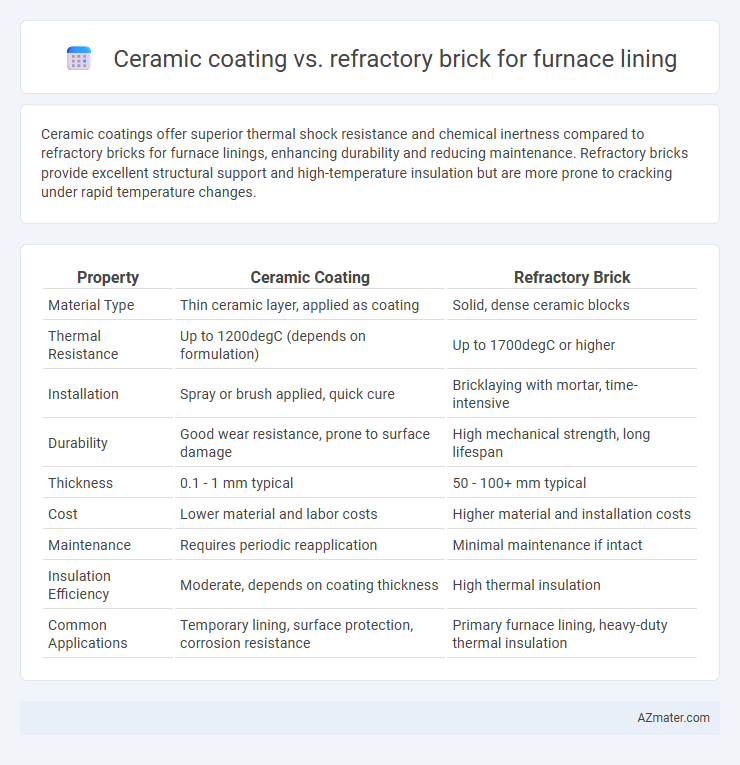
Ceramic coatings offer superior thermal shock resistance and chemical inertness compared to refractory bricks for furnace linings, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance. Refractory bricks provide excellent structural support and high-temperature insulation but are more prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Coating | Refractory Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thin ceramic layer, applied as coating | Solid, dense ceramic blocks |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 1200degC (depends on formulation) | Up to 1700degC or higher |
| Installation | Spray or brush applied, quick cure | Bricklaying with mortar, time-intensive |
| Durability | Good wear resistance, prone to surface damage | High mechanical strength, long lifespan |
| Thickness | 0.1 - 1 mm typical | 50 - 100+ mm typical |
| Cost | Lower material and labor costs | Higher material and installation costs |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic reapplication | Minimal maintenance if intact |
| Insulation Efficiency | Moderate, depends on coating thickness | High thermal insulation |
| Common Applications | Temporary lining, surface protection, corrosion resistance | Primary furnace lining, heavy-duty thermal insulation |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Solutions
Furnace lining solutions play a critical role in enhancing thermal efficiency and durability in high-temperature industrial applications. Ceramic coatings provide a thin, heat-resistant barrier that improves surface performance by reducing corrosion and oxidation, while refractory bricks offer robust structural insulation designed to withstand extreme thermal and mechanical stresses. Choosing between ceramic coating and refractory bricks depends on specific operational requirements such as temperature range, mechanical load, and maintenance needs.
Overview of Ceramic Coating Technology
Ceramic coating technology for furnace lining provides a thin, durable layer that enhances thermal insulation and protects metal surfaces from high temperatures and chemical corrosion. This advanced coating forms a heat-resistant barrier that extends furnace life while reducing maintenance costs compared to traditional refractory bricks. Ceramic coatings offer improved thermal efficiency and faster heat transfer, leading to energy savings and optimized furnace performance.
Understanding Refractory Brick Linings
Refractory brick linings provide superior thermal insulation and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature furnace environments where durability is critical. Unlike ceramic coatings, refractory bricks maintain structural integrity under prolonged thermal cycling and mechanical stress, effectively protecting furnace walls from extreme heat and corrosive gases. Their dense composition and tailored formulation ensure consistent performance in industrial furnaces, optimizing energy efficiency and extending maintenance intervals.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Ceramic coatings and refractory bricks both provide essential thermal insulation for furnace linings but differ significantly in thermal performance. Ceramic coatings offer superior thermal shock resistance and faster heat dissipation due to their thin, uniform layers, enabling efficient energy use and rapid temperature cycling. Refractory bricks provide high thermal mass and durability, maintaining stable temperatures over longer periods but with slower heat transfer and less responsiveness to rapid temperature changes.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Ceramic coatings offer superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, enhancing furnace lining durability through their ability to withstand rapid temperature fluctuations and aggressive environments. Refractory bricks provide robust mechanical strength and long-term structural stability, ensuring extended service life under consistent high-temperature exposure. An optimized furnace lining often integrates ceramic coatings to protect and prolong the lifespan of refractory bricks, combining the benefits of both materials for maximum durability and longevity.
Installation Process and Complexity
Ceramic coating offers a streamlined installation process involving surface cleaning and spraying, resulting in a thin, uniform protective layer that adheres quickly to furnace interiors. Refractory brick lining requires skilled masonry work with precise brick placement and mortar curing, leading to a more labor-intensive and time-consuming installation. The complexity of refractory brick installation demands specialized craftsmanship to ensure thermal stability, whereas ceramic coatings provide faster turnaround with less structural alteration.
Maintenance Requirements and Cost
Ceramic coating for furnace lining offers low maintenance due to its resistance to chemical corrosion and ease of cleaning, with initial costs typically lower than refractory bricks. Refractory bricks, while more expensive and requiring skilled installation, provide superior durability and thermal resistance, necessitating periodic inspection and potential replacement to maintain efficiency. Over time, ceramic coatings reduce maintenance downtime, whereas refractory bricks incur higher maintenance costs linked to crack repairs and lining renewal.
Resistance to Chemical and Thermal Shock
Ceramic coatings offer superior resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock due to their dense, non-porous structure, effectively protecting furnace linings from aggressive slags and high temperature fluctuations. Refractory bricks provide durability and thermal mass but are more susceptible to chemical attack and cracking under rapid temperature changes, which can compromise the integrity of the furnace lining. The advanced formulation of ceramic coatings enhances longevity and performance in chemically harsh and thermally unstable environments compared to traditional refractory bricks.
Suitability for Various Furnace Types
Ceramic coatings provide excellent heat resistance and chemical stability, making them suitable for high-temperature furnaces with rapid thermal cycling such as glass melting or metal heat treatment furnaces. Refractory bricks offer superior mechanical strength and insulation, ideal for blast furnaces, cement kilns, and industrial furnaces requiring robust structural support and prolonged high-temperature exposure. Selecting between ceramic coatings and refractory bricks depends on furnace operating temperature, thermal shock resistance, and physical durability needs specific to the furnace type.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic coatings for furnace lining offer a lightweight, energy-efficient solution by reducing heat loss and lowering fuel consumption, which subsequently decreases greenhouse gas emissions. Refractory bricks, composed of dense, natural materials like alumina and silica, provide durability and thermal insulation but require significant energy for manufacturing and often result in higher carbon footprints. Choosing ceramic coatings can enhance sustainability by improving thermal efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of furnace operation, while refractory bricks contribute to longevity but may involve more resource-intensive production processes.
Infographic: Ceramic coating vs Refractory brick for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com