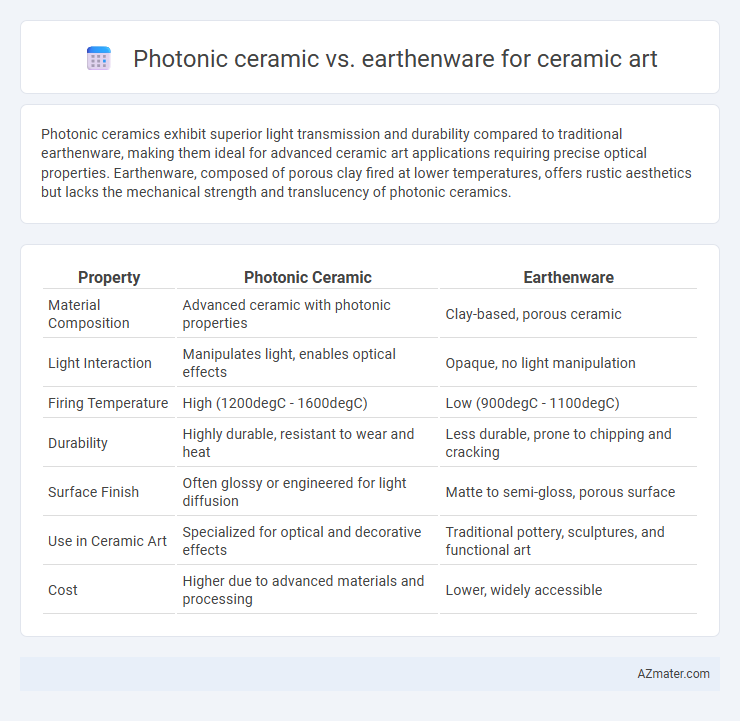
Photonic ceramics exhibit superior light transmission and durability compared to traditional earthenware, making them ideal for advanced ceramic art applications requiring precise optical properties. Earthenware, composed of porous clay fired at lower temperatures, offers rustic aesthetics but lacks the mechanical strength and translucency of photonic ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Photonic Ceramic | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Advanced ceramic with photonic properties | Clay-based, porous ceramic |
| Light Interaction | Manipulates light, enables optical effects | Opaque, no light manipulation |
| Firing Temperature | High (1200degC - 1600degC) | Low (900degC - 1100degC) |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear and heat | Less durable, prone to chipping and cracking |
| Surface Finish | Often glossy or engineered for light diffusion | Matte to semi-gloss, porous surface |
| Use in Ceramic Art | Specialized for optical and decorative effects | Traditional pottery, sculptures, and functional art |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced materials and processing | Lower, widely accessible |
Introduction to Ceramic Art Materials
Photonic ceramics, known for their advanced optical properties and high thermal stability, offer innovative possibilities in ceramic art by enabling light manipulation and enhanced durability. Earthenware, a traditional ceramic material, is porous and fired at lower temperatures, making it easier to shape but less resilient than photonic ceramics. Artists choose between these materials based on the desired balance of aesthetic qualities, structural strength, and functional performance in their ceramic artworks.
Overview of Photonic Ceramic
Photonic ceramics are advanced materials engineered to manipulate light through their unique microstructures, offering superior optical properties compared to traditional earthenware. Unlike earthenware, which is porous and primarily used for decorative or utilitarian purposes, photonic ceramics are designed for high precision in light transmission, reflection, and refraction, making them ideal for innovative ceramic art with interactive light effects. Their ability to incorporate photonic bandgap structures enables artists to create dynamic visual experiences that extend beyond conventional ceramic aesthetics.
Defining Earthenware in Ceramic Art
Earthenware in ceramic art refers to a porous, low-fired clay body typically fired between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, known for its reddish to buff color palette and relatively soft texture. Unlike photonic ceramics, which incorporate engineered microstructures to manipulate light and achieve optical effects, earthenware emphasizes traditional craftsmanship and surface decoration techniques such as glazing and painting. Its accessibility and versatility make earthenware a fundamental medium for artists seeking tactile expression and historical continuity in ceramic art.
Material Properties: Photonic Ceramic vs Earthenware
Photonic ceramic exhibits superior thermal stability and enhanced optical properties due to its engineered microstructure, making it ideal for light manipulation in ceramic art. Earthenware, composed primarily of porous clay fired at lower temperatures, offers greater absorbency and a rustic texture but lacks the strength and translucency found in photonic ceramics. Material density and refractive index differences highlight photonic ceramic's suitability for intricate, high-performance artworks compared to earthenware's traditional aesthetic and tactile qualities.
Aesthetic Qualities and Color Effects
Photonic ceramic offers vibrant, iridescent color effects due to its nanostructured surface that manipulates light, creating dynamic and luminous aesthetics not achievable with traditional earthenware. Earthenware, with its porous texture and warm, earthy tones, provides a natural, rustic charm that enhances hand-painted or glazed finishes with organic depth. The choice between photonic ceramic and earthenware significantly influences the visual impact and tactile experience of ceramic art through their distinct color vibrancy and surface qualities.
Durability and Functional Performance
Photonic ceramics offer superior durability compared to traditional earthenware due to their advanced microstructure, resulting in enhanced resistance to thermal shock and mechanical wear. Earthenware, while more porous and less durable, remains favored for its ease of shaping and traditional aesthetic in ceramic art. Functional performance of photonic ceramics excels in applications requiring high strength and stability, whereas earthenware suits decorative and low-impact functional pieces.
Creative Applications in Contemporary Art
Photonic ceramics offer innovative possibilities in contemporary ceramic art through their unique optical properties, enabling artists to manipulate light and color in ways traditional earthenware cannot. Earthenware remains favored for its tactile qualities and rustic aesthetic, providing a versatile medium for expressive, hand-crafted forms that emphasize texture and earth-toned hues. The integration of photonic ceramics with earthenware techniques fosters new creative applications, expanding artistic expression by combining luminescence and traditional ceramic forms.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Photonic ceramics and earthenware differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with photonic ceramics often requiring high-energy processes like sintering at elevated temperatures, resulting in a larger carbon footprint compared to the traditionally low-fired earthenware. Earthenware utilizes natural clay and often incorporates locally sourced materials, reducing transportation emissions and supporting sustainable practices through its biodegradability and ease of recycling. The high durability and energy-intensive production of photonic ceramics can pose sustainability challenges, while earthenware offers a more environmentally friendly alternative in ceramic art due to its minimal processing and lower resource consumption.
Cost and Accessibility for Artists
Photonic ceramics typically involve advanced materials and fabrication techniques, resulting in higher production costs compared to traditional earthenware, which uses readily available natural clays and simpler kiln processes. Earthenware remains more accessible to artists due to lower material expenses and the widespread availability of supplies and equipment in local markets. The cost-effectiveness and user-friendly nature of earthenware make it a preferred choice for artists working within budget constraints or seeking easily sourced materials.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Ceramic Art
Photonic ceramics, known for their advanced light-manipulating properties and durability, offer innovative possibilities for contemporary ceramic art that requires precision and complex visual effects. Earthenware, a traditional clay material, provides warmth and earthy texture ideal for rustic and tactile ceramic pieces, favored for its ease of shaping and firing at lower temperatures. Selecting the right material depends on the desired aesthetic, functional requirements, and firing capabilities, with photonic ceramics suited for high-tech and intricate designs, while earthenware excels in organic, classic art forms.
Infographic: Photonic ceramic vs Earthenware for Ceramic art
 azmater.com
azmater.com