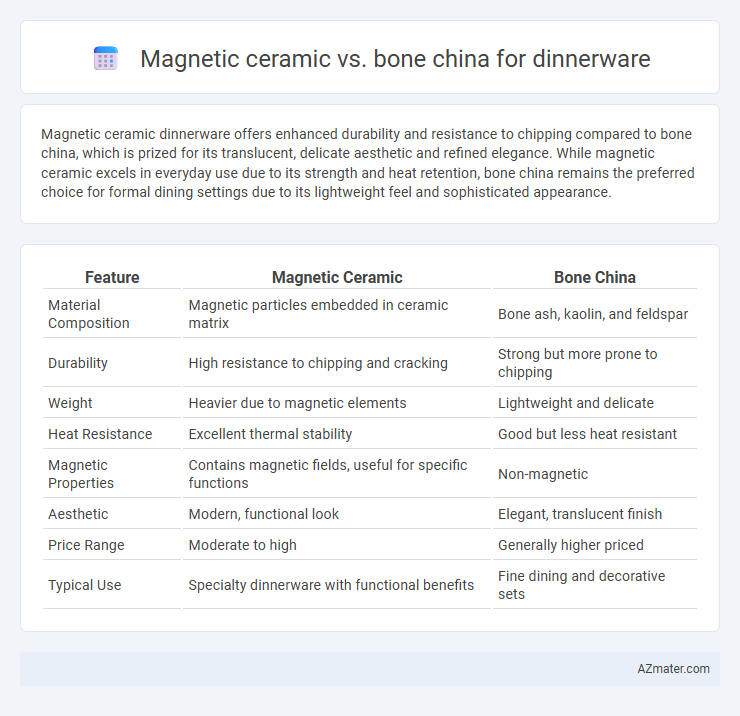
Magnetic ceramic dinnerware offers enhanced durability and resistance to chipping compared to bone china, which is prized for its translucent, delicate aesthetic and refined elegance. While magnetic ceramic excels in everyday use due to its strength and heat retention, bone china remains the preferred choice for formal dining settings due to its lightweight feel and sophisticated appearance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Magnetic Ceramic | Bone China |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Magnetic particles embedded in ceramic matrix | Bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar |
| Durability | High resistance to chipping and cracking | Strong but more prone to chipping |
| Weight | Heavier due to magnetic elements | Lightweight and delicate |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent thermal stability | Good but less heat resistant |
| Magnetic Properties | Contains magnetic fields, useful for specific functions | Non-magnetic |
| Aesthetic | Modern, functional look | Elegant, translucent finish |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Generally higher priced |
| Typical Use | Specialty dinnerware with functional benefits | Fine dining and decorative sets |
Introduction to Magnetic Ceramic and Bone China
Magnetic ceramic, known for its durability and high thermal shock resistance, is a versatile material commonly used for everyday dinnerware, offering a sturdy and chip-resistant option. Bone china, prized for its delicate translucency and lightweight feel, contains bone ash that enhances strength while providing an elegant, smooth finish ideal for formal dining settings. Both materials combine functionality with distinctive aesthetics, catering to different preferences in dinnerware performance and style.
Material Composition: Magnetic Ceramic vs Bone China
Magnetic ceramic dinnerware combines traditional ceramic materials with iron particles, enabling magnetic properties that facilitate heat retention and compatibility with induction cooktops. Bone china is composed primarily of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin clay, resulting in a lightweight, translucent material known for its strength and delicate appearance. The iron content in magnetic ceramic enhances durability and thermal efficiency, whereas bone china emphasizes fine aesthetics and chip resistance due to its unique bone ash composition.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Magnetic ceramic dinnerware is produced through advanced sintering techniques that incorporate magnetic materials into the ceramic matrix, resulting in enhanced durability and heat resistance. Bone china manufacturing involves blending bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar, followed by high-temperature firing to achieve its signature translucency and strength. The manufacturing of magnetic ceramics often requires specialized equipment to integrate magnetic properties, whereas bone china relies on traditional porcelain kilns for precise temperature control during firing.
Durability and Strength Differences
Magnetic ceramic dinnerware features high-density materials with exceptional resistance to chipping and cracking, making it highly durable for everyday use. Bone china, composed mainly of kaolin and bone ash, offers a delicate appearance but is more prone to chipping and requires careful handling. The enhanced strength of magnetic ceramic surpasses bone china, providing superior longevity and suitability for heavy-duty kitchen environments.
Weight and Thickness: Which Is Lighter?
Magnetic ceramic dinnerware is generally thicker and heavier due to its denser material composition, making it more durable but less lightweight compared to bone china. Bone china features a finer, thinner structure that results in a lighter feel and more delicate appearance, preferred for elegant dining settings. Choosing between the two depends on balancing weight preferences with durability and aesthetic appeal.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Varieties
Magnetic ceramic offers a modern aesthetic with sleek finishes and vibrant color options that enhance contemporary table settings, while bone china is renowned for its classic elegance, translucency, and delicate patterns, making it a timeless choice for formal dining. Bone china's design varieties often include intricate floral motifs, gold or platinum accents, and traditional shapes, whereas magnetic ceramic boasts innovative textures and bold, minimalist designs catering to eclectic and casual dining styles. The choice between magnetic ceramic and bone china depends largely on desired aesthetic appeal, with magnetic ceramic appealing to trend-conscious users and bone china favored for its refined sophistication.
Heat Retention and Microwave Safety
Magnetic ceramic dinnerware offers superior heat retention due to its dense, vitrified structure, keeping food warm longer compared to bone china, which has a more porous composition. Bone china excels in microwave safety, being lightweight and less prone to thermal shock, whereas some magnetic ceramic plates may contain metal oxides that can interfere with microwave use. Choosing between these materials depends on prioritizing consistent heat retention or versatile microwave compatibility for dining needs.
Maintenance: Cleaning and Stain Resistance
Magnetic ceramic dinnerware offers exceptional stain resistance due to its dense, non-porous surface, making cleaning easier and less prone to discoloration from food and beverages. Bone china, while elegant and lightweight, requires gentler handling and cleaning to prevent surface scratches and yellowing, particularly when exposed to harsh detergents or abrasive scrubbing pads. Both materials benefit from mild detergents and hand washing, but magnetic ceramic excels in durability and low-maintenance care for everyday use.
Cost Comparison and Value for Money
Magnetic ceramic dinnerware typically offers a more affordable price point compared to bone china, making it ideal for budget-conscious consumers. Bone china, while generally more expensive due to its refined materials and delicate crafting process, provides superior durability and a luxurious finish that enhances its long-term value. When assessing value for money, magnetic ceramic excels in everyday practicality, whereas bone china is preferred for formal settings and those seeking prestige in their dinnerware collection.
Choosing the Right Dinnerware for Your Needs
Magnetic ceramic offers exceptional durability and heat retention, making it ideal for everyday use and high-temperature cooking. Bone china is prized for its delicate translucency and lightweight feel, providing an elegant option suited for formal dining and special occasions. Selecting between magnetic ceramic and bone china depends on whether you prioritize resilience and practicality or refined aesthetics and tradition in your dinnerware collection.
Infographic: Magnetic ceramic vs Bone china for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com