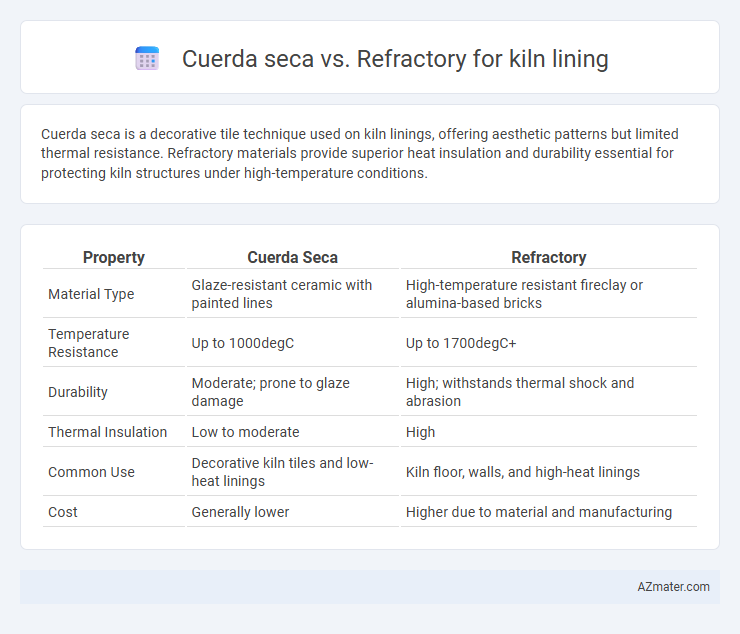
Cuerda seca is a decorative tile technique used on kiln linings, offering aesthetic patterns but limited thermal resistance. Refractory materials provide superior heat insulation and durability essential for protecting kiln structures under high-temperature conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cuerda Seca | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glaze-resistant ceramic with painted lines | High-temperature resistant fireclay or alumina-based bricks |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1700degC+ |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to glaze damage | High; withstands thermal shock and abrasion |
| Thermal Insulation | Low to moderate | High |
| Common Use | Decorative kiln tiles and low-heat linings | Kiln floor, walls, and high-heat linings |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to material and manufacturing |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Techniques
Kiln lining techniques such as cuerda seca and refractory materials are essential for thermal insulation and durability in high-temperature environments. Cuerda seca, an artistic method using wax resist and colored glazes, provides decorative yet functional ceramic tile linings, commonly found in traditional kilns with moderate thermal stress. In contrast, refractory linings, composed of high-quality firebricks and castables, offer superior heat resistance and structural integrity, making them ideal for modern industrial kilns operating at extremely high temperatures.
What is Cuerda Seca?
Cuerda seca is a traditional ceramic glazing technique used in kiln lining that involves applying colored glazes separated by a greasy resist to prevent colors from mixing, creating intricate, vibrant patterns. This method contrasts with refractory linings, which prioritize high heat resistance and structural stability using materials like firebricks or castables to withstand extreme kiln temperatures. Cuerda seca offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and precise color definition but is less focused on thermal durability compared to refractory kiln linings designed for prolonged high-temperature exposure.
Understanding Refractory Material
Refractory materials used in kiln linings are designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal stress, with composition ranging from fireclay, alumina, to silica-based bricks. Cuerda seca refers to a decorative technique and does not influence the thermal insulation or durability properties critical in kiln lining performance. Selecting the right refractory involves analyzing thermal conductivity, melting point, and chemical stability to ensure energy efficiency and longevity in industrial kiln operations.
Historical Context of Cuerda Seca and Refractory
Cuerda seca, a traditional ceramic glazing technique originating in medieval Islamic art, was later adapted for kiln linings due to its heat-resistant properties and decorative appeal. Refractory materials, developed during the Industrial Revolution, offered superior thermal insulation and durability for modern kiln applications, surpassing the limitations of cuerda seca. The historical evolution from cuerda seca to refractory linings reflects advancements in material science and industrial demands for higher temperature resistance and energy efficiency.
Material Properties: Cuerda Seca vs Refractory
Cuerda seca tiles offer excellent decorative appeal with moderate thermal resistance, typically composed of glazed ceramic materials that resist thermal shock but have lower insulation properties compared to refractory bricks. Refractory linings, made from alumina, silica, or fireclay, provide superior heat resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal insulation essential for prolonged exposure to extreme kiln temperatures exceeding 1400degC. The choice between cuerda seca and refractory materials hinges on balancing thermal performance, durability, and aesthetic requirements in kiln lining applications.
Installation Methods and Techniques
Cuerda seca kiln lining involves applying a resistive slip pattern to create distinct colored areas before glazing, requiring precise hand-painting techniques and drying times to prevent smudging, making it more labor-intensive and suitable for decorative surfaces. Refractory lining installation uses castable refractories or brickwork, demanding accurate mixing and proper curing processes to ensure thermal stability and durability under high heat conditions. The choice affects maintenance and longevity, with refractory methods favoring structural integrity and cuerda seca emphasizing aesthetic detailing.
Durability and Maintenance Comparison
Cuerda seca kiln linings offer moderate durability but require frequent maintenance due to the potential for glaze cracking and tile detachment under high thermal stress. Refractory linings, composed of high-grade firebricks or castables, provide superior durability and resist thermal shock, significantly reducing maintenance intervals. The choice between cuerda seca and refractory influences kiln longevity, with refractory linings preferred for heavy-duty industrial applications demanding extended service life and lower upkeep costs.
Cost Analysis: Cuerda Seca vs Refractory
Cuerda seca kiln linings offer a lower initial cost compared to traditional refractory materials due to reduced installation time and labor requirements. However, refractory linings provide greater durability and longer lifespan, potentially lowering long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Cost analysis should weigh upfront savings of cuerda seca against the extended service life and thermal efficiency benefits of refractory linings.
Suitability for Different Types of Kilns
Cuerda seca linings are best suited for decorative kiln applications and low-temperature ceramics due to their glazed surface, which resists oxidation but may degrade under high thermal stress. Refractory linings, composed of heat-resistant materials like alumina and silica, are ideal for high-temperature kilns such as those used in industrial ceramics, glass melting, and metallurgical processes, providing superior insulation and durability. The choice between cuerda seca and refractory materials depends on kiln operating temperatures, atmosphere, and the required longevity of the lining.
Choosing the Best Kiln Lining Solution
Choosing the best kiln lining solution involves comparing Cuerda Seca and refractory materials based on thermal resistance and durability. Refractory linings offer superior heat retention and structural integrity at high temperatures, making them ideal for continuous kiln operations. Cuerda Seca techniques provide decorative and thermal insulating benefits but typically lack the long-term resilience required for industrial kiln environments.
Infographic: Cuerda seca vs Refractory for Kiln lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com