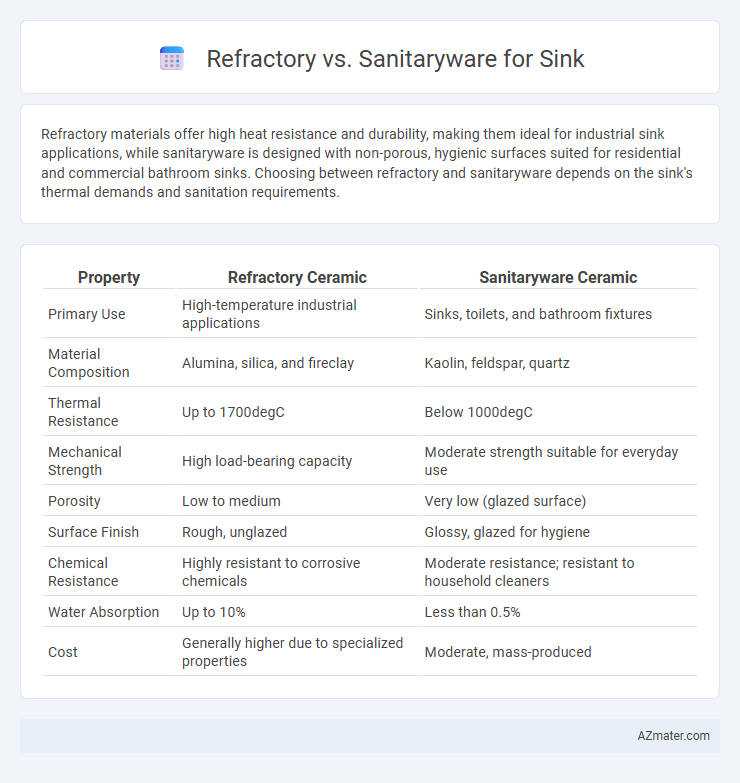
Refractory materials offer high heat resistance and durability, making them ideal for industrial sink applications, while sanitaryware is designed with non-porous, hygienic surfaces suited for residential and commercial bathroom sinks. Choosing between refractory and sanitaryware depends on the sink's thermal demands and sanitation requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Refractory Ceramic | Sanitaryware Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-temperature industrial applications | Sinks, toilets, and bathroom fixtures |
| Material Composition | Alumina, silica, and fireclay | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 1700degC | Below 1000degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High load-bearing capacity | Moderate strength suitable for everyday use |
| Porosity | Low to medium | Very low (glazed surface) |
| Surface Finish | Rough, unglazed | Glossy, glazed for hygiene |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to corrosive chemicals | Moderate resistance; resistant to household cleaners |
| Water Absorption | Up to 10% | Less than 0.5% |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized properties | Moderate, mass-produced |
Introduction to Sink Materials: Refractory vs Sanitaryware
Refractory materials used in sinks are known for their high heat resistance and durability, making them ideal for industrial kitchens and heavy-use environments. Sanitaryware sinks, typically made from vitreous china or porcelain, offer smooth, non-porous surfaces that resist stains, bacteria, and chemical damage, ensuring hygienic conditions. Choosing between refractory and sanitaryware depends on the application's thermal demands and hygiene requirements, with refractory excelling in heat tolerance and sanitaryware providing superior cleanliness and aesthetic appeal.
What is Refractory? Key Properties and Applications
Refractory materials are heat-resistant substances capable of withstanding high temperatures without melting or breaking down, commonly composed of fireclay, silica, alumina, and other ceramic compounds. Key properties of refractory materials include excellent thermal stability, resistance to chemical corrosion, high mechanical strength, and low thermal conductivity, making them ideal for environments subjected to intense heat. These materials are widely applied in industrial furnaces, kilns, reactors, and other high-temperature processing equipment, contrasting with sanitaryware used for sinks that prioritize water resistance and hygiene over heat endurance.
