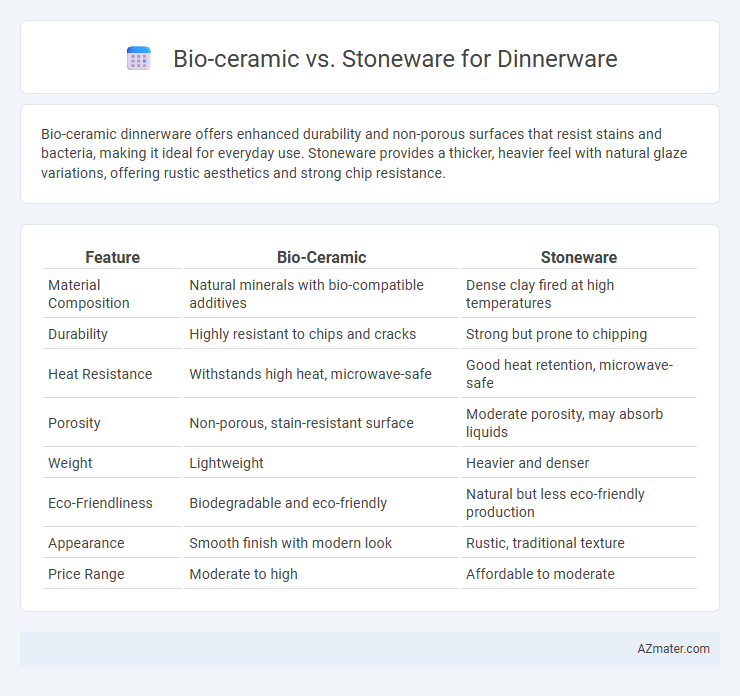
Bio-ceramic dinnerware offers enhanced durability and non-porous surfaces that resist stains and bacteria, making it ideal for everyday use. Stoneware provides a thicker, heavier feel with natural glaze variations, offering rustic aesthetics and strong chip resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bio-Ceramic | Stoneware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural minerals with bio-compatible additives | Dense clay fired at high temperatures |
| Durability | Highly resistant to chips and cracks | Strong but prone to chipping |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high heat, microwave-safe | Good heat retention, microwave-safe |
| Porosity | Non-porous, stain-resistant surface | Moderate porosity, may absorb liquids |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier and denser |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Natural but less eco-friendly production |
| Appearance | Smooth finish with modern look | Rustic, traditional texture |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Affordable to moderate |
Introduction to Bio-ceramic and Stoneware Dinnerware
Bio-ceramic dinnerware is crafted from advanced mineral-based materials combining natural elements like silica and kaolin, offering enhanced durability, chip resistance, and non-porous surfaces ideal for hygienic use. Stoneware dinnerware, made from dense clay fired at high temperatures, provides robust strength with a rustic, handcrafted appearance but tends to be more porous and heavier. Both materials deliver excellent heat retention, but bio-ceramic often excels in modern durability and stain resistance compared to traditional stoneware.
Material Composition: Bio-ceramic vs Stoneware
Bio-ceramic dinnerware is composed of natural materials such as sand and minerals combined with bio-based organic compounds, resulting in a lightweight, durable, and non-porous surface that resists staining and chipping. Stoneware is made from refined clay fired at high temperatures, creating a dense, heavy material that absorbs moisture and offers excellent heat retention but can be more porous and prone to chipping compared to bio-ceramic. The distinct compositions influence durability, maintenance, and aesthetic qualities, with bio-ceramic offering enhanced resistance to everyday wear and stoneware providing a more rustic, handcrafted appeal.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bio-ceramic dinnerware offers exceptional durability by combining natural minerals with advanced firing techniques, resulting in a lightweight yet highly resistant material that withstands daily use and temperature changes without chipping or cracking. Stoneware is known for its robust strength and ability to endure heavy use, but it tends to be heavier and more prone to surface scratches and chips over time. When comparing both, bio-ceramic provides superior resilience against impact and thermal shock, making it a durable choice for long-lasting dinnerware.
Design and Aesthetic Differences
Bio-ceramic dinnerware features a sleek, lightweight design with a smooth, matte finish that offers a modern and minimalist aesthetic, often available in soft, natural tones. Stoneware presents a heavier, more rustic feel with textured surfaces and rich, earthy glazes that emphasize handcrafted, artisanal qualities. The design of bio-ceramic prioritizes contemporary elegance and durability, while stoneware emphasizes warmth and traditional craftsmanship.
Heat Resistance and Microwave Safety
Bio-ceramic dinnerware offers exceptional heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1200degF, making it safe for direct microwave use without cracking or leaching. Stoneware, while durable and able to handle moderate oven temperatures around 500degF, may become prone to thermal shock and is less reliable for microwave safety due to potential glaze cracking. Choosing bio-ceramic ensures superior microwave compatibility and long-term durability under high heat conditions compared to traditional stoneware.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bio-ceramic dinnerware uses natural materials that require lower firing temperatures, reducing energy consumption compared to stoneware, which often needs higher heat processing. Stoneware production relies on clay sourced through mining, which can contribute to habitat disruption, whereas bio-ceramics typically incorporate renewable resources and eco-friendly additives. Both materials are durable and long-lasting, but bio-ceramics generally offer a greener lifecycle by minimizing carbon footprint and supporting circular economy practices in dinnerware manufacturing.
Health and Safety Considerations
Bio-ceramic dinnerware is made from natural materials like silica and minerals, offering non-toxic, lead-free, and cadmium-free properties that enhance health safety by preventing harmful chemical leaching. Stoneware, while durable and resistant to chipping, may sometimes contain traces of lead or other heavy metals if not properly glazed and fired, posing potential health risks. Choosing bio-ceramic dinnerware ensures enhanced food safety due to its hypoallergenic and non-porous surface that inhibits bacteria growth and chemical contamination.
Price and Value for Money
Bio-ceramic dinnerware typically offers higher durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to traditional stoneware, justifying its higher price point with long-term value for money. Stoneware is generally more affordable upfront, making it a budget-friendly choice, though it may chip more easily and lack the advanced performance features of bio-ceramics. For consumers prioritizing cost-effectiveness and enhanced longevity, bio-ceramic provides a superior investment despite the initial premium.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Bio-ceramic dinnerware offers superior stain resistance and is highly durable, requiring minimal effort to clean with standard dishwashing detergents and is often dishwasher-safe without risk of damage. Stoneware, while robust and chip-resistant, can absorb oils and stains due to its porous nature, necessitating more careful cleaning and occasional sealing to maintain its appearance and hygiene. Both materials benefit from gentle handling, but bio-ceramics generally provide easier maintenance and longer-lasting aesthetic appeal for busy households.
Which is Better for Everyday Use?
Bio-ceramic dinnerware offers superior durability and resistance to chipping compared to traditional stoneware, making it ideal for everyday use in busy households. Stoneware is typically heavier and less resistant to thermal shock, which can lead to cracking or breakage with frequent temperature changes. Bio-ceramics also provide a non-porous surface that resists staining and absorbs less moisture, enhancing hygiene and longevity for daily dining needs.
Infographic: Bio-ceramic vs Stoneware for Dinnerware
 azmater.com
azmater.com