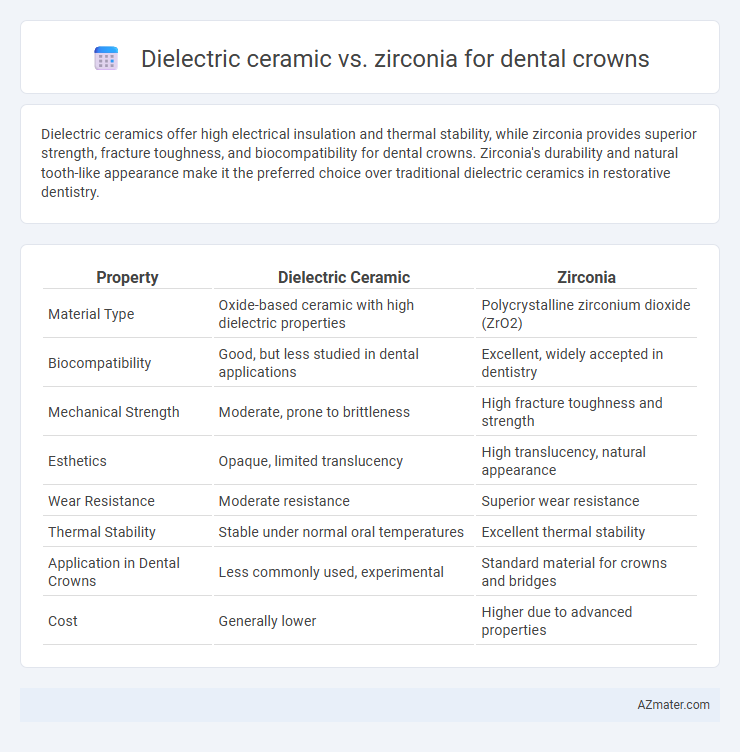
Dielectric ceramics offer high electrical insulation and thermal stability, while zirconia provides superior strength, fracture toughness, and biocompatibility for dental crowns. Zirconia's durability and natural tooth-like appearance make it the preferred choice over traditional dielectric ceramics in restorative dentistry.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dielectric Ceramic | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Oxide-based ceramic with high dielectric properties | Polycrystalline zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) |
| Biocompatibility | Good, but less studied in dental applications | Excellent, widely accepted in dentistry |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, prone to brittleness | High fracture toughness and strength |
| Esthetics | Opaque, limited translucency | High translucency, natural appearance |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate resistance | Superior wear resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Stable under normal oral temperatures | Excellent thermal stability |
| Application in Dental Crowns | Less commonly used, experimental | Standard material for crowns and bridges |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to advanced properties |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Dielectric ceramics and zirconia represent two advanced dental crown materials known for their distinct properties and clinical applications. Dielectric ceramics offer excellent biocompatibility and aesthetic translucency, making them suitable for front teeth restorations. Zirconia crowns provide superior strength and fracture resistance, ideal for molars and high-stress areas requiring durability.
Overview of Dielectric Ceramics in Dentistry
Dielectric ceramics in dentistry are valued for their excellent electrical insulation properties and biocompatibility, making them suitable for dental crowns and implants. These materials offer high resistance to wear and corrosion, providing improved longevity and stability in the oral environment compared to traditional materials. Unlike zirconia, which is known for its superior mechanical strength and toughness, dielectric ceramics focus on reducing electrical conductivity, enhancing patient safety and comfort in restorative dental applications.
Understanding Zirconia as a Dental Crown Material
Zirconia dental crowns offer exceptional strength, biocompatibility, and aesthetic appeal compared to traditional dielectric ceramics. Known for their high fracture toughness and resistance to wear, zirconia crowns provide long-lasting durability in oral environments. Their ability to mimic natural tooth color and translucency makes zirconia a preferred choice for both posterior and anterior dental restorations.
Mechanical Strength: Dielectric Ceramic vs Zirconia
Zirconia dental crowns exhibit superior mechanical strength, boasting flexural strength between 900 to 1200 MPa compared to dielectric ceramics, which typically range from 150 to 300 MPa. This high fracture toughness of zirconia enhances resistance to chipping and cracking under masticatory forces, making it ideal for posterior restorations. Dielectric ceramics, while offering better aesthetic translucency, are more prone to mechanical failure in high-load areas due to their lower flexural strength and brittleness.
Aesthetic Properties and Natural Appearance
Dielectric ceramic crowns exhibit superior translucency and color-matching capabilities, closely mimicking natural tooth enamel for highly aesthetic dental restorations. Zirconia crowns, while exceptionally strong and biocompatible, often display a more opaque and less lifelike appearance, making them less ideal for highly visible anterior teeth. Advances in multi-layered zirconia aim to improve translucency, but dielectric ceramics remain the preferred choice when prioritizing natural appearance and aesthetic properties in dental crowns.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Zirconia dental crowns exhibit superior biocompatibility due to their bioinert properties, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and inflammation compared to dielectric ceramics. Zirconia's high resistance to corrosion and low ion release enhances patient safety by minimizing adverse tissue responses. Dielectric ceramics may pose a higher risk of biocompatibility issues due to potential ion leaching, making zirconia the preferred choice for long-term dental crown applications.
Durability and Longevity in Oral Environment
Dielectric ceramics exhibit high fracture resistance and chemical stability, making them durable under the mechanical stresses of the oral environment. Zirconia crowns surpass dielectric ceramics with superior toughness and resistance to wear and chipping, contributing to exceptional longevity in dental restorations. Clinical studies confirm that zirconia maintains structural integrity and aesthetics over extended periods, outperforming many other ceramic options in long-term oral durability.
Ease of Fabrication and Clinical Handling
Dielectric ceramics exhibit excellent ease of fabrication due to their lower sintering temperatures and compatibility with conventional dental lab equipment, enabling precise adjustments and smoother milling processes. Zirconia crowns, while offering superior strength, require high-temperature sintering and more complex machinery, which can complicate fabrication and increase production time. Clinically, dielectric ceramics offer better translucency and handling ease during adjustments, whereas zirconia's hardness can challenge chairside modifications but provides enhanced durability and resistance to fracture.
Cost Comparison: Dielectric Ceramic vs Zirconia Crowns
Dielectric ceramic crowns generally cost less than zirconia crowns due to lower material and manufacturing expenses, offering an affordable option for dental restorations. Zirconia crowns, while more expensive, provide superior strength and durability, justifying their higher price for long-term performance. Patients and dentists often weigh upfront costs against longevity and aesthetic preferences when selecting between dielectric ceramic and zirconia options.
Clinical Recommendations and Best Use Cases
Zirconia dental crowns offer superior strength, biocompatibility, and durability, making them ideal for posterior teeth subjected to high masticatory forces, especially in patients with bruxism. Dielectric ceramic crowns, while less robust, provide excellent esthetics and are recommended for anterior teeth where translucency and color matching with natural dentition are critical. Clinical guidelines emphasize zirconia for long-term functional restoration and dielectric ceramics for cases prioritizing optimal esthetic results with moderate functional demands.
Infographic: Dielectric ceramic vs Zirconia for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com