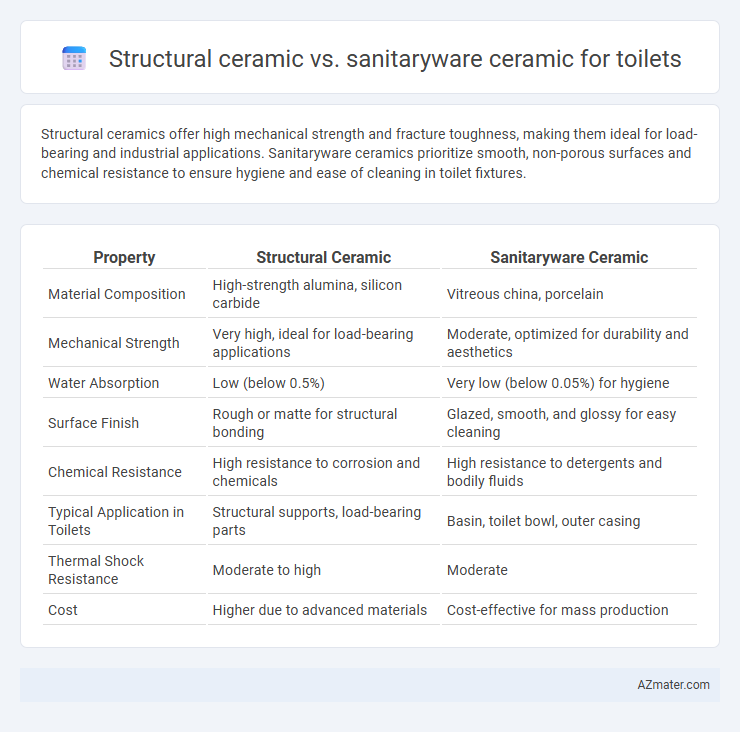
Structural ceramics offer high mechanical strength and fracture toughness, making them ideal for load-bearing and industrial applications. Sanitaryware ceramics prioritize smooth, non-porous surfaces and chemical resistance to ensure hygiene and ease of cleaning in toilet fixtures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Structural Ceramic | Sanitaryware Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-strength alumina, silicon carbide | Vitreous china, porcelain |
| Mechanical Strength | Very high, ideal for load-bearing applications | Moderate, optimized for durability and aesthetics |
| Water Absorption | Low (below 0.5%) | Very low (below 0.05%) for hygiene |
| Surface Finish | Rough or matte for structural bonding | Glazed, smooth, and glossy for easy cleaning |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to corrosion and chemicals | High resistance to detergents and bodily fluids |
| Typical Application in Toilets | Structural supports, load-bearing parts | Basin, toilet bowl, outer casing |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced materials | Cost-effective for mass production |
Introduction: Understanding Structural Ceramics and Sanitaryware Ceramics
Structural ceramics, designed for high-strength and durability applications, exhibit exceptional resistance to wear, heat, and corrosion, making them ideal for industrial and engineering use. Sanitaryware ceramics prioritize hygiene, smooth surface finish, and water resistance, specifically tailored for bathroom fixtures like toilets to prevent bacterial growth and ensure easy cleaning. Understanding the distinct material properties and functional priorities of structural ceramics versus sanitaryware ceramics is essential for selecting the right ceramic type in toilet manufacturing.
Material Composition: Structural vs. Sanitaryware Ceramics
Structural ceramics for toilets primarily consist of dense, high-strength materials like alumina and zirconia, designed to withstand mechanical stress and resist wear. Sanitaryware ceramics are typically composed of porcelain or vitreous china, which include a mixture of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, optimized for smooth surfaces, hygiene, and ease of cleaning. The distinct material compositions impact durability, aesthetic finish, and functionality in bathroom applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Differences and Techniques
Structural ceramics for toilets involve advanced manufacturing processes like dry pressing and isostatic pressing to achieve high density and mechanical strength, essential for withstanding heavy loads and impacts. Sanitaryware ceramics typically utilize slip casting, where liquid clay slip is poured into molds, followed by drying and firing to create complex shapes with a smooth, glossy finish suitable for hygiene and aesthetics. The firing temperatures for structural ceramics are generally higher to enhance durability, while sanitaryware ceramics emphasize glaze application and precise molding techniques to ensure water resistance and cleanliness.
