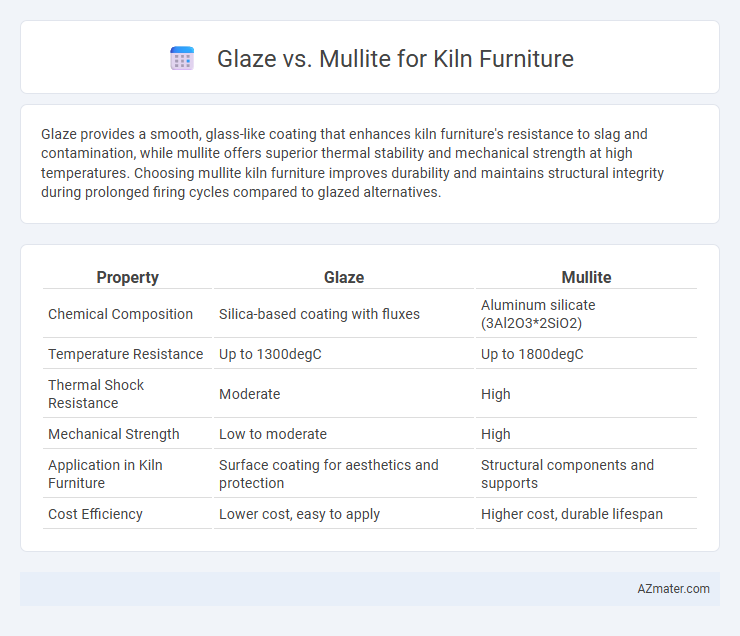
Glaze provides a smooth, glass-like coating that enhances kiln furniture's resistance to slag and contamination, while mullite offers superior thermal stability and mechanical strength at high temperatures. Choosing mullite kiln furniture improves durability and maintains structural integrity during prolonged firing cycles compared to glazed alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glaze | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Silica-based coating with fluxes | Aluminum silicate (3Al2O3*2SiO2) |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1300degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High |
| Application in Kiln Furniture | Surface coating for aesthetics and protection | Structural components and supports |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost, easy to apply | Higher cost, durable lifespan |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Kiln furniture materials like glaze and mullite offer distinct thermal and mechanical properties crucial for kiln operation efficiency. Mullite, a high-temperature ceramic, provides excellent thermal shock resistance and structural strength, making it ideal for supporting heavy loads in high-temperature environments. Glaze, often applied as a protective coating, enhances durability and thermal stability by reducing surface wear and chemical attack, thereby extending the lifespan of kiln furniture components.
Understanding Glaze: Composition and Uses
Glaze for kiln furniture typically consists of a mixture of silica, fluxes, and alumina, providing a glassy coating that enhances surface durability and thermal resistance. Its application improves kiln shelf lifespan by reducing adherence of glaze drips and facilitating easier cleaning during high-temperature firings. Understanding glaze formulations allows optimization of properties such as thermal expansion and chemical resistance, crucial for maintaining kiln furniture integrity in various firing atmospheres.
Mullite: Properties and Applications
Mullite, a key material in kiln furniture, offers exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-temperature kiln environments. Its low thermal expansion and high mechanical strength ensure durability under repeated heating and cooling cycles. Widely used in kiln shelves, setters, and furniture supports, mullite enhances energy efficiency and prolongs kiln life due to its superior refractory properties compared to glazed alternatives.
Key Differences Between Glaze and Mullite
Glaze forms a glassy surface coating on kiln furniture, enhancing thermal insulation and surface durability, while mullite is a high-temperature ceramic material known for its exceptional mechanical strength and thermal stability. Glaze typically improves resistance to kiln atmosphere and reduces porosity, whereas mullite provides structural support and maintains integrity under repeated thermal cycles. The key difference lies in glaze acting as a protective coating, compared to mullite serving as the core material within kiln furniture components.
Thermal Stability: Glaze vs Mullite
Mullite offers superior thermal stability compared to glaze, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1750degC, essential for kiln furniture exposed to extreme heat cycles. Glaze, while providing a protective coating, tends to melt or degrade at lower temperatures around 1200degC, limiting its effectiveness under high-heat conditions. The inherent refractory nature of mullite ensures longer lifespan and resistance to thermal shock, making it the preferred material for kiln shelves and posts in industrial ceramics firing.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Glaze and mullite differ significantly in chemical resistance for kiln furniture applications. Mullite exhibits exceptional resistance to acidic and basic slags, maintaining structural integrity at high temperatures up to 1750degC, whereas glazed surfaces may degrade or crack when exposed to aggressive chemicals. The crystalline structure of mullite provides superior durability against corrosive environments compared to the glassy phase in glazes, making mullite the preferred choice for prolonged chemical exposure in kiln operations.
Durability and Longevity in Kiln Environments
Glaze kiln furniture offers a smooth, non-porous surface that resists thermal shock but may develop cracks over extended high-temperature use, impacting durability. Mullite kiln furniture, composed primarily of aluminum silicate, exhibits exceptional thermal stability and superior resistance to creep and thermal shock, leading to enhanced longevity in severe kiln environments. The inherent strength and refractory properties of mullite make it a preferred choice for long-term kiln furniture applications where consistent performance is critical.
Cost and Availability Factors
Mullite kiln furniture typically has a higher upfront cost but offers greater durability and thermal shock resistance, leading to longer service life and lower replacement expenses. Glaze-coated kiln furniture is generally more affordable and widely available, making it suitable for budget-conscious operations with less demanding firing cycles. Availability of mullite products can be limited in some regions, whereas glaze options are more commonly stocked by suppliers, influencing procurement decisions based on project timelines and local inventory.
Suitability for Different Firing Conditions
Mullite kiln furniture exhibits exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it highly suitable for high-temperature and rapid firing conditions commonly found in advanced ceramic production. Glaze kiln furniture offers a smooth, non-porous surface that promotes even heat distribution and prevents glaze adhesion, ideal for low to medium firing ranges where surface quality is paramount. Selecting between glaze and mullite kiln furniture depends on the firing cycle's peak temperature and duration, with mullite favored for extreme heat and glaze preferred for ensuring clean finishes in moderate firings.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Kiln Furniture
Selecting the appropriate kiln furniture material between glaze and mullite hinges on thermal stability and durability under high temperatures. Mullite offers superior resistance to thermal shock and maintains structural integrity at temperatures up to 1780degC, making it ideal for consistent high-heat firing. Glaze materials provide a protective coating that reduces contamination and wear but may not withstand extreme temperature fluctuations as effectively as mullite.
Infographic: Glaze vs Mullite for Kiln Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com