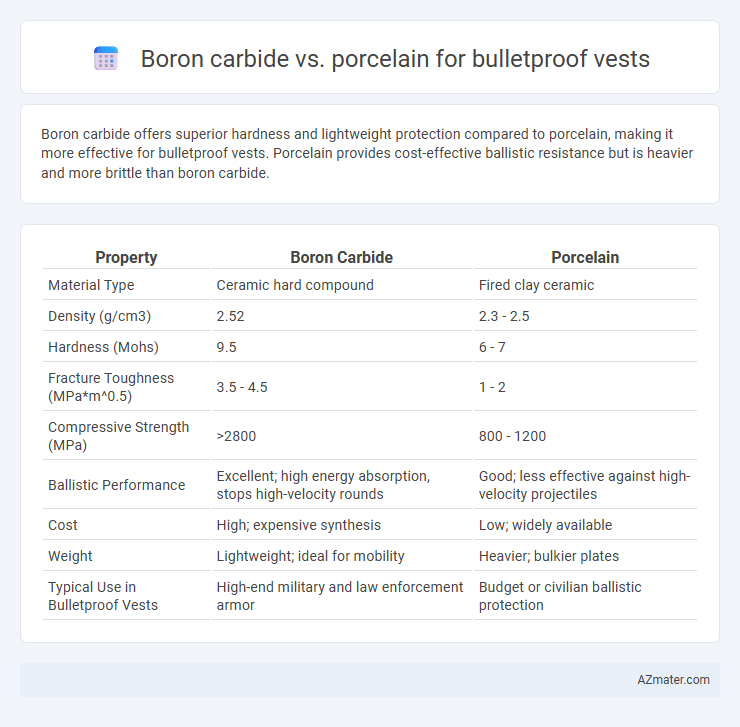
Boron carbide offers superior hardness and lightweight protection compared to porcelain, making it more effective for bulletproof vests. Porcelain provides cost-effective ballistic resistance but is heavier and more brittle than boron carbide.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Boron Carbide | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic hard compound | Fired clay ceramic |
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.52 | 2.3 - 2.5 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 9.5 | 6 - 7 |
| Fracture Toughness (MPa*m^0.5) | 3.5 - 4.5 | 1 - 2 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | >2800 | 800 - 1200 |
| Ballistic Performance | Excellent; high energy absorption, stops high-velocity rounds | Good; less effective against high-velocity projectiles |
| Cost | High; expensive synthesis | Low; widely available |
| Weight | Lightweight; ideal for mobility | Heavier; bulkier plates |
| Typical Use in Bulletproof Vests | High-end military and law enforcement armor | Budget or civilian ballistic protection |
Introduction: Boron Carbide vs Porcelain in Ballistic Armor
Boron carbide and porcelain are two common materials used in ballistic armor, each offering distinct advantages in bulletproof vests. Boron carbide provides exceptional hardness and lightweight protection, making it highly effective against armor-piercing rounds. Porcelain, while heavier and more brittle, offers cost-effective resistance and is often used in multilayered armor systems for enhanced impact dispersion.
Material Composition and Structure
Boron carbide, a ceramic composed primarily of boron and carbon atoms, features a highly dense and crystalline structure that provides exceptional hardness and lightweight properties ideal for bulletproof vests. Porcelain, made from kaolin clay mixed with feldspar and silica, has a more brittle and less dense microstructure, resulting in lower impact resistance compared to boron carbide. The superior mechanical strength and toughness of boron carbide make it more effective at dissipating kinetic energy and preventing projectile penetration in body armor applications.
Ballistic Protection Performance
Boron carbide offers superior ballistic protection due to its exceptional hardness and low density, making it ideal for stopping high-velocity projectiles while maintaining a lightweight profile. Porcelain, while cost-effective and hard, tends to be more brittle and heavier, leading to increased risk of fragmentation upon impact and reduced multi-hit capability. The ballistic performance of boron carbide plates consistently surpasses porcelain in terms of energy absorption, spall resistance, and durability in body armor applications.
Weight Comparison and Mobility Impact
Boron carbide is significantly lighter than porcelain, typically weighing about 2.52 g/cm3 compared to porcelain's density of approximately 2.4-2.8 g/cm3 but with superior ballistic performance, resulting in lighter and more effective bulletproof vests. The reduced weight of boron carbide plates enhances wearer mobility, allowing for quicker and less fatigued movement in tactical situations. Porcelain plates, while more affordable, add bulk and weight that can restrict agility and endurance during prolonged use.
Durability and Multi-hit Resistance
Boron carbide offers superior durability and multi-hit resistance compared to porcelain in bulletproof vests due to its exceptional hardness and lightweight properties, enabling it to effectively absorb and disperse ballistic impacts without cracking. Porcelain, while hard and cost-effective, tends to be more brittle, often resulting in cracks or fractures after multiple hits, reducing its protective reliability over time. The advanced structural integrity of boron carbide ceramics ensures sustained protection in high-threat scenarios, making it the preferred choice for military-grade armor applications.
Cost and Accessibility of Materials
Boron carbide provides exceptional hardness and lightweight protection but comes with a higher price due to complex manufacturing and limited raw material availability, making it less accessible for large-scale bulletproof vest production. Porcelain, while less durable and heavier, offers a significantly lower cost and easier access to materials, allowing for more widespread use in budget-conscious armor solutions. Cost efficiency and material supply constraints often dictate the choice between boron carbide and porcelain in bulletproof vest manufacturing.
Comfort and Ergonomics for End Users
Boron carbide offers superior hardness-to-weight ratio compared to porcelain, resulting in lighter bulletproof vests that enhance user comfort and reduce fatigue during extended wear. The material's inherent toughness allows for thinner plates, improving ergonomics by enabling greater mobility and flexibility without compromising protection. In contrast, porcelain is more brittle and heavier, often requiring thicker layers that can hinder movement and cause discomfort for end users over time.
Maintenance and Longevity
Boron carbide plates exhibit superior longevity due to their high hardness and resistance to wear, maintaining structural integrity under repeated impact without significant degradation. Porcelain plates, while cost-effective, are more prone to chipping and cracking over time, requiring more frequent maintenance and careful handling to preserve ballistic performance. The low porosity and chemical inertness of boron carbide contribute to easier maintenance and longer service life compared to the more brittle and fragile nature of porcelain armor.
Use Cases: Military, Law Enforcement, and Civilian Applications
Boron carbide offers superior hardness and lightweight protection, making it ideal for military and law enforcement use where mobility and high-level ballistic resistance are critical. Porcelain armor provides cost-effective, durable protection suitable for civilian applications such as personal security and lower-threat law enforcement roles, though it is heavier and more brittle than boron carbide. Each material's performance varies by impact resistance and weight, influencing its suitability for different tactical environments and operational demands.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Bulletproof Vests
Boron carbide offers exceptional hardness and lighter weight, making it ideal for high-performance bulletproof vests requiring superior ballistic protection. Porcelain provides a more cost-effective solution with decent hardness but generally adds more weight and lower impact resistance compared to boron carbide. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors like budget, mobility, and the specific threat level, with boron carbide favored for advanced protection and porcelain suited for economical applications.
Infographic: Boron carbide vs Porcelain for Bulletproof Vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com