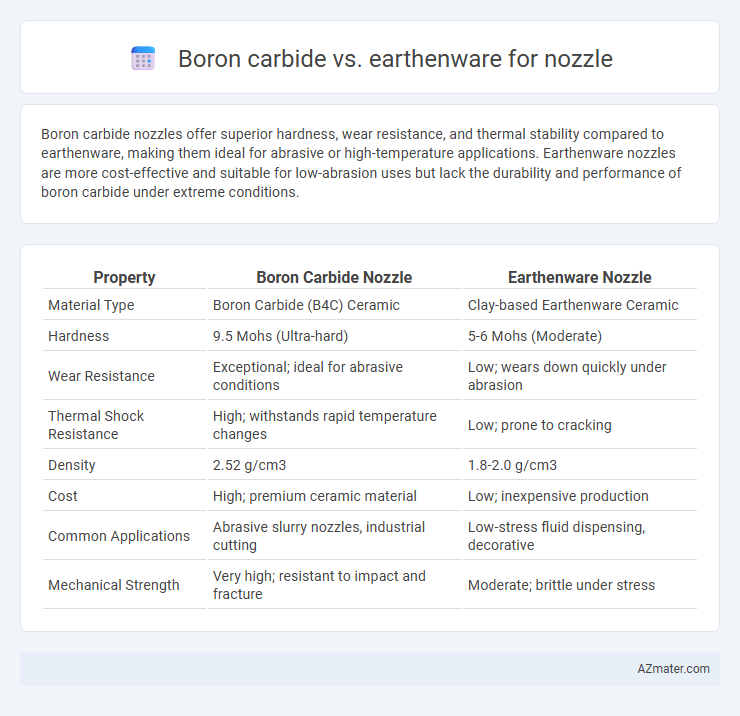
Boron carbide nozzles offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability compared to earthenware, making them ideal for abrasive or high-temperature applications. Earthenware nozzles are more cost-effective and suitable for low-abrasion uses but lack the durability and performance of boron carbide under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Boron Carbide Nozzle | Earthenware Nozzle |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Boron Carbide (B4C) Ceramic | Clay-based Earthenware Ceramic |
| Hardness | 9.5 Mohs (Ultra-hard) | 5-6 Mohs (Moderate) |
| Wear Resistance | Exceptional; ideal for abrasive conditions | Low; wears down quickly under abrasion |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High; withstands rapid temperature changes | Low; prone to cracking |
| Density | 2.52 g/cm3 | 1.8-2.0 g/cm3 |
| Cost | High; premium ceramic material | Low; inexpensive production |
| Common Applications | Abrasive slurry nozzles, industrial cutting | Low-stress fluid dispensing, decorative |
| Mechanical Strength | Very high; resistant to impact and fracture | Moderate; brittle under stress |
Introduction: Boron Carbide vs Earthenware Nozzles
Boron carbide nozzles offer exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-abrasion applications compared to earthenware nozzles, which are more brittle and prone to chipping. Boron carbide's chemical stability and thermal resistance enhance nozzle lifespan in harsh environments, whereas earthenware nozzles often experience quicker degradation under similar conditions. The superior durability of boron carbide results in lower maintenance costs and improved performance efficiency in industrial uses.
Material Composition and Properties
Boron carbide, composed primarily of boron and carbon atoms, is one of the hardest materials with exceptional hardness (9.5 on Mohs scale), high thermal stability, and outstanding wear resistance, making it ideal for nozzles subject to abrasive materials. Earthenware, made from natural clays fired at lower temperatures, offers moderate hardness, porosity, and lower thermal shock resistance, which limits its durability under high-temperature or abrasive conditions. The superior mechanical strength and chemical inertness of boron carbide significantly outperform earthenware, resulting in longer nozzle life and enhanced performance in industrial applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Boron carbide nozzles exhibit exceptional durability and wear resistance due to their ultra-hard ceramic composition, making them ideal for abrasive applications. Earthenware nozzles, while cost-effective, are significantly more prone to wear and chipping, resulting in reduced lifespan under high-stress conditions. The superior hardness of boron carbide, ranking just below diamond on the Mohs scale, ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance compared to earthenware counterparts.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Resistance
Boron carbide nozzles exhibit superior thermal conductivity and exceptional heat resistance compared to earthenware, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Boron carbide's thermal conductivity typically ranges around 30 W/m*K, enabling efficient heat dissipation, whereas earthenware has significantly lower thermal conductivity, usually below 1 W/m*K. The heat resistance of boron carbide surpasses 2700degC, while earthenware typically withstands temperatures only up to about 1200degC, limiting its use in extreme heat environments.
Chemical Corrosion Resistance
Boron carbide exhibits superior chemical corrosion resistance compared to earthenware, maintaining stability in highly acidic and alkaline environments, which makes it ideal for industrial nozzle applications exposed to aggressive chemicals. Earthenware, being a ceramic material, offers moderate resistance but tends to degrade or erode faster under prolonged exposure to strong corrosive agents. The exceptional durability of boron carbide against chemical corrosion significantly enhances nozzle lifespan and performance in harsh processing conditions.
Manufacturing Cost and Availability
Boron carbide nozzles offer superior hardness and wear resistance but come with significantly higher manufacturing costs due to complex sintering processes and limited raw material availability. Earthenware nozzles, made from abundant clay materials, provide a cost-effective and widely available option, though they lack the durability of boron carbide under abrasive conditions. The choice between the two often hinges on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements in high-wear industrial applications.
Performance in Industrial Applications
Boron carbide nozzles exhibit superior hardness and wear resistance compared to earthenware, making them ideal for abrasive slurry operations in industries such as mining and ceramics manufacturing. Their high thermal conductivity and chemical inertness ensure consistent performance under extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. Earthenware nozzles, while cost-effective, lack the durability and abrasion resistance required for heavy-duty industrial applications, leading to more frequent replacements and downtime.
Maintenance and Lifespan Comparison
Boron carbide nozzles offer superior hardness and wear resistance compared to earthenware, resulting in longer service life and less frequent maintenance cycles in abrasive and high-pressure applications. Earthenware nozzles, while more affordable, wear out faster due to their lower density and brittleness, requiring more frequent replacements and increased downtime. The extended lifespan and minimal maintenance of boron carbide nozzles make them ideal for industrial processes demanding durability and reduced operational costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Boron carbide nozzles offer superior durability and wear resistance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste compared to earthenware nozzles, which are more prone to chipping and breakage. The production of boron carbide involves energy-intensive processes and mining of boron minerals, which can have environmental impacts, whereas earthenware manufacturing relies on natural clay, a more abundant and less energy-demanding material. Boron carbide's longer lifespan and recyclability contribute to sustainability through reduced material consumption, while earthenware's biodegradability supports environmental friendliness but may result in higher resource use over time due to shorter service life.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Nozzle Material
Boron carbide nozzles offer superior hardness and wear resistance compared to earthenware, making them ideal for abrasive material applications and extending nozzle lifespan significantly. Earthenware nozzles, while more cost-effective and easier to manufacture, lack the durability needed for high-wear environments and are prone to faster degradation. Selecting boron carbide ensures optimal performance and longevity in industrial settings where nozzle durability directly impacts operational efficiency and maintenance costs.
Infographic: Boron carbide vs Earthenware for Nozzle
 azmater.com
azmater.com