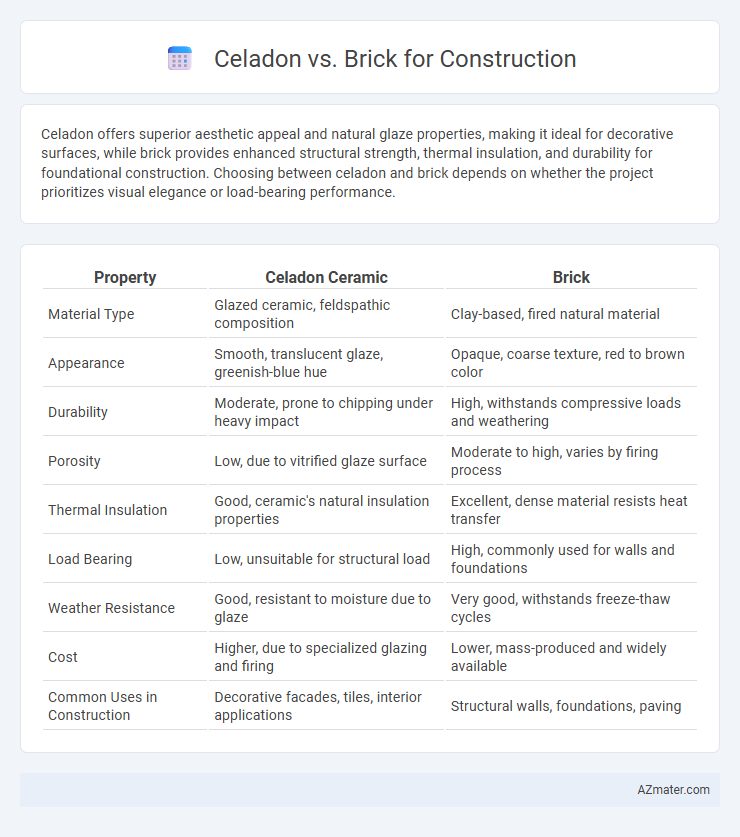
Celadon offers superior aesthetic appeal and natural glaze properties, making it ideal for decorative surfaces, while brick provides enhanced structural strength, thermal insulation, and durability for foundational construction. Choosing between celadon and brick depends on whether the project prioritizes visual elegance or load-bearing performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Celadon Ceramic | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic, feldspathic composition | Clay-based, fired natural material |
| Appearance | Smooth, translucent glaze, greenish-blue hue | Opaque, coarse texture, red to brown color |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping under heavy impact | High, withstands compressive loads and weathering |
| Porosity | Low, due to vitrified glaze surface | Moderate to high, varies by firing process |
| Thermal Insulation | Good, ceramic's natural insulation properties | Excellent, dense material resists heat transfer |
| Load Bearing | Low, unsuitable for structural load | High, commonly used for walls and foundations |
| Weather Resistance | Good, resistant to moisture due to glaze | Very good, withstands freeze-thaw cycles |
| Cost | Higher, due to specialized glazing and firing | Lower, mass-produced and widely available |
| Common Uses in Construction | Decorative facades, tiles, interior applications | Structural walls, foundations, paving |
Introduction to Celadon and Brick in Construction
Celadon, a glazed ceramic material known for its durability and aesthetic appeal, offers unique advantages in construction through its resistance to moisture and elegant finish. Brick, a traditional construction material made from baked clay, provides exceptional strength, thermal insulation, and structural support for buildings. Both materials serve distinct functional and design purposes, with celadon often used for decorative elements and bricks for foundational and load-bearing structures.
Historical Use of Celadon and Brick
Brick has been a fundamental building material for thousands of years, with origins tracing back to ancient Mesopotamia around 7000 BCE, providing durable and versatile construction suited for various climates. Celadon, primarily a type of ceramic glaze originating in China during the Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220 CE), was historically used in architectural tiles and decorative elements rather than structural construction. The use of celadon in historical architecture highlights its cultural significance and aesthetic appeal, contrasting with the practical and structural role of brick in construction history.
Material Composition and Properties
Celadon pottery is crafted from high-quality porcelain clay, known for its fine texture and translucency, whereas bricks are primarily composed of clay or shale mixed with sand and fired at high temperatures to achieve hardness and durability. Celadon's glaze contains iron oxide, which reacts during firing to produce its characteristic pale green to blue hues, enhancing its aesthetic and weather-resistant properties. In contrast, bricks exhibit high compressive strength, porosity regulated by firing techniques, and excellent thermal mass, making them suitable for structural applications in construction.
Aesthetic Differences: Celadon vs Brick
Celadon features a smooth, glossy finish with a subtle greenish-blue hue, offering a sleek and modern aesthetic ideal for contemporary construction designs. Brick provides a textured, earthy appearance with warm red, brown, and orange tones, delivering a classic and rustic charm commonly used in traditional architecture. The choice between celadon and brick impacts the overall visual appeal, with celadon conveying elegance and minimalism, while brick emphasizes warmth and timelessness.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Celadon pottery, known for its glaze and aesthetic appeal, lacks the structural strength required for construction compared to brick, which is specifically engineered for durability and load-bearing purposes. Bricks exhibit superior weather resistance and longevity, often lasting over 100 years with minimal maintenance, while celadon materials are brittle and prone to cracking under stress. The inherent composition and manufacturing process of bricks offer enhanced thermal insulation and compressive strength, making them more reliable for long-term structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Celadon vs Brick
Celadon tiles typically cost 15-25% more than traditional clay bricks due to their specialized glazing and firing processes. Bricks offer a more economical option for large-scale construction, with prices averaging $0.50-$1.00 per unit compared to celadon tiles priced at $0.75-$1.25. Maintenance and durability also impact long-term expenses, with celadon providing enhanced resistance to moisture and staining that may reduce lifecycle costs despite higher upfront investment.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Celadon bricks offer a sustainable advantage due to their production from natural clay materials that require lower kiln temperatures, resulting in reduced carbon emissions compared to traditional brick manufacturing. The durability and high thermal mass of celadon bricks enhance energy efficiency in buildings by maintaining stable indoor temperatures, which reduces heating and cooling demands. In contrast, conventional brick production often involves higher energy consumption and greater environmental degradation, making celadon a more eco-friendly choice for environmentally conscious construction projects.
Structural Performance and Strength
Celadon bricks are renowned for their high compressive strength and durability, making them ideal for structural applications in construction. Compared to traditional bricks, Celadon offers superior resistance to weathering and load-bearing capacity, ensuring enhanced stability in building frameworks. Their uniform size and low porosity contribute to consistent performance under stress and long-term structural integrity.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Celadon tiles offer easier installation due to their uniform size and smooth surface, reducing alignment errors and cutting time compared to brick. Maintenance for Celadon involves simple cleaning with mild detergents to prevent stains, while bricks require regular sealing to protect against moisture and prevent efflorescence. Brick installation demands skilled labor to ensure proper mortar application and curing, increasing labor costs and time relative to Celadon.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations
Celadon offers a smooth, glazed finish with superior water resistance, making it ideal for areas requiring aesthetic appeal and durability against moisture. Brick provides robust structural strength, excellent thermal insulation, and fire resistance, suitable for load-bearing walls and energy-efficient construction. When choosing between Celadon and Brick, consider factors such as environmental exposure, desired architectural style, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Celadon vs Brick for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com