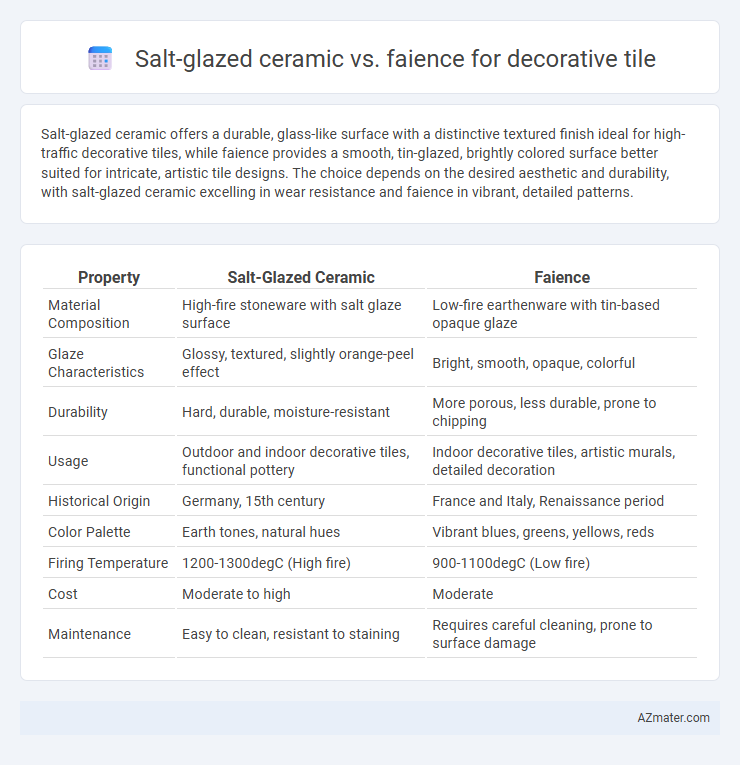
Salt-glazed ceramic offers a durable, glass-like surface with a distinctive textured finish ideal for high-traffic decorative tiles, while faience provides a smooth, tin-glazed, brightly colored surface better suited for intricate, artistic tile designs. The choice depends on the desired aesthetic and durability, with salt-glazed ceramic excelling in wear resistance and faience in vibrant, detailed patterns.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Salt-Glazed Ceramic | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-fire stoneware with salt glaze surface | Low-fire earthenware with tin-based opaque glaze |
| Glaze Characteristics | Glossy, textured, slightly orange-peel effect | Bright, smooth, opaque, colorful |
| Durability | Hard, durable, moisture-resistant | More porous, less durable, prone to chipping |
| Usage | Outdoor and indoor decorative tiles, functional pottery | Indoor decorative tiles, artistic murals, detailed decoration |
| Historical Origin | Germany, 15th century | France and Italy, Renaissance period |
| Color Palette | Earth tones, natural hues | Vibrant blues, greens, yellows, reds |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1300degC (High fire) | 900-1100degC (Low fire) |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, resistant to staining | Requires careful cleaning, prone to surface damage |
Introduction to Decorative Ceramic Tiles
Salt-glazed ceramics feature a distinctive glossy surface created by introducing salt into the kiln during firing, resulting in a durable, textured finish ideal for decorative tiles with a rustic appeal. Faience tiles, known for their tin-glazed, brightly colored, and smooth surfaces, offer vibrant patterns and intricate designs that enhance ornamental interior spaces. Both materials provide unique aesthetic qualities and functional benefits, making them popular choices for decorative ceramic tile applications.
Understanding Salt-Glazed Ceramics
Salt-glazed ceramics are created by introducing salt into the kiln at high temperatures, causing a chemical reaction that forms a distinctive, glossy, and textured surface that is both durable and water-resistant. This glazing technique contrasts with faience, which uses a tin-based glaze to achieve a smooth, opaque finish often highlighted with intricate painted designs. Understanding the salt-glazed process is essential for selecting decorative tiles that emphasize rustic charm, durability, and a natural glaze finish.