What is Sanitaryware? Features and Common Uses
Sanitaryware refers to ceramic or porcelain fixtures, including sinks, toilets, and bidets, designed for hygiene and water drainage in bathrooms and kitchens. Key features include smooth, non-porous surfaces resistant to stains, bacteria, and chemicals, ensuring easy cleaning and durability. Common uses encompass residential and commercial bathrooms, kitchens, hospitals, and public restrooms due to their sanitary properties and aesthetic appeal.
Refractory Sinks: Advantages and Disadvantages
Refractory sinks, crafted from heat-resistant materials such as fireclay and refractory ceramics, offer exceptional durability and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for high-temperature environments like professional kitchens and industrial settings. These sinks provide outstanding strength against chipping and cracking, but their heavier weight and higher cost compared to standard sanitaryware can pose installation challenges. Despite limited design variations, refractory sinks excel in longevity and heat endurance, balancing practical functionality with long-term investment benefits.
Sanitaryware Sinks: Pros and Cons
Sanitaryware sinks offer durability, stain resistance, and easy maintenance due to their glazed surface, making them ideal for kitchens and bathrooms. Their smooth finish resists bacterial growth, promoting hygiene, but they can chip or crack under heavy impact, which may require repairs or replacement. While refractory sinks excel in heat resistance and industrial use, sanitaryware provides aesthetic appeal and versatility for residential settings.
Durability Comparison: Refractory vs Sanitaryware
Refractory materials used in sinks offer superior heat resistance and structural durability compared to standard sanitaryware, making them ideal for high-temperature environments. Sanitaryware sinks, typically made from ceramic or porcelain, provide good durability under normal household conditions but are more prone to chipping and cracking under heavy impact or thermal shock. The enhanced thermal properties of refractory sinks ensure longer lifespan and better performance in industrial or commercial settings where durability is critical.
Aesthetic and Design Choices: Which Material Wins?
Refractory materials offer a rugged, industrial aesthetic with heat-resistant properties ideal for modern, minimalist kitchen designs, while sanitaryware provides a sleek, glossy finish that complements classic and contemporary styles with ease. Sanitaryware sinks allow for smoother, seamless integration into countertops, enhancing design fluidity and visual appeal. For homeowners prioritizing elegance and design versatility, sanitaryware often emerges as the preferred choice due to its polished look and broad stylistic compatibility.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Ease of Care
Sanitaryware sinks offer superior ease of care due to their smooth, non-porous surfaces that resist stains and require minimal maintenance with standard household cleaners. Refractory sinks, made from fireclay or composite materials, may demand specialized cleaning agents to prevent surface damage and maintain their integrity over time. Regular upkeep for sanitaryware involves simple wiping, whereas refractory sinks benefit from periodic sealing to extend durability and ease cleaning.
Cost Analysis: Refractory vs Sanitaryware Sinks
Refractory sinks, made from materials like fireclay and cast iron, typically incur higher upfront costs due to their durability and heat resistance, making them a long-term investment for industrial or heavy-duty use. Sanitaryware sinks, commonly fabricated from ceramic or porcelain, offer a more budget-friendly option with lower initial expenses but may require more frequent replacement or maintenance. Cost analysis highlights that refractory sinks justify their premium through extended lifespan and resilience, while sanitaryware sinks cater to cost-conscious buyers prioritizing immediate affordability.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider for Sinks
Refractory materials offer excellent heat resistance and durability for sinks used in industrial or high-temperature environments, while sanitaryware provides aesthetic appeal and ease of cleaning, ideal for residential and commercial bathrooms. Key factors to consider include thermal resistance, maintenance requirements, durability, and installation environment when selecting between refractory and sanitaryware sinks. Prioritizing usage context and functional needs ensures optimal performance and longevity of the sink material.
Infographic: Refractory vs Sanitaryware for Sink
 azmater.com
azmater.com