The manufacturing process of refractory bricks emphasizes uniformity and durability to withstand thermal shock and chemical corrosion, whereas zellige prioritizes intricate design and surface finish suitable for decorative applications.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Tolerance
Zellige tiles offer moderate thermal resistance but are generally less heat tolerant than refractory bricks, which are specifically engineered for extreme furnace conditions withstanding temperatures up to 1700degC (3092degF). Refractory bricks provide superior insulation and durability under prolonged high-temperature exposure, making them ideal for furnace lining in industrial applications. Their dense composition reduces thermal conductivity, ensuring effective heat retention and structural integrity at elevated temperatures.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Zellige tiles offer moderate chemical resistance and durability suitable for decorative applications but may falter under extreme furnace conditions. Refractory bricks, specifically engineered for high-temperature environments, provide superior chemical resistance to corrosive slags and slag attacks, ensuring long-lasting durability in furnace linings. Their dense structure and thermal stability make refractory bricks the optimal choice for industrial furnaces requiring robust chemical resilience and mechanical integrity.
Installation Methods and Ease of Application
Zellige tiles require skilled craftsmen for precise cutting and fitting due to their irregular shapes, making installation labor-intensive and time-consuming compared to refractory bricks. Refractory bricks are engineered for straightforward stacking and mortar application, allowing faster installation and uniform lining in furnaces. The choice impacts furnace downtime, with refractory bricks offering easier and quicker application for efficient maintenance schedules.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Zellige tiles offer a cost-effective option for furnace lining with lower initial material prices compared to refractory bricks, which tend to be more expensive due to their specialized high-temperature durability. Zellige's lower installation costs can reduce upfront expenses, but refractory bricks provide longer service life and better thermal resistance, potentially lowering maintenance and replacement costs over time. Evaluating economic considerations involves balancing upfront affordability against long-term durability and operational efficiency to determine the most cost-efficient solution for specific furnace applications.
Aesthetic and Functional Differences
Zellige tiles offer a handcrafted, glossy finish with intricate geometric patterns, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of furnace linings in decorative or low-heat environments. Refractory bricks provide superior thermal resistance and structural durability, making them essential for high-temperature furnace linings where functionality and safety are critical. While Zellige emphasizes visual elegance, refractory bricks prioritize heat insulation and longevity under extreme conditions.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Zellige tiles, known for their handcrafted, glazed surface, require regular cleaning to maintain their aesthetic but may develop cracks under extreme heat, impacting their lifespan in furnace lining applications. Refractory bricks, composed of high-temperature resistant materials like fireclay and alumina, offer superior durability and low maintenance, lasting significantly longer in harsh furnace environments due to their excellent thermal stability and resistance to abrasion. Choosing refractory brick over Zellige for furnace lining ensures prolonged service life and minimal upkeep, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Choosing the Best Material for Furnace Lining
Zellige tiles offer excellent thermal shock resistance and aesthetic versatility but lack the high-temperature durability of refractory bricks specifically engineered for furnace lining. Refractory bricks, made from fireclay and alumina, provide superior insulation, high strength at extreme temperatures, and long-term structural integrity essential for industrial furnaces. Selecting the best material depends on operational temperature requirements, thermal conductivity, and mechanical stress, making refractory bricks the preferred choice for high-performance furnace lining applications over decorative but less resilient Zellige tiles.
Infographic: Zellige vs Refractory Brick for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com