What is Faience?
Faience is a type of tin-glazed ceramic known for its bright, opaque white surface that provides an ideal canvas for vibrant hand-painted designs. Unlike salt-glazed ceramics, which achieve a glossy, textured finish through a salt vapor reaction in the kiln, faience features a smooth, glass-like glaze applied before firing. This glazing technique enhances faience's decorative appeal, making it a preferred choice for intricate, colorful tile work in historical and artistic settings.
Historical Background of Salt-Glazed Tiles
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles originated in 15th-century Germany, where potters introduced salt into the kiln during firing, creating a distinctive glossy, textured surface through chemical reaction with the silica in the clay. This technique gained popularity across Europe for its durability and unique aesthetic, commonly used in both architectural and decorative applications. In contrast, faience tiles, with roots in ancient Egypt and the Mediterranean, are characterized by their tin-glazed, opaque surfaces and vibrant colors, serving different artistic and functional purposes in historic tile production.
Faience Tile Production Techniques
Faience tile production involves tin-glazing a porous earthenware body, creating a bright white, opaque surface ideal for intricate painted decoration. The technique includes applying a lead glaze fused with tin oxide, which provides a durable, glassy finish that enhances color vibrancy and detail precision. Unlike salt-glazed ceramics, faience tiles allow for a broader palette and finer artistic expression, making them highly valued in decorative tile craftsmanship.
Aesthetic Differences: Salt-Glazed vs. Faience
Salt-glazed ceramics feature a glossy, textured surface with subtle variations in glaze thickness, creating a distinctive, tactile finish prized for its rustic, earthy aesthetic. Faience tiles offer a smooth, brightly colored, and often intricately painted surface that delivers a polished and vibrant appearance ideal for ornamental and detailed decorative work. The aesthetic differences lie in salt-glazed tiles' natural, muted tones and rugged texture versus faience's crisp, colorful, and highly detailed visual appeal.
Durability and Longevity of Each Tile Type
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles exhibit superior durability due to their vitrified, glass-like surface formed during high-temperature salt firing, making them highly resistant to scratches and moisture penetration. Faience tiles, with their porous bisque body and lead-based glaze, are more prone to chipping and wear over time, requiring careful sealing to maintain their aesthetic appeal. The longevity of salt-glazed tiles in high-traffic or outdoor environments surpasses faience, which is better suited for low-traffic decorative applications indoors.
Common Applications in Modern Interior Design
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles are prized for their durable, glossy surfaces and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for kitchens, bathrooms, and fireplace surrounds in modern interior design. Faience tiles, characterized by their vibrant, hand-painted designs and matte finish, are commonly used as accent pieces in wall murals, backsplashes, and decorative borders to add artistic flair. Both materials offer unique aesthetic qualities, with salt-glazed ceramics providing a rustic, tactile appeal and faience delivering intricate, colorful patterns that complement vintage and eclectic decor styles.
Maintenance and Care Considerations
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles exhibit a durable, glass-like surface that resists stains and moisture, requiring minimal maintenance compared to faience tiles, which have a delicate, porous glaze prone to chipping and staining. Regular sealing and gentle cleaning with pH-neutral products are essential for faience tiles to preserve their vibrant colors and intricate patterns, while salt-glazed ceramics can withstand more aggressive cleaning agents without damage. Choosing salt-glazed ceramics reduces long-term upkeep and the risk of water damage, making them ideal for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas.
Choosing the Right Tile: Salt-Glazed vs. Faience
Salt-glazed ceramic tiles offer a durable, glossy finish achieved through high-temperature salt vapor glazing, making them ideal for areas prone to moisture and wear. Faience tiles, characterized by their tin-glazed, opaque surface and vibrant colors, excel in intricate decorative patterns for indoor use with lower resistance to abrasion. Selecting between salt-glazed ceramic and faience involves balancing durability requirements and aesthetic preferences, with salt-glazed suited for functional spaces and faience preferred for artistic, ornamental installations.
Infographic: Salt-glazed ceramic vs Faience for Decorative Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com