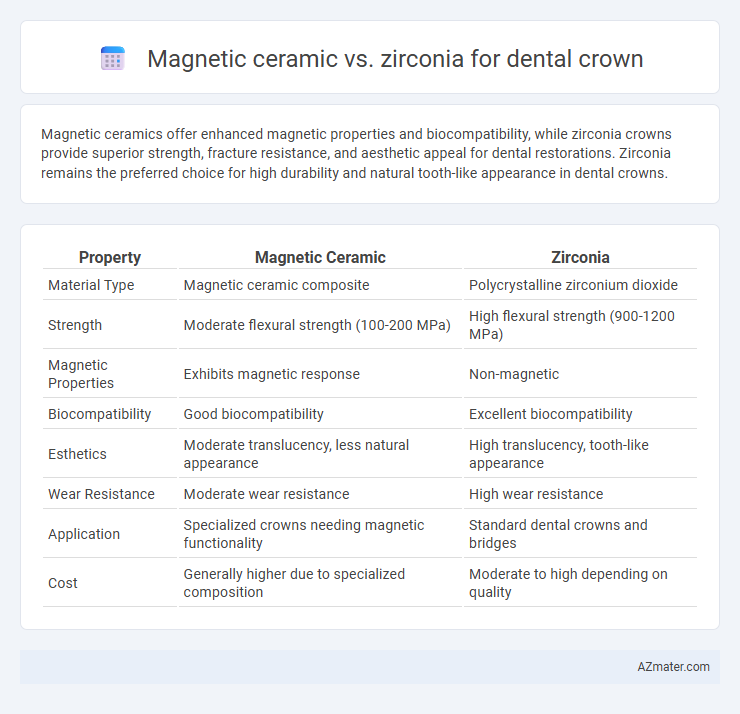
Magnetic ceramics offer enhanced magnetic properties and biocompatibility, while zirconia crowns provide superior strength, fracture resistance, and aesthetic appeal for dental restorations. Zirconia remains the preferred choice for high durability and natural tooth-like appearance in dental crowns.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Ceramic | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Magnetic ceramic composite | Polycrystalline zirconium dioxide |
| Strength | Moderate flexural strength (100-200 MPa) | High flexural strength (900-1200 MPa) |
| Magnetic Properties | Exhibits magnetic response | Non-magnetic |
| Biocompatibility | Good biocompatibility | Excellent biocompatibility |
| Esthetics | Moderate translucency, less natural appearance | High translucency, tooth-like appearance |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate wear resistance | High wear resistance |
| Application | Specialized crowns needing magnetic functionality | Standard dental crowns and bridges |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized composition | Moderate to high depending on quality |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dental crowns require materials that offer durability, biocompatibility, and aesthetic appeal, with magnetic ceramics and zirconia being prominent options. Magnetic ceramics provide enhanced bonding capabilities and improved mechanical strength, while zirconia crowns are widely favored for their exceptional toughness and natural tooth-like appearance. Selecting the appropriate dental crown material depends on factors such as patient-specific needs, crown location, and long-term performance expectations.
Overview of Magnetic Ceramic Crowns
Magnetic ceramic crowns utilize embedded magnetic components to enhance retention and stability by attracting corresponding magnetic elements in dental restorations. These crowns combine advanced ceramic materials with biocompatible magnets, offering improved fitting precision and durability compared to traditional zirconia crowns. Their unique magnetic properties facilitate easier placement and removal, making them a promising option for patients requiring removable or hybrid dental prosthetics.
Zirconia Crowns: Properties and Applications
Zirconia crowns offer exceptional strength, durability, and biocompatibility, making them a preferred choice for dental restorations requiring high resistance to fracture and wear. Their aesthetic properties include a natural tooth-like translucency and color, which can be customized to match surrounding teeth, enhancing patient satisfaction. Commonly used in both anterior and posterior crowns, zirconia's resistance to corrosion and minimal thermal conductivity contribute to long-lasting performance and patient comfort.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Magnetic ceramic crowns offer moderate strength and good durability due to their metal-infused structure, making them suitable for patients needing enhanced retention. Zirconia crowns exhibit superior strength and exceptional durability, resisting fractures and wear even under high bite forces, making them ideal for molars and long-term restorations. Comparative studies show zirconia outperforms magnetic ceramic in fracture toughness and lifespan, ensuring better performance in demanding dental applications.
Esthetics: Color and Translucency
Magnetic ceramic crowns offer enhanced esthetics with superior translucency and a natural color match that mimics the light-reflecting properties of natural teeth. Zirconia crowns provide high strength but often lack the same level of translucency, resulting in a more opaque appearance that can compromise natural-looking aesthetics. Advances in magnetic ceramic technology make it an ideal choice when precise color blending and lifelike translucency are essential for dental restorations.
Biocompatibility and Oral Health
Magnetic ceramic crowns offer excellent biocompatibility with minimal allergic reactions, promoting healthy gum tissue and reducing inflammation risks. Zirconia crowns are highly biocompatible, known for their chemical inertness and resistance to plaque accumulation, which helps maintain oral hygiene and prevent gum disease. Both materials support oral health, but zirconia's superior strength and lower bacterial adhesion make it a preferred choice for long-term dental restorations.
Longevity and Wear Resistance
Magnetic ceramics for dental crowns exhibit enhanced longevity due to their superior resistance to fracture and chipping compared to traditional zirconia. Zirconia crowns, known for their high wear resistance and biocompatibility, maintain durability under occlusal forces but may experience gradual surface wear over time. Advanced magnetic ceramics combine magnetic properties with optimized microstructure, resulting in crowns with improved wear resistance and extended service life in restorative dentistry.
Preparation and Placement Differences
Magnetic ceramic crowns require minimal tooth preparation due to their adhesive capabilities, preserving more natural enamel compared to zirconia crowns, which often necessitate more aggressive tooth reduction for proper thickness and strength. Placement of magnetic ceramic crowns involves precise alignment with magnetic inserts to enhance retention and stability, whereas zirconia crowns typically rely on traditional luting cements and physical fit for secure placement. The differing preparation depths impact chair time, patient comfort, and long-term durability of the restoration.
Cost Analysis: Magnetic Ceramic vs Zirconia
Magnetic ceramic dental crowns typically offer a cost-effective option compared to zirconia crowns, often priced 20-30% lower due to simpler manufacturing processes and less expensive raw materials. Zirconia crowns, although more costly initially, provide superior durability and strength, potentially reducing long-term replacement expenses. Cost analysis should also consider factors such as aesthetic appeal, patient preferences, and treatment complexity, where zirconia may justify the higher upfront investment.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Dental Needs
Magnetic ceramics offer excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for patients with metal sensitivities, while zirconia crowns are highly favored for their superior strength, durability, and natural tooth-like appearance. Zirconia's resistance to wear and fracture suits high-stress areas like molars, whereas magnetic ceramics excel in aesthetic zones requiring metal-free solutions. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as bite force, esthetic demands, and potential allergies, ensuring long-lasting performance and patient comfort.
Infographic: Magnetic ceramic vs Zirconia for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com