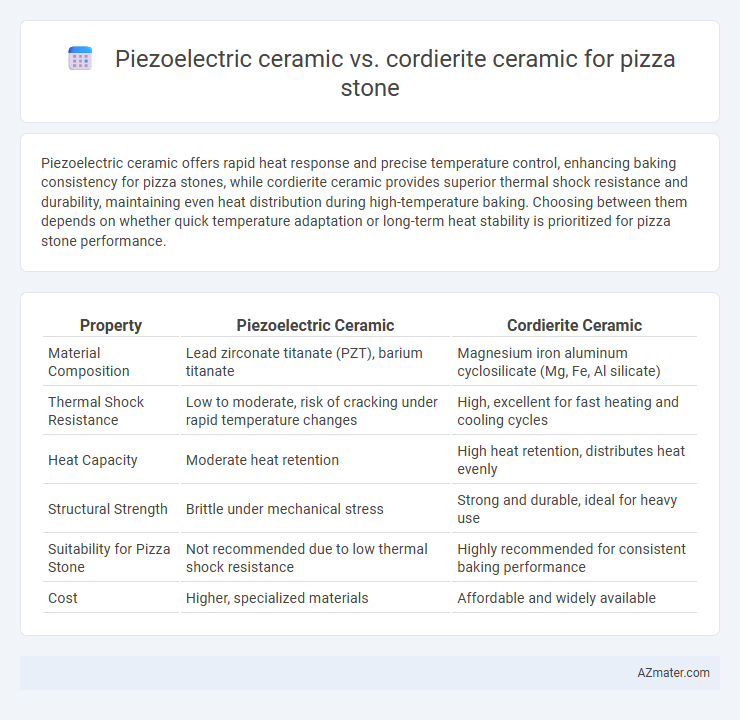
Piezoelectric ceramic offers rapid heat response and precise temperature control, enhancing baking consistency for pizza stones, while cordierite ceramic provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, maintaining even heat distribution during high-temperature baking. Choosing between them depends on whether quick temperature adaptation or long-term heat stability is prioritized for pizza stone performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Piezoelectric Ceramic | Cordierite Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Lead zirconate titanate (PZT), barium titanate | Magnesium iron aluminum cyclosilicate (Mg, Fe, Al silicate) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low to moderate, risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes | High, excellent for fast heating and cooling cycles |
| Heat Capacity | Moderate heat retention | High heat retention, distributes heat evenly |
| Structural Strength | Brittle under mechanical stress | Strong and durable, ideal for heavy use |
| Suitability for Pizza Stone | Not recommended due to low thermal shock resistance | Highly recommended for consistent baking performance |
| Cost | Higher, specialized materials | Affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Pizza Stone Materials
Piezoelectric ceramic and cordierite ceramic are two materials used for pizza stones, each offering distinct thermal properties essential for baking. Cordierite ceramic is favored for its excellent thermal shock resistance and ability to evenly distribute heat, making it ideal for producing crispy pizza crusts. Piezoelectric ceramics, although less common in culinary applications, possess unique electrical properties but lack the thermal resilience and heat distribution qualities that cordierite ceramics provide for pizza baking.
What is Piezoelectric Ceramic?
Piezoelectric ceramic is a crystalline material that generates an electric charge when mechanical stress is applied, making it ideal for sensors and actuators rather than high-heat applications like pizza stones. Cordierite ceramic, commonly used for pizza stones, excels in thermal shock resistance and heat retention, ensuring even cooking and durability under extreme oven temperatures. Choosing cordierite ceramic over piezoelectric ceramic is essential for efficient pizza baking due to its superior heat tolerance and structural stability.
What is Cordierite Ceramic?
Cordierite ceramic is a magnesium iron aluminum cyclosilicate known for its exceptional thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for pizza stones exposed to rapid temperature changes. Its low thermal expansion and high mechanical strength ensure durability and even heat distribution, resulting in perfectly cooked pizzas with crispy crusts. In contrast, piezoelectric ceramic lacks the specialized heat tolerance needed for cooking applications, limiting its effectiveness as a pizza stone material.
Heat Retention: Piezoelectric vs Cordierite
Cordierite ceramic pizza stones exhibit superior heat retention due to their high thermal mass and slow cooling properties, ensuring consistent and even heat distribution throughout the baking process. Piezoelectric ceramics, while known for their electrical properties, generally display lower heat retention, which can result in less stable baking temperatures and inconsistent crust quality. Cordierite's ability to withstand rapid temperature changes also enhances its performance for heat retention compared to piezoelectric ceramics.
Thermal Shock Resistance Comparison
Piezoelectric ceramics exhibit moderate thermal shock resistance due to their inherent electrical properties and microstructure, but they may be prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Cordierite ceramics are renowned for exceptional thermal shock resistance, attributed to their low thermal expansion coefficient and stable crystal structure, making them highly durable for pizza stones subjected to quick heating and cooling cycles. Compared to piezoelectric ceramics, cordierite ensures superior performance and longevity in high-temperature cooking applications by effectively minimizing thermal stress damage.
Cooking Performance: Crust Texture & Baking Evenness
Piezoelectric ceramics offer moderate heat retention but tend to produce uneven baking due to their lower thermal conductivity, resulting in less consistent crust texture. Cordierite ceramics are renowned for exceptional thermal shock resistance and superior heat distribution, ensuring even baking and a crisp, well-developed pizza crust. The dense structure of cordierite promotes uniform heat transfer, significantly enhancing crust texture and overall cooking performance compared to piezoelectric ceramics.
Durability and Longevity
Piezoelectric ceramic exhibits high durability due to its ability to withstand mechanical stress and thermal cycling, making it suitable for applications requiring repeated heating and cooling. Cordierite ceramic is renowned for its exceptional thermal shock resistance and longevity, which prevents cracking under abrupt temperature changes common in pizza baking. Compared to piezoelectric ceramics, cordierite generally offers superior lifespan and structural integrity in high-temperature cooking environments like pizza stones.
Food Safety and Chemical Composition
Piezoelectric ceramics contain lead-based compounds such as lead zirconate titanate (PZT), raising concerns about potential lead contamination when used in direct food contact applications like pizza stones, despite their strong piezoelectric properties. Cordierite ceramic, composed primarily of magnesium iron aluminosilicate, is non-toxic, chemically inert, and resistant to thermal shock, making it a safer and more stable choice for cooking surfaces in terms of food safety and chemical composition. The absence of harmful heavy metals in cordierite significantly reduces the risk of chemical leaching, ensuring a safer preparation environment for pizza and other baked goods.
Cost and Availability
Piezoelectric ceramics are generally more expensive and less readily available compared to Cordierite ceramics, making Cordierite the preferred choice for pizza stones due to its cost-effectiveness and widespread market availability. Cordierite ceramic offers excellent thermal shock resistance and durability at a lower price point, contributing to its popularity among commercial and home pizza stone users. Due to the specialized manufacturing process and niche applications of piezoelectric ceramics, their use in pizza stones is uncommon and economically impractical.
Which Ceramic is Better for Pizza Stones?
Piezoelectric ceramics, known for their ability to generate electric charge under mechanical stress, are not typically used for pizza stones due to their brittleness and higher cost. Cordierite ceramic, favored in pizza stones, offers exceptional thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking. Therefore, cordierite ceramic is better suited for pizza stones because it provides consistent heat distribution and long-lasting performance without cracking under rapid temperature changes.
Infographic: Piezoelectric ceramic vs Cordierite ceramic for Pizza stone
 azmater.com
azmater.com