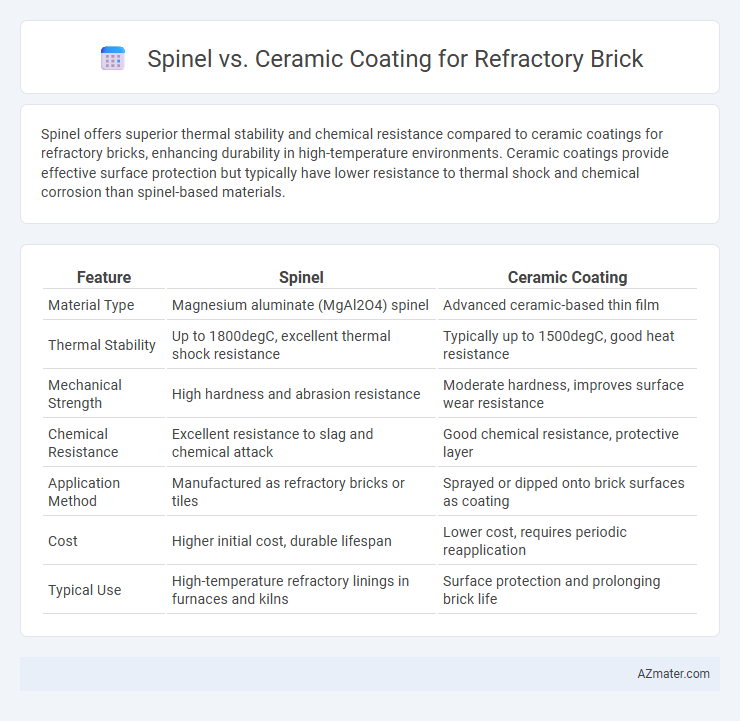
Spinel offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance compared to ceramic coatings for refractory bricks, enhancing durability in high-temperature environments. Ceramic coatings provide effective surface protection but typically have lower resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion than spinel-based materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spinel | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) spinel | Advanced ceramic-based thin film |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1800degC, excellent thermal shock resistance | Typically up to 1500degC, good heat resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High hardness and abrasion resistance | Moderate hardness, improves surface wear resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to slag and chemical attack | Good chemical resistance, protective layer |
| Application Method | Manufactured as refractory bricks or tiles | Sprayed or dipped onto brick surfaces as coating |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, durable lifespan | Lower cost, requires periodic reapplication |
| Typical Use | High-temperature refractory linings in furnaces and kilns | Surface protection and prolonging brick life |
Introduction to Refractory Brick Protection
Refractory brick protection relies heavily on advanced coatings like spinel and ceramic to enhance durability and thermal stability. Spinel coatings offer excellent resistance to slag and high-temperature corrosion due to their unique crystalline structure. Ceramic coatings provide superior thermal insulation and chemical resistance, extending the lifespan of refractory bricks in extreme industrial environments.
Overview of Spinel Coatings
Spinel coatings for refractory bricks provide exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance, enhancing durability in high-temperature industrial environments. Composed primarily of magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4), spinel forms a dense, adherent layer that protects bricks from corrosion and slag penetration. This coating's superior hardness and resistance to thermal shock make it a preferred choice over traditional ceramic coatings for extending refractory brick lifespan.
Overview of Ceramic Coatings
Ceramic coatings provide a durable, heat-resistant layer that enhances the performance and longevity of refractory bricks by protecting against high temperatures and chemical corrosion. Spinel coatings, while offering excellent thermal stability and resistance to slag attack, are often less flexible in application compared to ceramic coatings, which form a more uniform and adherent surface. The advanced microstructure of ceramic coatings improves thermal insulation and mechanical strength, making them a preferred choice for extending refractory brick lifespan in extreme industrial environments.
Key Properties Comparison: Spinel vs Ceramic
Spinel refractory bricks exhibit superior thermal stability and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications, while ceramic coatings provide exceptional surface hardness and wear resistance with enhanced protection against slag and abrasion. Spinel's key properties include high melting points above 2135degC and strong resistance to lime and alkali attack, whereas ceramic coatings offer lower thermal conductivity and greater flexibility to accommodate thermal expansion. In terms of durability, spinel bricks tend to maintain structural integrity under prolonged thermal cycling, whereas ceramic coatings extend service life by minimizing surface degradation and improving cleanliness.
Thermal Resistance Performance
Spinel coatings exhibit superior thermal resistance due to their ability to maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1500degC, making them ideal for refractory bricks exposed to extreme heat. Ceramic coatings provide excellent thermal barrier properties and chemical stability, typically effective up to 1300degC, but may experience degradation under prolonged high-temperature cycling. The choice between spinel and ceramic coatings hinges on specific thermal exposure conditions, with spinel preferred for ultra-high-temperature applications requiring enhanced durability and thermal shock resistance.
Chemical Corrosion Resistance
Spinel coatings exhibit superior chemical corrosion resistance for refractory bricks due to their stable crystal structure and strong bonding with the substrate, effectively resisting slag and acidic environments. Ceramic coatings also provide good protection but tend to be more porous and less chemically inert than spinel, leading to faster degradation under aggressive chemical attacks. The enhanced durability of spinel coatings in high-temperature, corrosive settings makes them ideal for extending the service life of refractory bricks in industrial furnaces and kilns.
Mechanical Durability and Wear
Spinel coatings offer superior mechanical durability for refractory bricks due to their high hardness and excellent thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for environments subjected to intense mechanical stress. Ceramic coatings provide enhanced wear resistance by forming a dense, chemically stable barrier that protects refractory surfaces from abrasion and corrosion. Selecting spinel or ceramic coatings depends on balancing the need for impact resistance versus long-term wear protection in high-temperature industrial applications.
Application Methods and Ease of Installation
Spinel coatings typically require high-temperature curing and precise mixing ratios, making their application more complex and time-consuming compared to ceramic coatings. Ceramic coatings offer easier application methods such as spraying or brushing without the need for intense heat curing, enabling faster installation on refractory bricks. The simpler preparation and curing process of ceramic coatings results in reduced labor costs and minimizes application errors on-site.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Spinel coatings offer moderate cost-effectiveness for refractory bricks by providing good thermal stability and corrosion resistance at a lower price point compared to advanced ceramic coatings. Ceramic coatings, while more expensive upfront, deliver superior durability and longer service life, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over time. In high-temperature industrial environments, investing in ceramic coatings can yield better long-term economic benefits despite the initial higher cost.
Choosing the Best Coating for Your Refractory Needs
Spinel coatings offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature refractory brick applications in industrial furnaces. Ceramic coatings provide excellent abrasion resistance and lower thermal conductivity, enhancing the lifespan and insulating properties of refractory surfaces. Selecting the best coating depends on specific operational conditions, with Spinel favored for extreme heat and chemical exposure, while ceramic coatings are preferred for wear resistance and thermal insulation.
Infographic: Spinel vs Ceramic coating for Refractory brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com