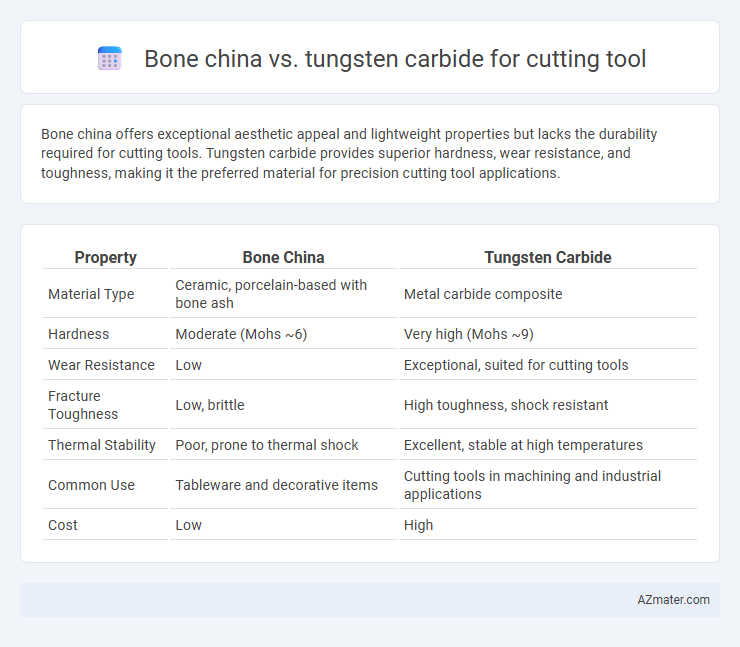
Bone china offers exceptional aesthetic appeal and lightweight properties but lacks the durability required for cutting tools. Tungsten carbide provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, making it the preferred material for precision cutting tool applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bone China | Tungsten Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic, porcelain-based with bone ash | Metal carbide composite |
| Hardness | Moderate (Mohs ~6) | Very high (Mohs ~9) |
| Wear Resistance | Low | Exceptional, suited for cutting tools |
| Fracture Toughness | Low, brittle | High toughness, shock resistant |
| Thermal Stability | Poor, prone to thermal shock | Excellent, stable at high temperatures |
| Common Use | Tableware and decorative items | Cutting tools in machining and industrial applications |
| Cost | Low | High |
Introduction: Comparing Bone China and Tungsten Carbide in Cutting Tools
Bone china, a porcelain material known for its strength and translucency, is rarely used in cutting tools due to its brittleness and low wear resistance. Tungsten carbide, an extremely hard and durable metal composite, is the preferred choice for cutting tools because of its superior hardness, toughness, and resistance to high temperatures and wear. This fundamental difference in material properties makes tungsten carbide vastly more effective and reliable for industrial cutting applications compared to bone china.
Material Composition: Bone China vs Tungsten Carbide
Bone china is composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and bone ash, which gives it a unique blend of strength and translucency but limited hardness, making it unsuitable for cutting tools. Tungsten carbide consists of tungsten and carbon atoms combined to form an extremely hard and dense material, offering superior wear resistance and cutting performance in industrial applications. The fundamental difference in material composition drives tungsten carbide's dominance in cutting tools due to its hardness and durability compared to the brittle and fragile nature of bone china.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Tungsten carbide exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength and durability compared to bone china, making it the preferred material for cutting tools in demanding industrial applications. Its exceptional hardness and resistance to wear enable prolonged cutting performance and minimal tool degradation under extreme conditions. Bone china, while offering aesthetic appeal and moderate toughness, lacks the sustained mechanical resilience required for high-precision, heavy-duty cutting operations.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
Tungsten carbide exhibits superior hardness, typically ranging from 1600 to 1800 HV, making it highly resistant to deformation and ideal for cutting tools requiring durability. Bone china, although valued for its aesthetic qualities and moderate hardness around 500-700 HV, lacks the wear resistance necessary for high-performance cutting applications. The advanced wear resistance of tungsten carbide significantly outperforms bone china, ensuring longer tool life in rigorous industrial environments.
Sharpness Retention and Edge Quality
Tungsten carbide exhibits superior sharpness retention compared to bone china, maintaining cutting edges under heavy use without rapid dulling. Bone china, while offering a smooth edge quality, lacks the hardness necessary for prolonged edge stability in cutting tools. The microstructure of tungsten carbide enables consistent edge integrity, making it the preferred material for high-performance cutting applications.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Tungsten carbide excels in cutting tool applications due to its superior heat resistance and exceptional thermal stability, allowing it to maintain hardness and cutting efficiency at temperatures exceeding 1000degC. Bone china, while prized for its durability and aesthetic qualities, lacks the high-temperature resilience necessary for demanding cutting tasks, as it softens and loses structural integrity well below 1000degC. Therefore, tungsten carbide remains the preferred material for cutting tools subjected to intense thermal conditions and continuous high-speed operation.
Applications in Cutting Tool Industries
Tungsten carbide outperforms bone china in cutting tool industries due to its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, making it ideal for high-precision machining and heavy-duty cutting applications. Bone china lacks the mechanical strength and durability required for industrial cutting tools, limiting its use to aesthetic or non-structural components. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and metalworking heavily rely on tungsten carbide tools for their superior cutting performance and extended tool life.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Tungsten carbide cutting tools offer superior cost efficiency due to their exceptional hardness and wear resistance, significantly extending tool life and reducing replacement frequency compared to bone china. Bone china tools, while less expensive upfront, suffer from brittleness and lower durability, leading to higher operational costs through frequent breakage and tool downtime. Economic considerations favor tungsten carbide for industrial applications that demand high precision and long-term performance, offsetting its higher initial investment with substantial savings in maintenance and productivity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bone china, primarily used in tableware, has limited application in cutting tools, whereas tungsten carbide is a prevalent material for industrial cutting due to its hardness and durability. Tungsten carbide production involves extensive mining and energy-intensive processes, contributing to significant environmental impacts, though its long tool life reduces waste and resource consumption over time. Sustainable practices focus on recycling tungsten carbide scrap and improving manufacturing efficiency to mitigate environmental burdens compared to the limited feasibility of bone china in cutting tool sustainability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Cutting Tools
Bone china offers excellent chemical resistance and moderate hardness, making it suitable for precision cutting in dry, non-metal applications. Tungsten carbide provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and toughness, ideal for heavy-duty metal cutting tasks requiring high-speed performance. Selecting the right cutting tool material depends on the application's hardness, toughness requirements, and operating environment to maximize tool life and cutting efficiency.
Infographic: Bone china vs Tungsten carbide for Cutting tool
 azmater.com
azmater.com