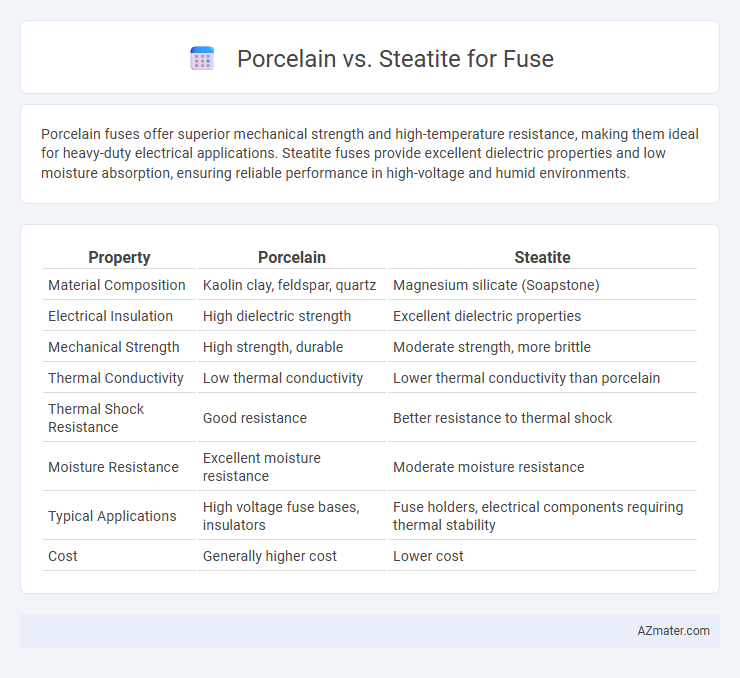
Porcelain fuses offer superior mechanical strength and high-temperature resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty electrical applications. Steatite fuses provide excellent dielectric properties and low moisture absorption, ensuring reliable performance in high-voltage and humid environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Kaolin clay, feldspar, quartz | Magnesium silicate (Soapstone) |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength | Excellent dielectric properties |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength, durable | Moderate strength, more brittle |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low thermal conductivity | Lower thermal conductivity than porcelain |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good resistance | Better resistance to thermal shock |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent moisture resistance | Moderate moisture resistance |
| Typical Applications | High voltage fuse bases, insulators | Fuse holders, electrical components requiring thermal stability |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Fuse Materials: Porcelain and Steatite
Porcelain and steatite are widely used materials in fuse construction due to their excellent insulating properties and thermal resistance. Porcelain, a ceramic made from kaolin, offers high mechanical strength and durability, making it ideal for high-voltage fuse applications. Steatite, composed primarily of talc, provides superior electrical insulation and thermal shock resistance, commonly utilized in medium to low-voltage fuse bases.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Porcelain fuses are composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, creating a dense, hard ceramic structure with excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength. Steatite fuses consist mainly of magnesium silicate, which offers superior thermal shock resistance and a more stable dielectric constant under varying temperatures. The crystalline structure of porcelain is more brittle but provides higher compressive strength, while steatite's granular microstructure enhances its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking.
Mechanical Strength: Porcelain vs Steatite
Porcelain offers superior mechanical strength compared to steatite, making it more resistant to breakage under high stress and impact conditions. Steatite, while durable, generally exhibits lower fracture toughness and is more prone to chipping or cracking when exposed to mechanical shocks. For fuse applications requiring robust mechanical endurance, porcelain is often preferred due to its enhanced structural integrity and longevity.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Porcelain and steatite are both used for fuse bodies due to their excellent electrical insulation properties, but porcelain offers superior dielectric strength and resistance to electrical stress, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Steatite, a dense ceramic material, provides good dielectric insulation with enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability, which improves the fuse's durability under thermal cycling. The choice between porcelain and steatite depends on specific requirements such as voltage rating, thermal conductivity, and mechanical robustness in electrical fuse applications.
Thermal Performance and Heat Resistance
Porcelain fuses exhibit superior thermal performance due to their high heat resistance and ability to withstand temperatures above 1000degC without deformation, making them ideal for high-current applications. Steatite fuses, while also offering excellent thermal stability, typically operate effectively up to around 800degC, providing reliable insulation and mechanical strength in moderate temperature environments. The choice between porcelain and steatite fuses depends on the specific thermal demands and operational conditions of the electrical system.
Moisture Absorption and Weather Resistance
Porcelain fuses exhibit extremely low moisture absorption, generally less than 0.05%, making them highly resistant to weathering and ideal for outdoor electrical applications. Steatite fuses, with moisture absorption rates around 0.5%, are more porous and can degrade faster under humid conditions, limiting their use in harsh environments. Porcelain's superior weather resistance ensures longer service life and stable insulation properties compared to steatite in moisture-prone settings.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Porcelain fuses exhibit superior durability due to their high resistance to heat and mechanical stress, maintaining structural integrity under frequent electrical faults. Steatite fuses, while also durable, typically offer enhanced thermal shock resistance and a longer lifespan in high-load applications thanks to their dense ceramic composition. Overall, porcelain provides excellent longevity in standard environments, whereas steatite excels in harsh conditions demanding greater endurance and stability.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Porcelain fuses offer superior durability and heat resistance, providing long-term cost savings despite a higher upfront price compared to steatite fuses. Steatite fuses are generally more affordable and widely available, making them a cost-effective option for standard applications where extreme thermal resistance is not critical. Availability of porcelain fuses may be limited in some regions, whereas steatite fuses benefit from broader market distribution and faster replacement times.
Industry Applications and Standards
Porcelain fuses are widely used in high-voltage industrial applications due to their excellent thermal stability, mechanical strength, and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Steatite fuses, on the other hand, are preferred in low to medium voltage industrial settings for their superior arc-quenching properties and resistance to thermal shock, making them suitable for protection in electrical equipment and machinery. Both materials comply with international standards such as IEC 60269 for low-voltage fuses and ANSI/IEEE standards for high-voltage applications, ensuring reliability and safety in various industry sectors.
Choosing the Right Material for Fuse Bases
Porcelain fuse bases offer exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-voltage applications requiring durability and thermal stability. Steatite fuse bases provide superior electrical insulation and moisture resistance due to their ceramic composition, which enhances performance in humid or corrosive environments. Selecting between porcelain and steatite depends on the specific electrical load, environmental conditions, and insulation requirements to ensure optimal fuse protection and longevity.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Steatite for Fuse
 azmater.com
azmater.com