Ferroelectric ceramics offer superior dielectric properties and temperature stability compared to traditional earthenware, making them more suitable for advanced decorative vases requiring durability and electrical functionality. Earthenware vases, while aesthetically rustic and porous, lack the mechanical strength and electrical responsiveness of ferroelectric ceramic materials.
Table of Comparison
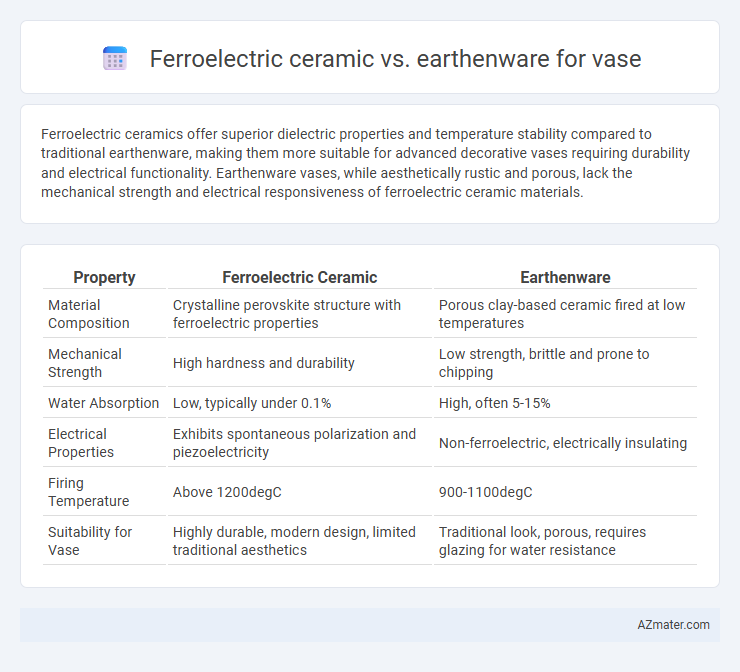
| Property | Ferroelectric Ceramic | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Crystalline perovskite structure with ferroelectric properties | Porous clay-based ceramic fired at low temperatures |
| Mechanical Strength | High hardness and durability | Low strength, brittle and prone to chipping |
| Water Absorption | Low, typically under 0.1% | High, often 5-15% |
| Electrical Properties | Exhibits spontaneous polarization and piezoelectricity | Non-ferroelectric, electrically insulating |
| Firing Temperature | Above 1200degC | 900-1100degC |
| Suitability for Vase | Highly durable, modern design, limited traditional aesthetics | Traditional look, porous, requires glazing for water resistance |
Introduction to Ferroelectric Ceramics and Earthenware
Ferroelectric ceramics are advanced materials exhibiting spontaneous electric polarization reversible by an external electric field, making them prized in high-tech applications and artistic ceramics requiring precise structural properties. Earthenware, a traditional ceramic made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, is renowned for its rustic appeal, earthy texture, and affordability. Comparing both, ferroelectric ceramics offer durability and functional benefits for specialized vases, while earthenware excels in classic aesthetics and accessibility for everyday decorative use.
Material Composition and Structure
Ferroelectric ceramic vases consist of perovskite-structured materials like lead zirconate titanate (PZT), characterized by their spontaneous electric polarization and crystal lattice alignment, offering enhanced durability and electrical properties. Earthenware vases are made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in an amorphous, less dense structure that tends to be more fragile and absorbent. The distinct material composition of ferroelectric ceramics provides superior mechanical strength and resistance to moisture compared to the traditional, porous earthenware structure.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Ferroelectric ceramic vases are produced through a precise sintering process at high temperatures, ensuring uniform grain structure and enhanced electrical properties, whereas earthenware vases are shaped using traditional hand-molding or wheel-throwing techniques followed by low-temperature firing, resulting in a porous and less dense material. Ferroelectric ceramics require controlled atmosphere conditions during manufacturing to maintain their functional properties, while earthenware relies on simpler kiln firing methods and glazing for aesthetic finishes. The complexity of manufacturing ferroelectric ceramics makes them more suitable for advanced decorative applications with potential sensor integration, contrasting with the rustic appeal and mass-production ease of earthenware vases.
Durability and Strength Assessment
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit superior durability and mechanical strength compared to earthenware, making them more resistant to cracking and chipping under stress. Their microstructure allows them to withstand higher thermal and mechanical loads, enhancing longevity in various environmental conditions. In contrast, earthenware, being more porous and brittle, tends to absorb moisture and is prone to damage with regular use, reducing its overall lifespan as a vase material.
Aesthetics and Surface Finish
Ferroelectric ceramic vases exhibit a smooth, glossy surface finish with a modern aesthetic characterized by a high degree of shine and vibrant color retention due to their polarized crystalline structure. Earthenware vases offer a rustic and matte appearance, featuring natural textures and earthy tones that emphasize handcrafted artistry and traditional charm. The overall aesthetic appeal of ferroelectric ceramic is sleek and contemporary, while earthenware provides a warm, organic feel suitable for vintage or bohemian decor.
Water Retention and Porosity
Ferroelectric ceramic vases exhibit low porosity and high water retention due to their dense crystalline structure, making them ideal for maintaining soil moisture in plants. In contrast, earthenware vases have a porous, coarse texture that allows significant water evaporation and drainage, leading to faster soil drying. The choice between ferroelectric ceramic and earthenware directly impacts water retention efficiency and the hydration needs of planted specimens.
Functional Advantages in Vase Usage
Ferroelectric ceramics offer superior durability and enhanced mechanical strength compared to traditional earthenware, making vases more resistant to chipping and breakage. Their inherent piezoelectric properties allow for innovative designs incorporating sensor technology for humidity or temperature monitoring within the vase environment. Earthenware, while aesthetically pleasing and cost-effective, lacks the advanced functional benefits provided by ferroelectric ceramics, limiting its application in smart or high-performance vase designs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ferroelectric ceramic vases typically have a higher environmental footprint due to the energy-intensive manufacturing process and the use of rare materials, whereas earthenware vases are made from natural clay with lower energy consumption and greater biodegradability. Earthenware supports sustainability through its use of abundant, naturally sourced materials and simpler production techniques that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Ferroelectric ceramics may offer durability but their production often involves mining and processing chemicals that pose environmental challenges compared to the eco-friendlier earthenware alternatives.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Ferroelectric ceramics generally have higher production costs than earthenware due to advanced material processing and specialized manufacturing techniques, making them less accessible for mass-market vases. Earthenware remains more cost-effective and widely available, benefiting from traditional craftsmanship and abundant raw materials, which drives its dominant market share in decorative pottery. The market for ferroelectric ceramic vases is niche, catering to specific high-tech or luxury applications, while earthenware maintains broad consumer appeal through affordability and extensive retail distribution.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Vase
Ferroelectric ceramic offers superior durability and enhanced aesthetic appeal due to its high dielectric constant and piezoelectric properties, making it ideal for modern, elegant vases. Earthenware, while more porous and less durable, provides a traditional, rustic look with natural textures that appeal to those seeking an artisanal style. Choosing between ferroelectric ceramic and earthenware depends on whether you prioritize long-lasting strength and contemporary design or a classic, handcrafted appearance for your vase.
Infographic: Ferroelectric ceramic vs Earthenware for Vase
 azmater.com
azmater.com