Mullite offers superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance for kiln lining compared to traditional ceramic coatings, enhancing durability under extreme temperatures. Its low thermal expansion and high mechanical strength reduce cracking and maintenance costs in industrial kiln applications.
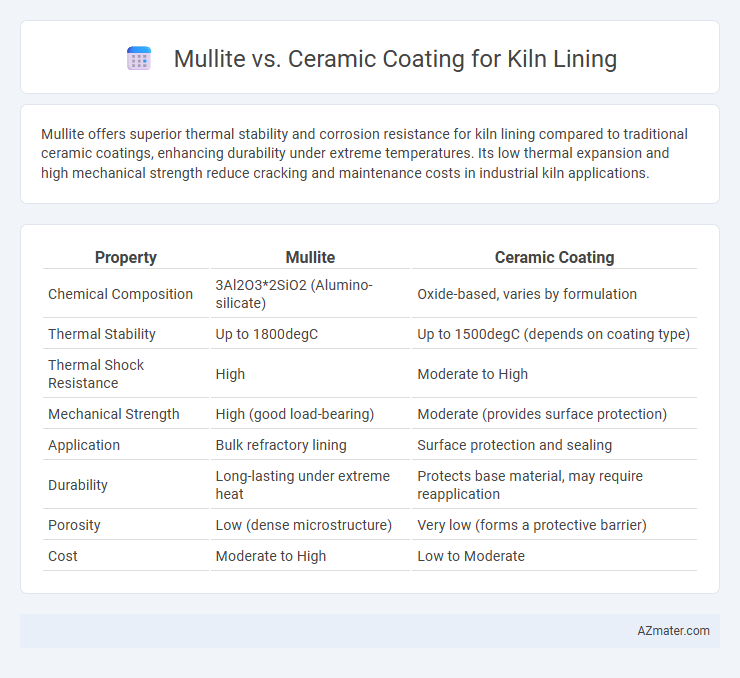
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mullite | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumino-silicate) | Oxide-based, varies by formulation |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1800degC | Up to 1500degC (depends on coating type) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High | Moderate to High |
| Mechanical Strength | High (good load-bearing) | Moderate (provides surface protection) |
| Application | Bulk refractory lining | Surface protection and sealing |
| Durability | Long-lasting under extreme heat | Protects base material, may require reapplication |
| Porosity | Low (dense microstructure) | Very low (forms a protective barrier) |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
Introduction to Kiln Lining Materials
Kiln lining materials such as mullite and ceramic coatings are essential for ensuring high-temperature resistance and thermal insulation in industrial kilns. Mullite, a crystalline aluminosilicate with excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion, is preferred for its durability and resistance to thermal shock. Ceramic coatings provide a protective barrier that enhances the kiln lining's lifespan by reducing wear and chemical corrosion, making them suitable for extending maintenance intervals.
What is Mullite?
Mullite is a crystalline aluminum silicate mineral commonly used in kiln linings for its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures above 1600degC. Unlike generic ceramic coatings, mullite forms a durable, refractory layer that minimizes thermal expansion and structural deformation. Its unique microstructural properties enhance kiln longevity by preventing corrosion and thermal shock damage during repeated heating cycles.
Overview of Ceramic Coatings
Ceramic coatings for kiln lining provide a high-temperature resistant barrier that enhances the durability and thermal efficiency of the kiln. These coatings form a protective layer that resists oxidation, corrosion, and abrasion, extending the lifespan of the kiln lining compared to traditional mullite bricks. Their superior adhesion and thermal shock resistance make ceramic coatings a cost-effective solution for maintaining structural integrity in harsh kiln environments.
Thermal Stability: Mullite vs Ceramic Coating
Mullite offers exceptional thermal stability with a melting point of approximately 1840degC, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and suitable for prolonged high-temperature kiln lining applications. Ceramic coatings typically provide a protective barrier with thermal stability up to 1200-1500degC but lack the intrinsic structural integrity of Mullite under extreme heat. Therefore, Mullite is preferred for kiln linings requiring enhanced durability and thermal resistance in high-temperature industrial environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Mullite offers superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to standard ceramic coatings used for kiln linings, making it highly durable under extreme temperature fluctuations. The intrinsic crystalline structure of mullite provides enhanced resistance to abrasion and mechanical wear, extending the lifespan of kiln linings in industrial applications. Ceramic coatings, while effective in protecting surfaces, generally lack the robust mechanical properties of mullite, resulting in quicker degradation and reduced service life in high-stress environments.
Thermal Shock Resistance Performance
Mullite offers superior thermal shock resistance due to its low thermal expansion coefficient and excellent structural stability at high temperatures, making it ideal for kiln linings subjected to rapid temperature fluctuations. Ceramic coatings, while providing a protective barrier and some thermal insulation, generally exhibit lower resistance to thermal shock compared to mullite, increasing the risk of cracking or spalling under intense heating and cooling cycles. The exceptional durability of mullite under thermal stress significantly enhances the longevity and performance of kiln linings in industrial applications.
Chemical Resistance in High-Temperature Environments
Mullite offers excellent chemical resistance in high-temperature kiln environments due to its stable aluminosilicate structure, which withstands alkalis and acidic slags effectively. Ceramic coatings enhance chemical resistance by providing a dense, impermeable barrier that protects the underlying lining from corrosive gases and molten materials. Both materials improve kiln lining longevity, but mullite's inherent chemical stability often outperforms ceramic coatings under extreme thermal and chemical stress.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Mullite kiln linings offer superior dimensional stability and thermal shock resistance, reducing maintenance frequency compared to ceramic coatings, which may require more frequent touch-ups due to potential flaking under extreme conditions. Installation of mullite bricks typically demands precise alignment and skilled labor to ensure tight joints and optimal thermal performance, while ceramic coatings can be applied more quickly but need surface preparation to achieve effective adhesion. Maintenance of mullite linings involves periodic inspections for cracks, whereas ceramic coatings require regular recoating to maintain protective properties against chemical and thermal wear.
Cost Efficiency and Longevity
Mullite kiln linings offer superior cost efficiency due to their excellent thermal stability and resistance to corrosion, reducing maintenance frequency and downtime. Ceramic coatings, while initially cheaper, often require more frequent recoating and replacement because of lower durability under high-temperature cycling. Mullite's enhanced longevity in harsh kiln environments ultimately provides better return on investment by minimizing operational costs and extending service life.
Choosing the Best Option for Kiln Lining Applications
Mullite offers superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for kiln lining in high-temperature industrial applications, while ceramic coatings provide excellent surface protection and reduce wear by enhancing thermal insulation and chemical resistance. Choosing between mullite refractory bricks and ceramic coatings depends on factors such as operating temperature, mechanical stress, and maintenance costs, with mullite favored for durability and ceramic coatings preferred for extending lifespan and reducing material degradation. Optimal kiln lining solutions often involve combining mullite's robustness with ceramic coatings' protective properties to maximize performance and longevity.
Infographic: Mullite vs Ceramic coating for Kiln lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com