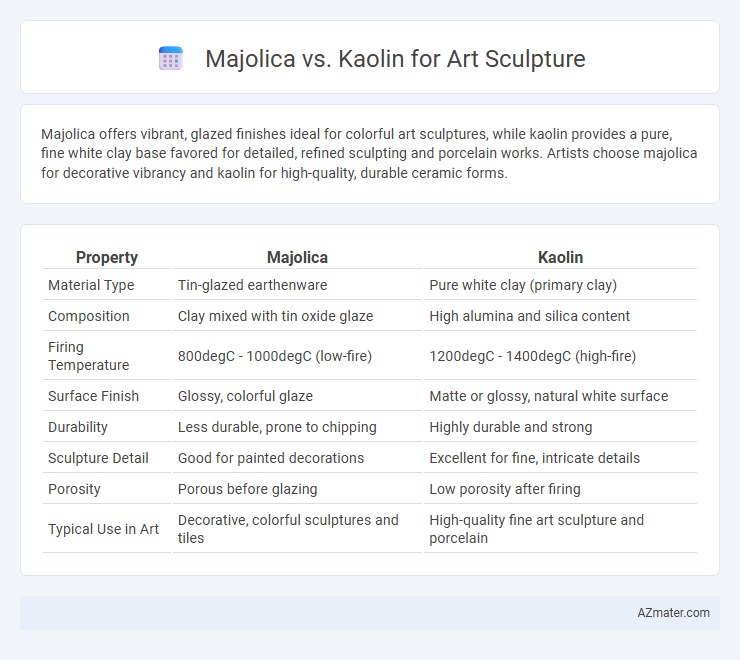
Majolica offers vibrant, glazed finishes ideal for colorful art sculptures, while kaolin provides a pure, fine white clay base favored for detailed, refined sculpting and porcelain works. Artists choose majolica for decorative vibrancy and kaolin for high-quality, durable ceramic forms.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Majolica | Kaolin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Tin-glazed earthenware | Pure white clay (primary clay) |
| Composition | Clay mixed with tin oxide glaze | High alumina and silica content |
| Firing Temperature | 800degC - 1000degC (low-fire) | 1200degC - 1400degC (high-fire) |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, colorful glaze | Matte or glossy, natural white surface |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to chipping | Highly durable and strong |
| Sculpture Detail | Good for painted decorations | Excellent for fine, intricate details |
| Porosity | Porous before glazing | Low porosity after firing |
| Typical Use in Art | Decorative, colorful sculptures and tiles | High-quality fine art sculpture and porcelain |
Understanding Majolica: Composition and Artistic Uses
Majolica is a tin-glazed pottery known for its vibrant, opaque white surface that serves as a perfect canvas for detailed, colorful decorations often used in art sculptures. Its composition includes a clay body covered with a lead glaze containing tin oxide, creating a smooth, glossy finish that enhances artistic expression and durability. Artists favor Majolica for its ability to capture fine brushwork and its compatibility with various pigment types, making it ideal for intricate, visually striking sculptural pieces.
Kaolin Clay: Properties and Sculptural Potential
Kaolin clay, prized for its fine particle size and high whiteness, offers exceptional plasticity and smooth texture ideal for detailed sculptural work. Its low shrinkage and high firing temperature enhance durability, making it suitable for both delicate and robust art sculptures. Unlike majolica, which is a glazed earthenware, kaolin provides a versatile, unglazed medium allowing artists greater control over texture and finish.
Key Differences Between Majolica and Kaolin
Majolica is a type of earthenware pottery characterized by its colorful tin-glazed surface, often used for decorative art sculptures, while Kaolin is a pure white clay primarily used for porcelain and fine ceramics due to its high plasticity and strength. Majolica's porous body requires a glaze to make it waterproof, unlike Kaolin, which can be fired to a dense, vitrified state producing a smooth, non-porous finish. The artistic application differs as Majolica allows vibrant painted designs on its glaze, whereas Kaolin supports intricate sculpting and is favored for high-detail, refined ceramic art.
