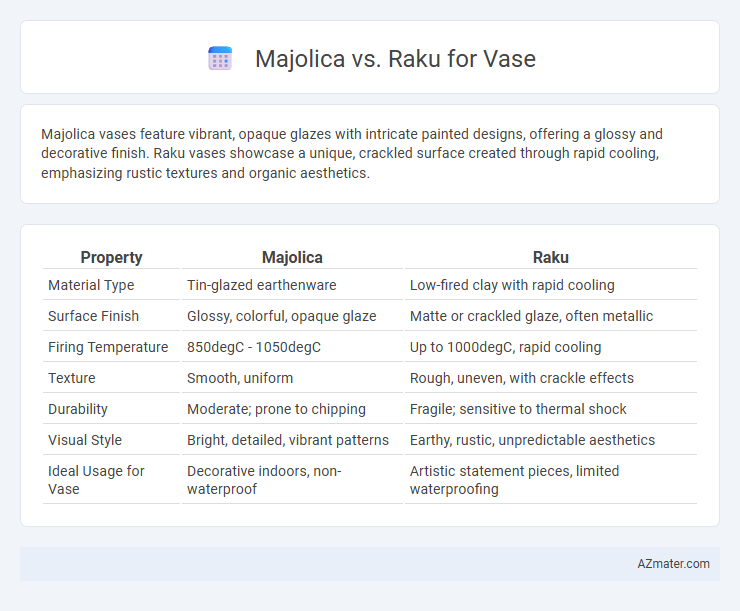
Majolica vases feature vibrant, opaque glazes with intricate painted designs, offering a glossy and decorative finish. Raku vases showcase a unique, crackled surface created through rapid cooling, emphasizing rustic textures and organic aesthetics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Majolica | Raku |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Tin-glazed earthenware | Low-fired clay with rapid cooling |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, colorful, opaque glaze | Matte or crackled glaze, often metallic |
| Firing Temperature | 850degC - 1050degC | Up to 1000degC, rapid cooling |
| Texture | Smooth, uniform | Rough, uneven, with crackle effects |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chipping | Fragile; sensitive to thermal shock |
| Visual Style | Bright, detailed, vibrant patterns | Earthy, rustic, unpredictable aesthetics |
| Ideal Usage for Vase | Decorative indoors, non-waterproof | Artistic statement pieces, limited waterproofing |
Introduction to Majolica and Raku
Majolica pottery features a vibrant tin-glazed finish that creates a glossy, opaque surface ideal for decorative vases, originating from the Italian Renaissance. Raku pottery, developed in 16th-century Japan, is distinguished by its rapid firing process and unique smoke patterns, producing organic textures and unpredictable crackle effects on vases. Both techniques offer distinctive aesthetic and tactile qualities, with Majolica showcasing intricate, colorful designs and Raku emphasizing natural, earthy imperfections.
Historical Background of Majolica and Raku
Majolica pottery, originating from the Italian Renaissance period in the 15th century, is renowned for its tin-glazed earthenware adorned with vibrant, detailed painted designs. Raku pottery, developed in 16th-century Japan, features a unique low-firing process that produces distinctive crackled surfaces and spontaneous glaze effects, deeply rooted in Zen Buddhist tea ceremonies. Both techniques reflect rich cultural heritages, with Majolica emphasizing ornamental storytelling and Raku embodying philosophical simplicity and natural aesthetics.
Materials and Clay Types Used
Majolica vases are crafted using refined white earthenware clay, coated with a tin-based, glossy glaze that creates a bright, opaque surface ideal for colorful, detailed designs. Raku vases employ a porous, low-fire clay body designed to withstand rapid temperature changes during the unique raku firing process, resulting in a textured, often crackled surface. The fundamental difference lies in Majolica's smooth, vibrant finish achieved through tin glazing versus Raku's raw, organic aesthetic influenced by its specialized firing and clay composition.
Glazing Techniques Compared
Majolica glazing features a tin-based white opaque glaze that provides a smooth, glossy surface ideal for vibrant, detailed painted designs, while Raku employs a low-temperature firing followed by rapid cooling, producing crackled, smoky, and often metallic finishes with unique textures. Majolica's glazing technique emphasizes bright, colorful motifs sealed under a clear glaze, preserving intricate patterns and enhancing durability. In contrast, Raku's glazing process creates unpredictable, organic effects with a matte or semi-gloss finish, valued for its artistic spontaneity and one-of-a-kind appearance in vases.
Firing Processes: Majolica vs Raku
Majolica vases undergo a low-temperature firing process around 980degC (1800degF), where a tin-based white glaze is applied before a second glaze firing, resulting in smooth, opaque, and brightly colored surfaces. Raku vases are fired rapidly at lower temperatures (approximately 800-1000degC or 1470-1830degF) and removed while glowing hot, then subjected to post-firing reduction by placing them in combustible materials, creating unique crackled textures and smoky, unpredictable glaze effects. The contrasting firing techniques directly influence the durability, surface finish, and aesthetic qualities distinctive to each ceramic style.
Color Palette and Surface Effects
Majolica vases showcase vibrant, glossy color palettes achieved through tin-glazed earthenware, producing rich blues, reds, and greens with a smooth, glassy surface. Raku vases feature more organic, unpredictable surface effects with metallic sheens and crackled textures, highlighted by a muted or smoky color palette ranging from earthy browns to iridescent blacks. The contrasting aesthetics make Majolica ideal for bold, decorative statements, while Raku suits rustic and wabi-sabi inspired spaces.
Durability and Functionality in Vases
Majolica vases offer superior durability due to their thick, glazed surface, making them resistant to chipping and suitable for both indoor and outdoor use. Raku vases, with their porous and often fragile nature, are primarily decorative and less functional for holding water or heavy use. The glazing process in Majolica enhances waterproof capabilities, whereas Raku's crackled finish requires additional sealing to ensure functionality as a vessel.
Artistic Styles and Aesthetic Appeal
Majolica vases feature vibrant, glossy glazes with intricate, colorful patterns inspired by Renaissance ceramics, emphasizing detailed hand-painted designs that evoke a lively, traditional aesthetic. Raku vases, on the other hand, showcase a more rustic and spontaneous artistic style, characterized by crackled textures, smoky hues, and unpredictable glaze effects that highlight the beauty of natural imperfections. The contrasting aesthetic appeal lies in Majolica's polished, ornamental charm versus Raku's raw, organic expression, making each style uniquely suited to different decorative themes and artistic preferences.
Common Uses and Decorative Trends
Majolica vases are commonly used for vibrant garden displays and indoor floral arrangements, characterized by their bright, glossy glazes and intricate, often floral or fruit-inspired designs. Raku vases, favored for their rustic textures and smoky, crackled finishes, serve as unique accent pieces in contemporary and minimalist decor, emphasizing handmade artistry and organic forms. Decorative trends show a growing preference for Majolica in traditional and Mediterranean-style interiors, while Raku appeals more to modern, eclectic spaces seeking natural imperfection and wabi-sabi aesthetics.
Choosing Between Majolica and Raku for Vases
Choosing between Majolica and Raku for vases depends on the desired aesthetic and durability. Majolica offers vibrant, glossy glazes with intricate hand-painted designs, ideal for colorful, decorative pieces. Raku vases feature unique, crackled textures and earthy tones resulting from rapid firing processes, preferred for rustic and artistic expressions.
Infographic: Majolica vs Raku for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com