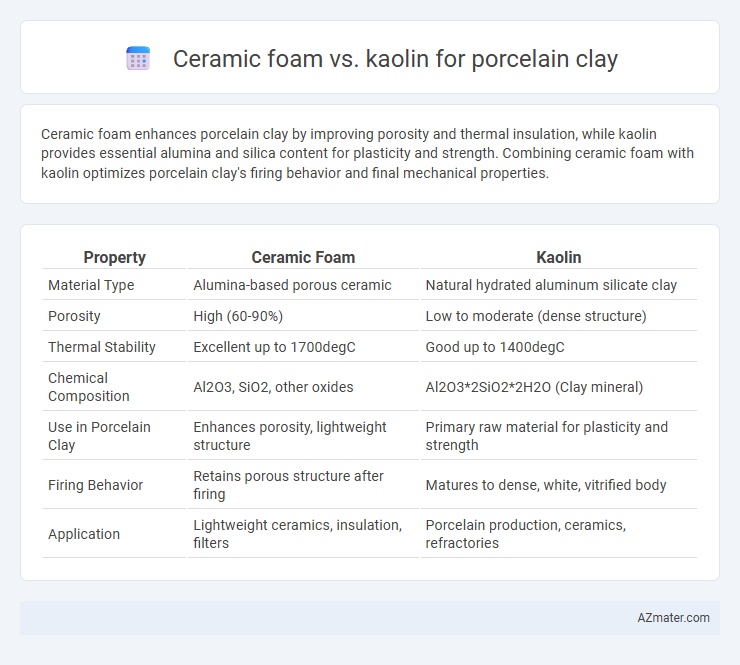
Ceramic foam enhances porcelain clay by improving porosity and thermal insulation, while kaolin provides essential alumina and silica content for plasticity and strength. Combining ceramic foam with kaolin optimizes porcelain clay's firing behavior and final mechanical properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Foam | Kaolin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alumina-based porous ceramic | Natural hydrated aluminum silicate clay |
| Porosity | High (60-90%) | Low to moderate (dense structure) |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent up to 1700degC | Good up to 1400degC |
| Chemical Composition | Al2O3, SiO2, other oxides | Al2O3*2SiO2*2H2O (Clay mineral) |
| Use in Porcelain Clay | Enhances porosity, lightweight structure | Primary raw material for plasticity and strength |
| Firing Behavior | Retains porous structure after firing | Matures to dense, white, vitrified body |
| Application | Lightweight ceramics, insulation, filters | Porcelain production, ceramics, refractories |
Introduction to Porcelain Clay Materials
Porcelain clay primarily consists of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, each playing a critical role in achieving its fine texture, translucency, and durability. Ceramic foam serves as a specialized additive that enhances the porosity and thermal insulation properties during the firing process, unlike kaolin which is a fundamental plastic component providing plasticity and whiteness. Understanding the distinct functions of ceramic foam and kaolin helps optimize the formulation for high-quality porcelain production with desired mechanical and aesthetic properties.
What is Ceramic Foam?
Ceramic foam is a highly porous material made from alumina or silicon carbide used to create lightweight, durable molds for high-temperature applications in porcelain clay production. Its cellular structure allows for excellent thermal insulation and gas permeability, leading to more consistent firing and reduced defects in fine ceramic pieces. Kaolin, a natural white clay rich in kaolinite, serves as the primary raw material for porcelain, providing plasticity and whiteness but lacks the porous, heat-resistant qualities essential in ceramic foams.
What is Kaolin?
Kaolin, a fine white clay primarily composed of kaolinite mineral, is essential in porcelain clay due to its purity, plasticity, and high firing temperature resistance. In contrast to ceramic foam, which is used mainly for insulation and filtration due to its porous structure, kaolin improves the strength, whiteness, and translucency of porcelain products. The mineral's fine particle size and chemical stability make it a critical ingredient in achieving the desirable characteristics of high-quality porcelain ceramics.
Key Properties of Ceramic Foam
Ceramic foam offers superior porosity and thermal insulation compared to kaolin, making it ideal for enhancing the firing process of porcelain clay by reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. Its high permeability supports better gas exchange during firing, which can help minimize defects such as cracks and warping in porcelain products. Unlike kaolin, ceramic foam also provides structural stability at elevated temperatures, ensuring consistent performance and longer mold life in porcelain manufacturing.
Key Properties of Kaolin
Kaolin, a primary component in porcelain clay, exhibits fine particle size, high plasticity, and excellent whiteness essential for achieving the desired translucency and strength in finished porcelain products. In contrast to ceramic foam, which provides structural support and insulation, kaolin contributes significantly to the clay's workability and firing characteristics, including its low shrinkage and high refractory properties. The purity and alumina content in kaolin directly influence the durability and smooth surface finish of porcelain, making it a critical mineral in ceramic manufacturing.
Performance Comparison: Ceramic Foam vs Kaolin
Ceramic foam offers superior porosity and thermal insulation compared to kaolin, enhancing the drying speed and reducing fire cracks in porcelain clay. Kaolin provides higher plasticity and whiteness, essential for achieving the fine texture and brightness in finished porcelain products. The choice depends on prioritizing either structural performance and thermal management with ceramic foam or aesthetic quality and workability with kaolin.
Porcelain Clay Composition: The Role of Each Material
Porcelain clay composition relies on ceramic foam to enhance thermal insulation and reduce firing defects, promoting uniform heat distribution within kiln environments. Kaolin, a primary component of porcelain clay, provides plasticity, whiteness, and strength due to its aluminosilicate mineral structure, crucial for achieving the characteristic translucency of porcelain. The combination of ceramic foam and kaolin in porcelain clay formulations balances mechanical durability with optimal firing performance, directly influencing the final product's aesthetics and structural integrity.
Pros and Cons: Ceramic Foam in Porcelain
Ceramic foam in porcelain clay enhances porosity and thermal insulation, improving firing efficiency and reducing cracking risks, but it may lower mechanical strength and increase brittleness. Kaolin, as a primary clay ingredient, offers excellent plasticity and whiteness, essential for high-quality porcelain; however, it lacks the porous benefits of ceramic foam, potentially causing slower drying and firing processes. Balancing ceramic foam's improved thermal properties with kaolin's structural integrity is crucial for optimal porcelain production.
Pros and Cons: Kaolin in Porcelain
Kaolin in porcelain clay offers superior whiteness, plasticity, and thermal stability, making it ideal for fine ceramics and high-quality porcelain products. However, its brittleness and higher firing temperature requirements can lead to increased production costs and potential cracking during the drying process. Compared to ceramic foam, kaolin's fine particle size enhances the smooth texture but limits porosity, affecting translucency and overall lightweight properties in porcelain.
Choosing the Best Material for Porcelain Clay
Ceramic foam offers superior porosity and thermal insulation compared to kaolin, making it ideal for lightweight porcelain clay bodies that require high strength and durability. Kaolin, a primary ingredient in traditional porcelain clay, provides excellent plasticity and whiteness but lacks the enhanced porosity and firing properties of ceramic foam. Selecting the best material depends on the desired characteristics of the final porcelain product, where ceramic foam enhances structural performance while kaolin maintains classic texture and color.
Infographic: Ceramic foam vs Kaolin for Porcelain clay
 azmater.com
azmater.com