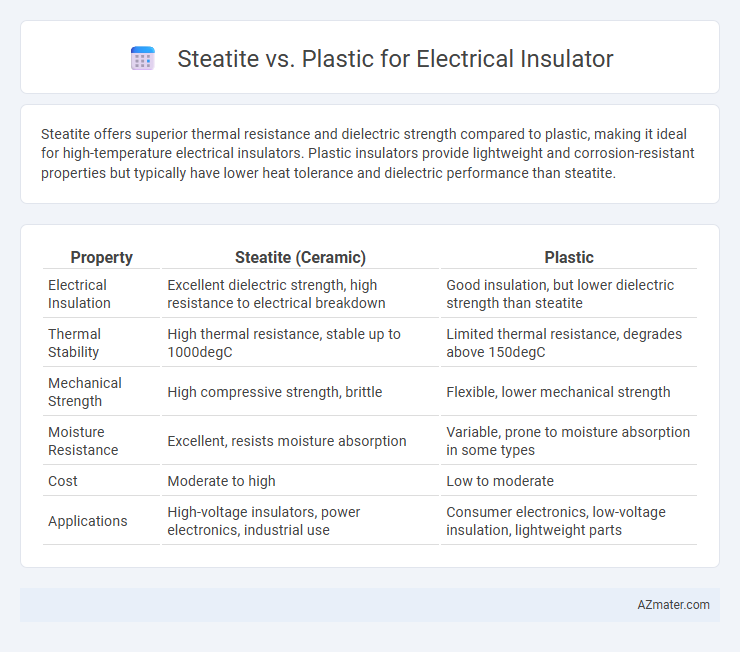
Steatite offers superior thermal resistance and dielectric strength compared to plastic, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical insulators. Plastic insulators provide lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties but typically have lower heat tolerance and dielectric performance than steatite.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Steatite (Ceramic) | Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, high resistance to electrical breakdown | Good insulation, but lower dielectric strength than steatite |
| Thermal Stability | High thermal resistance, stable up to 1000degC | Limited thermal resistance, degrades above 150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength, brittle | Flexible, lower mechanical strength |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, resists moisture absorption | Variable, prone to moisture absorption in some types |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Applications | High-voltage insulators, power electronics, industrial use | Consumer electronics, low-voltage insulation, lightweight parts |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Steatite, a dense ceramic material known for its excellent thermal stability and high dielectric strength, outperforms plastic in electrical insulation applications where heat resistance and durability are critical. Plastic insulators offer flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to moisture, making them suitable for less demanding environments. Choosing between steatite and plastic depends on specific electrical load requirements, environmental conditions, and mechanical stress factors.
What is Steatite?
Steatite, also known as soapstone, is a dense, non-porous ceramic material composed primarily of talc and other minerals, making it an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength and thermal stability. Unlike plastic insulators, steatite can withstand higher temperatures and mechanical stresses, which makes it suitable for heavy-duty electrical applications such as high-voltage insulators and electrical bushings. Its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and wear further enhances its reliability and longevity in demanding electrical environments.
What is Plastic as an Insulator?
Plastic as an electrical insulator offers excellent dielectric properties, high resistance to moisture, and easy moldability into various shapes and sizes, making it ideal for diverse electronic applications. Unlike steatite, plastic insulators are lightweight, cost-effective, and provide superior impact resistance, though they may have lower thermal stability. Common plastics used as insulators include polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC, each selected for specific voltage ratings and environmental resistances.
Key Properties of Steatite Insulators
Steatite insulators exhibit exceptional electrical insulation properties due to their high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for high-voltage applications. Their superior mechanical strength and resistance to moisture ensure reliability and longevity in harsh environmental conditions compared to plastic insulators. The natural mineral composition of steatite provides enhanced thermal stability and lower dielectric loss, optimizing performance in demanding electrical insulation tasks.
Key Properties of Plastic Insulators
Plastic insulators exhibit high dielectric strength, making them effective in preventing electrical current leakage and ensuring safety in various applications. Their resistance to moisture, chemicals, and environmental degradation provides long-term durability and reliable performance in demanding conditions. Lightweight and easy to mold, plastic insulators offer versatile design options and cost-effective manufacturing compared to traditional steatite materials.
Performance Comparison: Steatite vs Plastic
Steatite exhibits superior thermal stability and higher dielectric strength compared to plastic, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical insulation applications. Plastic insulators, while offering flexibility and lower manufacturing costs, tend to have lower heat resistance and can degrade more rapidly under electrical stress. Steatite's resistance to moisture and mechanical wear further enhances its performance and longevity in demanding electrical environments.
Durability and Life Span
Steatite exhibits superior durability compared to plastic as an electrical insulator due to its high resistance to thermal shock, mechanical stress, and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments. Its lifespan can exceed several decades, especially in high-temperature applications where plastic may degrade rapidly. While plastic insulators offer cost-effectiveness and flexibility, they generally have shorter service lives, often limited by UV exposure, aging, and lower thermal stability.
Cost Analysis
Steatite offers a cost-effective solution compared to high-performance plastics for electrical insulators, mainly due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. While plastics such as epoxy or PEEK incur higher initial costs because of complex processing and resin prices, steatite's ceramic composition ensures durability and long-term insulation at a fraction of the cost. Factoring in lifecycle costs, steatite insulators often provide superior value in high-temperature and high-voltage applications with minimal maintenance requirements.
Common Applications in Electrical Systems
Steatite, a high-grade ceramic material known for its excellent thermal stability and electrical insulation properties, is commonly used in high-temperature applications such as insulators in power transmission and microwave ovens. Plastic insulators, often made from materials like polyethylene or PVC, are prevalent in low-voltage electrical wiring and consumer electronics due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of molding into various shapes. The choice between steatite and plastic depends on environmental conditions and electrical load, with steatite preferred for high heat and mechanical stress and plastic favored for lightweight, low-stress applications.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Steatite or Plastic?
Steatite offers superior thermal stability and higher dielectric strength, making it ideal for high-temperature and high-voltage electrical insulation applications. Plastic insulators provide excellent mechanical flexibility, lightweight properties, and resistance to moisture, suitable for environments requiring impact resistance and lower thermal loads. Selecting between Steatite and plastic depends on the specific electrical, thermal, and environmental requirements of the application to ensure optimal insulation performance.
Infographic: Steatite vs Plastic for Electrical insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com