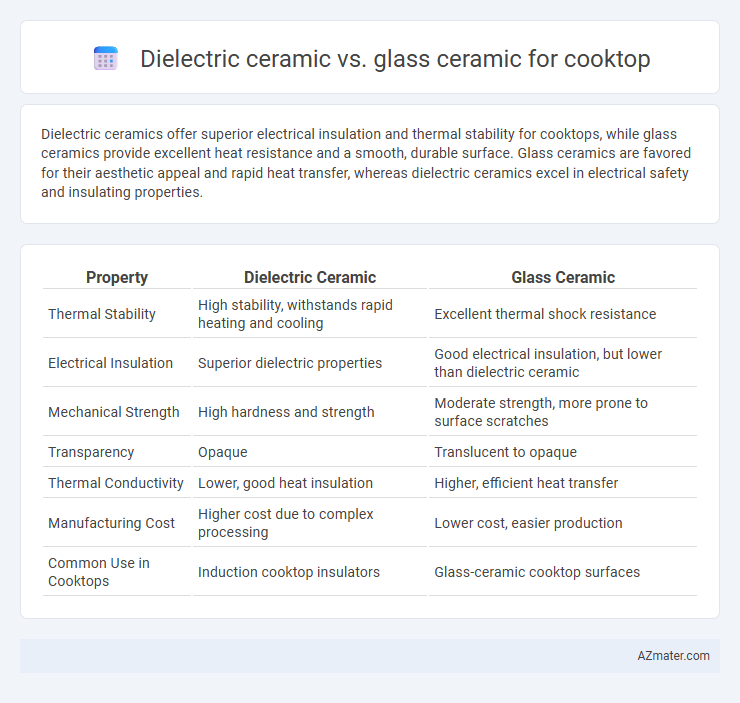
Dielectric ceramics offer superior electrical insulation and thermal stability for cooktops, while glass ceramics provide excellent heat resistance and a smooth, durable surface. Glass ceramics are favored for their aesthetic appeal and rapid heat transfer, whereas dielectric ceramics excel in electrical safety and insulating properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dielectric Ceramic | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High stability, withstands rapid heating and cooling | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Electrical Insulation | Superior dielectric properties | Good electrical insulation, but lower than dielectric ceramic |
| Mechanical Strength | High hardness and strength | Moderate strength, more prone to surface scratches |
| Transparency | Opaque | Translucent to opaque |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower, good heat insulation | Higher, efficient heat transfer |
| Manufacturing Cost | Higher cost due to complex processing | Lower cost, easier production |
| Common Use in Cooktops | Induction cooktop insulators | Glass-ceramic cooktop surfaces |
Introduction to Ceramic Cooktop Technologies
Dielectric ceramic and glass ceramic are fundamental materials in cooktop technologies, each offering distinct thermal and electrical properties crucial for efficient cooking performance. Dielectric ceramics provide excellent electrical insulation and high thermal stability, making them ideal for induction cooktops that require precise heat control without direct heating elements. Glass ceramics, known for their smooth surface and rapid heat transfer, dominate radiant cooktops by combining durability with aesthetic appeal and easy maintenance.
Understanding Dielectric Ceramics
Dielectric ceramics in cooktops provide superior electrical insulation and thermal stability, ensuring efficient induction heating without energy loss. These materials exhibit low dielectric loss and high dielectric constant, optimizing energy transfer to cookware while maintaining a cool surface. Compared to glass ceramics, dielectric ceramics offer enhanced durability and resistance to thermal shock, making them ideal for high-performance cooktops.
Overview of Glass Ceramics
Glass ceramics used in cooktops are engineered materials combining the transparency of glass with the thermal stability of ceramics, offering excellent resistance to thermal shock and high temperatures up to 700degC. Their low thermal expansion coefficient ensures durability and minimizes the risk of cracking during rapid temperature changes, making them ideal for induction and radiant cooktops. Glass ceramics also provide a smooth, easy-to-clean surface with good heat distribution, enhancing cooking efficiency and safety.
Material Composition and Properties
Dielectric ceramic cooktops are primarily composed of alumina (Al2O3) and other oxide compounds, offering high dielectric strength and excellent thermal insulation, making them efficient in preventing heat loss and electrical conduction. Glass ceramic cooktops consist mainly of lithium aluminosilicate with embedded nucleating agents, providing superior thermal shock resistance, smooth surface finish, and rapid heat conduction. The crystalline structure of dielectric ceramics ensures durability and electrical insulation, while glass ceramics excel in thermal stability and uniform heat distribution for cooktop applications.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Distribution
Dielectric ceramics typically exhibit lower thermal conductivity, around 2 to 5 W/m*K, resulting in slower heat transfer but better insulation on cooktops. Glass ceramics offer higher thermal conductivity values, approximately 7 to 12 W/m*K, enabling more efficient heat distribution and faster cooking performance. These differences impact energy efficiency and temperature uniformity, with glass ceramics providing more even heat spread compared to dielectric ceramics used in cooktop surfaces.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Dielectric ceramics for cooktops exhibit superior scratch resistance due to their hard, non-conductive surfaces, ensuring long-lasting durability under frequent use. Glass ceramics combine thermal shock resistance with a smooth finish but tend to be more susceptible to scratches and surface wear over time. Selecting dielectric ceramic cooktops offers enhanced structural integrity and maintains aesthetic appeal better than glass ceramic counterparts.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Dielectric ceramics exhibit superior energy efficiency on cooktops due to their low thermal conductivity, which minimizes heat loss and ensures rapid, focused heating. Glass ceramics offer moderate energy performance with better heat retention but slower heat transfer, leading to longer cooking times and increased energy consumption. Comparing both, dielectric ceramic cooktops often result in reduced energy usage and faster cooking cycles, making them more energy-efficient than glass ceramic alternatives.
Aesthetics and Design Flexibility
Dielectric ceramic cooktops offer a sleek, glossy finish with consistent color, enhancing modern kitchen aesthetics, while glass ceramic cooktops provide a smooth, reflective surface that allows for integrated touch controls and customizable designs. Glass ceramics exhibit greater design flexibility due to their ability to be formed into various shapes and sizes, accommodating innovative layouts and embedded heating elements. The visual appeal of glass ceramic surfaces tends to be more vibrant and versatile, which makes them preferable for contemporary, minimalist kitchen designs.
Safety Features and Considerations
Dielectric ceramic cooktops provide enhanced electrical insulation and heat resistance, reducing the risk of electric shock and ensuring stable performance during high-temperature cooking. Glass ceramic cooktops offer superior thermal shock resistance and are designed with smooth surfaces for easy cleaning and consistent heat distribution, but they may be more susceptible to cracking under sudden impact. Safety considerations favor dielectric ceramics for electrical safety, while glass ceramics are preferred for durability against thermal stress and maintaining a fracture-resistant cooking surface.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Dielectric ceramics in cooktops offer excellent electrical insulation and high thermal stability, resulting in minimal maintenance and a longer lifespan compared to glass ceramics. Glass ceramic cooktops require careful cleaning to avoid scratches and often need replacement sooner due to susceptibility to thermal shock and surface damage. Choosing dielectric ceramic enhances durability and reduces the frequency of repairs or replacements in high-use kitchen environments.
Infographic: Dielectric ceramic vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com