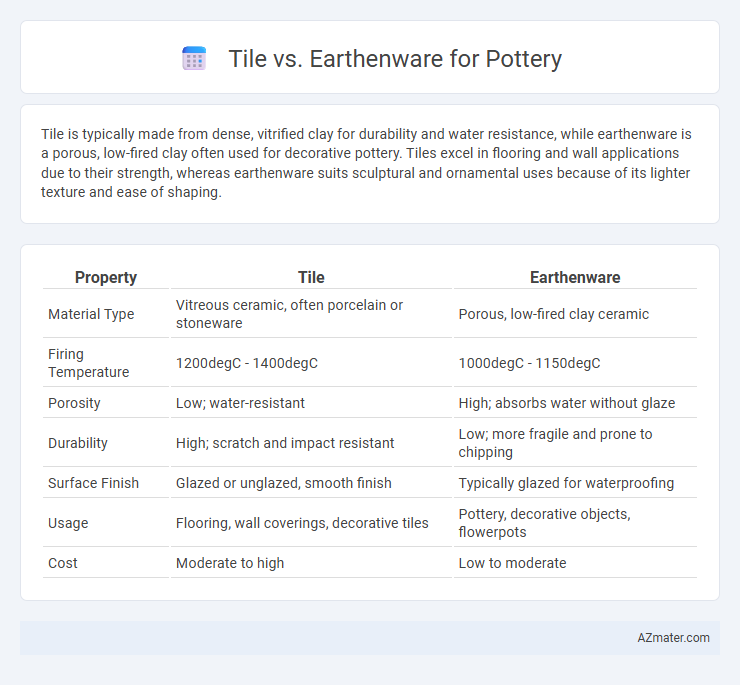
Tile is typically made from dense, vitrified clay for durability and water resistance, while earthenware is a porous, low-fired clay often used for decorative pottery. Tiles excel in flooring and wall applications due to their strength, whereas earthenware suits sculptural and ornamental uses because of its lighter texture and ease of shaping.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tile | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Vitreous ceramic, often porcelain or stoneware | Porous, low-fired clay ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC - 1400degC | 1000degC - 1150degC |
| Porosity | Low; water-resistant | High; absorbs water without glaze |
| Durability | High; scratch and impact resistant | Low; more fragile and prone to chipping |
| Surface Finish | Glazed or unglazed, smooth finish | Typically glazed for waterproofing |
| Usage | Flooring, wall coverings, decorative tiles | Pottery, decorative objects, flowerpots |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Pottery Materials: Tile vs Earthenware
Tile and earthenware represent two fundamental pottery materials with distinct properties and uses. Tile, often made from refined clay and fired at higher temperatures, offers durability and water resistance ideal for flooring and decorative surfaces. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures and more porous, is favored for its rustic aesthetic and is commonly used in functional pottery such as bowls and vases.
Defining Tiles and Earthenware: Key Differences
Tiles are typically thin, flat pieces of ceramic material used for covering surfaces like floors and walls, known for their durability and glazed finish that makes them water-resistant. Earthenware refers to porous, low-fired pottery made from clay, characterized by its relatively soft texture and need for glazing to hold liquids. The key difference lies in their manufacturing processes and functional properties, with tiles designed for structural and decorative uses, while earthenware serves primarily as functional pottery and decorative art.
Material Composition: What Sets Them Apart
Tile and earthenware pottery differ primarily in material composition, with tiles typically made from dense clay mixed with sand or grog, providing durability and water resistance. Earthenware consists of porous clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a softer, more porous final product. This distinction affects their usage, as tile suits flooring and roofing, while earthenware is often used for decorative or functional pottery.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Tiles typically offer higher durability and strength compared to earthenware due to their denser composition and firing process at higher temperatures, resulting in greater resistance to chipping and water absorption. Earthenware, while aesthetically versatile, remains more porous and prone to cracking or breakage under stress, making it less suitable for structural or high-traffic applications. For functional pottery requiring longevity and robustness, tile materials outperform earthenware in mechanical strength and durability metrics.
Aesthetic Appeal: Styles and Finishes
Tile offers a wide range of aesthetic appeal with styles ranging from sleek, glossy finishes to intricate patterns and vibrant colors, perfect for modern or decorative applications. Earthenware features a more natural, rustic look with matte or textured finishes, emphasizing handcrafted charm and traditional artistry. Both materials provide diverse design options, but tiles excel in uniformity and polish, while earthenware highlights organic warmth and artisanal uniqueness.
Common Uses in Art and Architecture
Tiles, typically made from fired clay with a glazed surface, are extensively used in architectural applications such as flooring, wall coverings, and decorative mosaics due to their durability and water resistance. Earthenware, a porous, unglazed pottery material, is favored in artistic pottery for sculptures, vases, and ornamental objects, emphasizing aesthetic texture over structural use. The distinction between tile and earthenware centers on functionality: tiles serve practical and ornamental purposes in built environments, while earthenware prioritizes artistic expression in ceramic art.
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for Your Pottery Project
Tile generally costs more than earthenware due to higher manufacturing and material expenses, making earthenware a budget-friendly option for pottery projects. Earthenware's affordability stems from its lower firing temperatures and more readily available clay, which reduce overall production costs. When budgeting for your pottery project, choosing earthenware can significantly minimize expenses without sacrificing versatility or aesthetic appeal.
Ease of Use: Workability and Firing Temperatures
Tile clay and earthenware differ significantly in ease of use, with earthenware offering greater workability due to its plasticity, making it ideal for hand-building and intricate designs. Earthenware typically fires at lower temperatures, ranging from 1,000degC to 1,150degC, allowing for shorter kiln times and energy efficiency. In contrast, tile clay requires higher firing temperatures, usually between 1,100degC and 1,250degC, resulting in increased durability but demanding more precise kiln control and longer firing cycles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Earthenware, often made from natural clay fired at lower temperatures, generally has a smaller carbon footprint compared to ceramic tiles, which require higher firing temperatures and energy-intensive manufacturing processes. Earthenware's biodegradability and potential for local sourcing reduce transportation emissions, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Tile production, while durable and long-lasting, may involve synthetic glazes and additives that contribute to environmental pollution and resource depletion.
Choosing the Right Material: Factors to Consider
When choosing between tile and earthenware for pottery, consider factors such as durability, porosity, and intended use; earthenware is more porous and less durable, making it ideal for decorative pieces, whereas tile offers greater strength and water resistance suited for functional surfaces. Temperature tolerance also plays a critical role, with earthenware firing at lower temperatures (around 1,000-1,150degC) compared to tiles, influencing the finish and stability of the final product. Cost and aesthetic preferences, including color variety and texture, help refine the choice, as tile generally provides a smoother surface and more vibrant glazes.
Infographic: Tile vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com