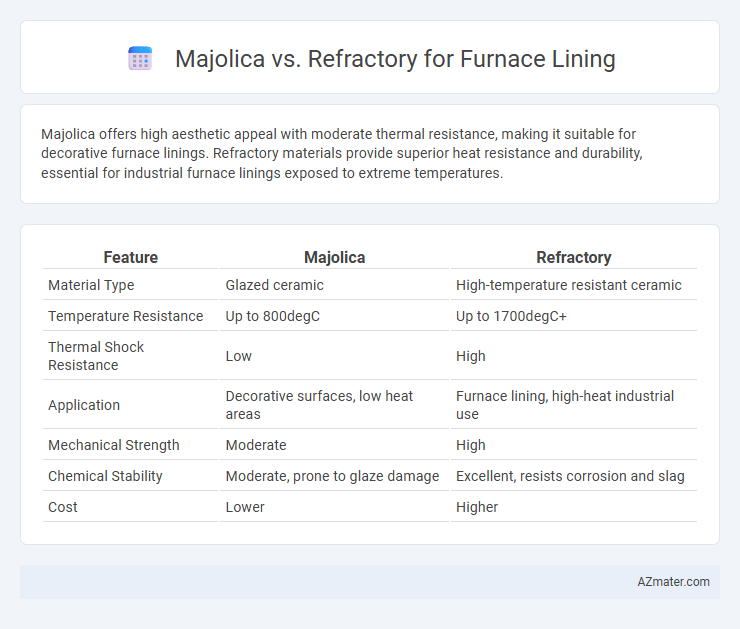
Majolica offers high aesthetic appeal with moderate thermal resistance, making it suitable for decorative furnace linings. Refractory materials provide superior heat resistance and durability, essential for industrial furnace linings exposed to extreme temperatures.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Majolica | Refractory |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic | High-temperature resistant ceramic |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 800degC | Up to 1700degC+ |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | High |
| Application | Decorative surfaces, low heat areas | Furnace lining, high-heat industrial use |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Stability | Moderate, prone to glaze damage | Excellent, resists corrosion and slag |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials play a crucial role in ensuring thermal efficiency and durability in high-temperature environments. Majolica, a glazed ceramic material, offers aesthetic appeal and moderate thermal resistance, making it suitable for decorative or lower-temperature applications. In contrast, refractory materials provide superior heat resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability, making them essential for lining furnaces operating at extreme temperatures in industrial settings.
What is Majolica?
Majolica is a glazed ceramic material commonly used for furnace linings due to its excellent thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures. It offers superior insulation and durability, making it ideal for withstanding the intense heat inside industrial furnaces. Compared to refractory materials, Majolica provides enhanced resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, extending the lifespan of furnace linings.
What are Refractory Materials?
Refractory materials are heat-resistant substances designed to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments in furnace linings, ensuring structural integrity and thermal efficiency. These materials include fireclay, alumina, silica, and magnesia, each offering specific thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. Majolica, often confused with decorative ceramics, lacks the high-temperature durability of true refractory materials, making refractories essential for industrial furnace applications.
Thermal Properties Comparison
Majolica, known for its moderate thermal conductivity and ability to retain heat, offers effective insulation in furnace linings but generally operates at lower maximum temperatures compared to refractory materials. Refractory linings exhibit superior thermal stability and higher melting points, often exceeding 1500degC, making them ideal for high-temperature furnace environments requiring durability and resistance to thermal shock. The enhanced thermal resistance of refractory materials ensures prolonged furnace lifespan and energy efficiency under extreme thermal cycling conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Majolica furnace linings offer moderate durability but tend to degrade faster under high-temperature cycling compared to refractory linings, which are specifically engineered for extreme heat resistance. Refractory materials exhibit superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, resulting in significantly longer service life and reduced maintenance in industrial furnace applications. Choosing refractory linings enhances overall furnace efficiency and longevity by withstanding thermal shock and chemical corrosion better than majolica alternatives.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Majolica furnace linings offer moderate resistance to chemical attack, primarily effective against acidic slags but less durable in highly alkaline environments. Refractory linings provide superior chemical resistance, capable of withstanding aggressive slags and molten metal interactions, making them ideal for harsh industrial furnace conditions. Selecting refractory materials with high alumina or silica content significantly enhances resistance to chemical corrosion and extends lining lifespan.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Majolica furnace linings offer easier installation due to their lightweight composition and ability to be molded into precise shapes, reducing the need for extensive curing time. Refractory linings, while more durable at high temperatures, often require skilled labor and longer drying periods to avoid cracks and ensure structural integrity. Maintenance of Majolica linings is generally simpler, as damaged sections can be replaced or repaired onsite, whereas refractory linings need more complex repairs involving high-temperature kiln treatments.
Cost Considerations
Majolica bricks typically offer a lower initial cost compared to refractory bricks, making them a budget-friendly option for furnace lining. Refractory bricks, although more expensive upfront due to their superior heat resistance and durability, often result in lower long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating total lifecycle cost is crucial when choosing between majolica and refractory materials for furnace applications.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Majolica, characterized by its vitreous, glazed surface, offers moderate thermal resistance but may suffer from thermal shock and cracking under extreme temperature fluctuations typical in furnace linings. Refractory materials, designed to withstand high temperatures exceeding 1500degC, provide superior structural integrity and thermal stability in harsh furnace environments. Their composition, often including alumina, silica, and fireclay, ensures enhanced durability, resistance to chemical attack, and minimal thermal expansion, making refractory linings the preferred choice for high-performance furnace operation.
Which is Better for Furnace Lining?
Majolica and refractory materials both serve as furnace linings but differ significantly in performance and durability. Refractory linings, made from materials like fireclay, alumina, and silica, offer superior heat resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength compared to Majolica, a glazed ceramic known for aesthetic qualities but lower thermal endurance. For industrial furnaces requiring long service life and high-temperature resistance, refractory linings are the better choice due to their ability to withstand intense thermal cycling and corrosive environments.
Infographic: Majolica vs Refractory for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com