Color and Glaze Interactions in Majolica and Kaolin
Majolica clay, rich in iron oxide, produces vibrant, warm hues that intensify under colorful lead-glazed surfaces, enhancing detailed painted decoration in art sculptures. Kaolin, a pure white porcelain clay, offers a smooth, bright base that allows for crisp, translucent glaze finishes, promoting subtle color variations and delicate brushwork effects. The interaction of Majolica's porous body with glazes creates pronounced texture and color depth, whereas Kaolin's vitrified surface yields a sleek, refined aesthetic with muted but luminous color reflections.
Workability: Sculpting Techniques for Each Clay
Majolica clay offers exceptional workability with its smooth texture and plasticity, making it ideal for detailed modeling and fine sculpting techniques such as carving and incising. In contrast, Kaolin clay, characterized by its higher purity and firmer consistency, excels in precision shaping and slip casting but requires advanced handling due to its lower plasticity and tendency to crack during drying. Each clay's unique properties influence sculptors' approach, with Majolica favored for intricate surface decoration and Kaolin preferred for clean, refined forms in art sculpture.
Firing Temperatures and Kiln Requirements
Majolica clay typically fires at lower temperatures ranging from cone 04 to cone 06 (approximately 1828degF to 1945degF), requiring a kiln capable of consistent low-fire heat. Kaolin, often used for porcelain, demands higher firing temperatures between cone 10 to cone 13 (about 2381degF to 2381degF or higher), necessitating a kiln designed for high-fire ceramics to achieve vitrification and strength. Choosing the right kiln temperature setting is critical since Majolica thrives in earthenware kilns, while Kaolin benefits from the intense heat of stoneware or porcelain kilns for optimal durability.
Surface Texture and Finish: A Comparative Study
Majolica offers a vibrant, glossy surface texture due to its tin-glazed earthenware body, resulting in a smooth, reflective finish ideal for detailed, colorful art sculptures. Kaolin, a primary ingredient in porcelain, provides a finer, matte or slightly translucent surface with a more refined, delicate finish, allowing for subtle textural nuances in sculptural works. Comparing these materials reveals majolica's suitability for bold, decorative pieces and kaolin's preference in creating elegant, understated textures with durable finishes.
Durability and Longevity in Art Sculptures
Majolica clay, known for its porous nature and vibrant glaze finish, offers moderate durability but may be prone to chipping and water absorption over time, potentially affecting the longevity of art sculptures in humid environments. Kaolin, a primary component of porcelain, provides superior strength and resistance to wear due to its dense, non-porous structure, making it highly durable and ideal for long-lasting art sculptures. Sculptors seeking longevity and structural integrity often prefer kaolin-based clays to ensure their artworks withstand environmental stress and aging.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Artistic Vision
Majolica clay offers vibrant surface glazing and a porous texture ideal for detailed, colorful sculptures, making it perfect for artists prioritizing intricate designs and vivid finishes. Kaolin clay, known for its pure white color and fine particle size, provides a smooth, durable base suited for minimalistic and refined sculptures requiring high precision and subtle elegance. Selecting between majolica and kaolin depends on the desired aesthetic, texture, and finishing techniques aligned with your artistic vision.
Expert Tips for Sculptors: Using Majolica vs Kaolin
Majolica clay offers vibrant glazing options with its porous, absorbent texture ideal for colorful, detailed sculpture finishes, while Kaolin provides a purer, fine-grained structure perfect for smooth, precise modeling and high-fired porcelain effects. Experts recommend using Majolica for expressive, visually rich surface treatments requiring lower firing temperatures, whereas Kaolin suits sculptors aiming for durability and intricate detail with higher firing thresholds. Selecting between Majolica and Kaolin depends on desired aesthetic outcomes, firing capabilities, and the sculptor's comfort with glazing techniques and surface textures.
Infographic: Majolica vs Kaolin for Art Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com