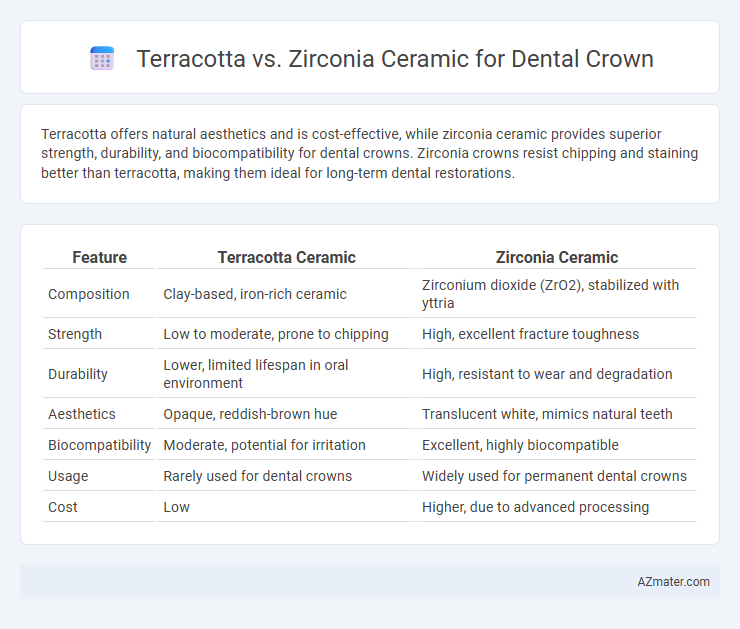
Terracotta offers natural aesthetics and is cost-effective, while zirconia ceramic provides superior strength, durability, and biocompatibility for dental crowns. Zirconia crowns resist chipping and staining better than terracotta, making them ideal for long-term dental restorations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Terracotta Ceramic | Zirconia Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay-based, iron-rich ceramic | Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), stabilized with yttria |
| Strength | Low to moderate, prone to chipping | High, excellent fracture toughness |
| Durability | Lower, limited lifespan in oral environment | High, resistant to wear and degradation |
| Aesthetics | Opaque, reddish-brown hue | Translucent white, mimics natural teeth |
| Biocompatibility | Moderate, potential for irritation | Excellent, highly biocompatible |
| Usage | Rarely used for dental crowns | Widely used for permanent dental crowns |
| Cost | Low | Higher, due to advanced processing |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crowns are primarily crafted from various ceramic materials, with terracotta and zirconia being notable examples. Terracotta crowns offer natural aesthetics and are composed of clay-based materials with a porcelain glaze, providing moderate durability suitable for anterior teeth. Zirconia crowns, made from zirconium dioxide, deliver superior strength, biocompatibility, and wear resistance, making them ideal for posterior restorations requiring long-lasting performance.
Overview of Terracotta Ceramics in Dentistry
Terracotta ceramics, composed primarily of natural clay and silica, are valued in dentistry for their biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal due to their warm, tooth-like color. Their porous structure allows for moderate strength but limits their use primarily to temporary or low-stress dental crowns. Advances in glazing techniques have improved their durability and resistance to wear, making terracotta a cost-effective option for non-load-bearing restorations.
What is Zirconia Ceramic?
Zirconia ceramic is a highly durable and biocompatible material used in dental crowns, known for its exceptional strength and natural tooth-like appearance. It is composed of zirconium dioxide, which provides resistance to fracture and wear, making it ideal for both anterior and posterior restorations. Compared to terracotta, zirconia ceramic offers superior longevity and esthetics, with increased resistance to staining and chipping.
Strength and Durability: Terracotta vs Zirconia
Zirconia ceramic crowns exhibit superior strength and durability compared to terracotta, with flexural strength typically ranging between 900 to 1200 MPa, while terracotta crowns have significantly lower strength and are prone to chipping and fracture under occlusal forces. The high fracture toughness and resistance to crack propagation in zirconia make it ideal for long-term dental restorations subjected to heavy masticatory stress. Terracotta's lower mechanical properties limit its use primarily to temporary or aesthetic applications rather than functional dental crowns.
Aesthetic Differences: Color and Translucency
Terracotta dental crowns offer a warm, natural hue that closely mimics the subtle variations in natural tooth enamel, providing excellent aesthetic appeal. Zirconia crowns excel in translucency, allowing light to pass through similarly to natural teeth, which enhances their lifelike appearance especially in the anterior region. The color stability of zirconia ensures long-term aesthetic durability, while terracotta is often preferred for its immediate, close-match color tone.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Zirconia ceramic crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to terracotta, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions and gum irritation due to their inert, non-porous surface. The high strength and durability of zirconia make it resistant to chipping and wear, enhancing patient safety by reducing the likelihood of crown failure. Terracotta, while aesthetically pleasing, often lacks the mechanical stability and biocompatibility necessary for long-term dental applications, increasing potential risks for inflammation and sensitivity.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Zirconia ceramic crowns exhibit superior wear resistance compared to terracotta, making them ideal for patients requiring durable dental restorations. The high fracture toughness and low wear rate of zirconia contribute to its longevity, often lasting 10-15 years or more under normal oral conditions. In contrast, terracotta crowns, while aesthetically pleasing, tend to wear down faster and may require replacement within 5-7 years due to lower hardness and susceptibility to chipping.
Cost Comparison: Terracotta vs Zirconia Crowns
Terracotta dental crowns typically cost between $800 and $1,500 per tooth, offering an affordable option with decent durability and aesthetics. Zirconia crowns, renowned for their superior strength and natural appearance, generally range from $1,000 to $2,500 per tooth, reflecting higher material and fabrication expenses. The cost difference is influenced by zirconia's advanced manufacturing technology and enhanced biocompatibility, making it a premium choice for long-term dental restoration.
Clinical Applications and Case Selection
Terracotta ceramics offer excellent esthetics and biocompatibility, making them suitable for anterior crowns where translucency and natural appearance are critical, especially in patients with low occlusal stress. Zirconia ceramic provides superior strength and fracture resistance, ideal for posterior crowns and bridges in cases requiring high masticatory load endurance and durability. Case selection depends on balancing esthetic demands with functional requirements, choosing terracotta for visible zones and zirconia for molar restorations or implant-supported prostheses.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations
Terracotta dental crowns offer natural aesthetics and affordability but have lower strength and wear resistance compared to zirconia ceramic crowns, which provide superior durability and biocompatibility. Key considerations when choosing between terracotta and zirconia include the crown's location in the mouth, patient's bite force, and esthetic demands. Zirconia is ideal for molars and high-stress areas, while terracotta suits front teeth with lower masticatory loads.
Infographic: Terracotta vs Zirconia Ceramic for Dental Crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com