Physical Properties and Performance Comparison
Structural ceramics exhibit high mechanical strength, low porosity, and excellent thermal shock resistance, making them ideal for load-bearing and high-stress applications. Sanitaryware ceramics prioritize smooth surface finish, low water absorption (typically below 0.5%), and resistance to staining and chemical corrosion to ensure hygiene and durability in toilet use. While structural ceramics offer superior fracture toughness and wear resistance, sanitaryware ceramics excel in water resistance and ease of cleaning, optimizing performance for plumbing fixtures.
Durability and Lifespan in Toilet Applications
Structural ceramics used in toilets exhibit superior durability due to their high resistance to mechanical stress, wear, and chemical corrosion, ensuring a longer lifespan in harsh bathroom environments. Sanitaryware ceramics, while designed specifically for hygiene and aesthetic appeal, tend to have lower resistance to impact and chipping, potentially reducing their longevity under frequent usage. The inherent material properties of structural ceramics make them more suitable for heavy-duty toilet applications where durability and lifespan are critical performance factors.
Water Absorption and Porosity: Analyzing Both Types
Structural ceramics typically exhibit lower water absorption rates, often below 0.5%, ensuring high mechanical strength and durability suitable for load-bearing applications. Sanitaryware ceramics for toilets usually have higher porosity and water absorption values, generally ranging from 0.5% to 3%, which are optimized to maintain surface smoothness and prevent staining. The differences in water absorption and porosity between these ceramics impact their functionality, with structural ceramics prioritizing strength and sanitaryware focusing on hygiene and maintenance efficiency.
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
Structural ceramics for toilets prioritize durability and strength, often featuring a matte or utilitarian surface finish that resists wear and mechanical stress. Sanitaryware ceramics emphasize a glossy, smooth surface finish that enhances aesthetics and ease of cleaning, achieved through advanced glazing techniques. The polished finish in sanitaryware not only boosts visual appeal but also provides a non-porous barrier to stains and bacteria, making it ideal for bathroom hygiene.
Cost Implications: Production and Market Prices
Structural ceramics used in toilets, primarily composed of alumina and zirconia, have higher production costs due to advanced raw materials and complex manufacturing processes, resulting in significantly elevated market prices. Sanitaryware ceramics, mainly porcelain with kaolin and feldspar, benefit from established mass production techniques, leading to lower costs and more affordable market pricing. The cost differential directly impacts consumer choice, with sanitaryware ceramics dominating the market due to economic accessibility despite structural ceramics offering enhanced durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Structural ceramics for toilets typically exhibit higher durability and longer lifespan compared to sanitaryware ceramics, reducing waste generation over time. Sanitaryware ceramics often require more frequent replacement due to lower mechanical strength, which increases resource consumption and environmental footprint. The production of structural ceramics also tends to use more energy-intensive processes, but their enhanced sustainability arises from reduced maintenance and disposal rates.
Which Ceramic Type is Best for Toilets?
Structural ceramics, known for their high mechanical strength and low porosity, offer superior durability and resistance to impact and wear in toilet applications. Sanitaryware ceramics, specifically formulated for hygiene and aesthetic appeal, provide excellent glaze finish, stain resistance, and ease of cleaning, making them ideal for maintaining sanitary conditions. For toilets, sanitaryware ceramic is generally preferred due to its specialized surface properties that enhance cleanliness and user comfort.
Infographic: Structural ceramic vs Sanitaryware ceramic for Toilet
 azmater.com
azmater.com