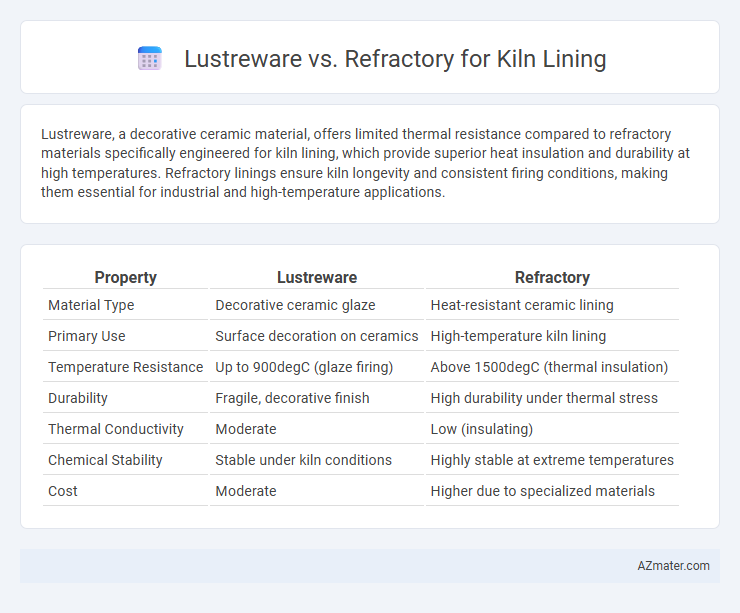
Lustreware, a decorative ceramic material, offers limited thermal resistance compared to refractory materials specifically engineered for kiln lining, which provide superior heat insulation and durability at high temperatures. Refractory linings ensure kiln longevity and consistent firing conditions, making them essential for industrial and high-temperature applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lustreware | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Decorative ceramic glaze | Heat-resistant ceramic lining |
| Primary Use | Surface decoration on ceramics | High-temperature kiln lining |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 900degC (glaze firing) | Above 1500degC (thermal insulation) |
| Durability | Fragile, decorative finish | High durability under thermal stress |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate | Low (insulating) |
| Chemical Stability | Stable under kiln conditions | Highly stable at extreme temperatures |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher due to specialized materials |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Kiln lining materials such as lustreware and refractory serve distinct roles in high-temperature environments. Lustreware provides decorative, heat-resistant coatings with moderate thermal protection, while refractory materials offer superior insulation and structural stability at extreme temperatures typically exceeding 1500degC. Selecting between lustreware and refractory linings depends on the kiln's operational temperature, durability requirements, and chemical resistance needed for optimal performance.
What is Lustreware?
Lustreware is a type of pottery coated with a metallic glaze that produces a shimmering, iridescent effect often achieved through the application of metal oxides fired in a kiln. Unlike refractory materials used for kiln linings, which prioritize durability and heat resistance to protect the kiln structure from extreme temperatures, lustreware is valued for its decorative qualities and surface finish. Kiln linings consist of specialized refractory bricks or castables designed to withstand thermal shock, whereas lustreware pertains to artistic ceramics rather than functional kiln components.
Understanding Refractory Materials
Refractory materials used for kiln lining provide superior resistance to high temperatures, thermal shock, and chemical corrosion compared to lustreware coatings, ensuring structural integrity and prolonged service life. These materials, typically made from alumina, silica, or magnesia, maintain their strength and insulating properties under intense heat, which is critical for efficient kiln operation. Understanding the composition and thermal performance of refractory bricks is essential for selecting optimal kiln linings that withstand continuous exposure to molten materials and fluctuating temperatures.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Lustreware glazing typically exhibits lower thermal shock resistance compared to refractory materials, which are engineered to withstand extreme kiln temperatures and rapid heating cycles. Refractory linings possess higher compressive strength and superior insulation properties, ensuring durability and energy efficiency in kiln operations. The mechanical toughness and chemical stability of refractory materials make them more suitable for prolonged exposure to molten materials and thermal cycling than lustreware coatings.
Heat Resistance and Durability
Lustreware glazes offer moderate heat resistance but tend to be less durable under extreme kiln temperatures compared to refractory linings designed specifically for high thermal stress. Refractory kiln linings, composed of fireclay, alumina, or silica-based materials, withstand temperatures often exceeding 1,600degC, providing superior thermal stability and longevity. The enhanced durability of refractory linings reduces thermal shock risk and extends the lifespan of industrial kilns used in ceramics and metallurgy.
Chemical Resistance of Lustreware vs Refractory
Lustreware, designed with a glassy, metallic glaze, offers moderate chemical resistance by protecting the ceramic surface from acidic and alkaline environments but can degrade under prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals. Refractory materials, specifically engineered for kiln linings, provide superior chemical resistance due to their dense, non-porous composition made from alumina, silica, and other oxides that withstand corrosive slags and fluxes at high temperatures. In kiln lining applications, refractory linings outperform lustreware coatings by maintaining structural integrity and resisting chemical attack during extended firing cycles.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Lustreware kiln linings typically require careful handling during installation due to their delicate surface finish, which can be prone to chipping and cracking, necessitating precise fitting and cushioning. Refractory linings offer higher durability and thermal resistance, allowing for easier installation with less risk of damage under high-temperature cycling, and often feature modular designs for quicker replacement. Maintenance of lustreware linings demands frequent inspections to detect surface degradation and avoid contamination of kiln atmospheres, while refractory linings benefit from lower maintenance needs, with occasional patching or replacement of worn sections to maintain kiln efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Lustreware vs Refractory
Lustreware kiln linings typically cost less upfront than refractory linings due to lower material expenses and simpler installation processes. However, refractory linings offer greater durability and thermal resistance, reducing maintenance frequency and long-term replacement costs. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses reveals that although lustreware may be initially economical, refractory linings provide better cost-efficiency for high-temperature, continuous kiln operations.
Best Applications for Each Material
Lustreware excels in kiln lining applications requiring high thermal conductivity and smooth surfaces, making it ideal for decorative pottery and ceramics where heat distribution and aesthetic finish are crucial. Refractory materials are best suited for high-temperature industrial kilns needing maximum heat resistance and durability, such as metal smelting or glass production, due to their ability to withstand extreme thermal shock and corrosive environments. Selecting between lustreware and refractory depends on the kiln's operational temperature, chemical exposure, and the desired ceramic finish quality.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Kiln Lining Solution
Lustreware offers excellent thermal shock resistance and decorative appeal, making it ideal for artistic kiln applications requiring both durability and aesthetics. Refractory materials provide superior high-temperature stability and mechanical strength, suited for industrial kilns operating under extreme heat and continuous use. Selecting the right kiln lining depends on the specific firing conditions, desired thermal performance, and production requirements to ensure longevity and optimal kiln efficiency.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Refractory for Kiln Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com