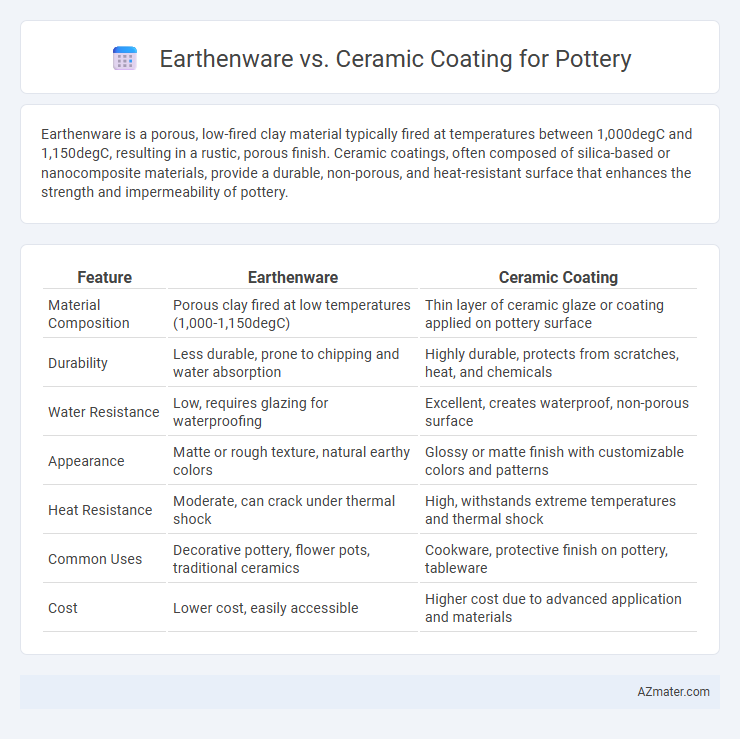
Earthenware is a porous, low-fired clay material typically fired at temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a rustic, porous finish. Ceramic coatings, often composed of silica-based or nanocomposite materials, provide a durable, non-porous, and heat-resistant surface that enhances the strength and impermeability of pottery.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Earthenware | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Porous clay fired at low temperatures (1,000-1,150degC) | Thin layer of ceramic glaze or coating applied on pottery surface |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to chipping and water absorption | Highly durable, protects from scratches, heat, and chemicals |
| Water Resistance | Low, requires glazing for waterproofing | Excellent, creates waterproof, non-porous surface |
| Appearance | Matte or rough texture, natural earthy colors | Glossy or matte finish with customizable colors and patterns |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate, can crack under thermal shock | High, withstands extreme temperatures and thermal shock |
| Common Uses | Decorative pottery, flower pots, traditional ceramics | Cookware, protective finish on pottery, tableware |
| Cost | Lower cost, easily accessible | Higher cost due to advanced application and materials |
Understanding Earthenware: Composition and Characteristics
Earthenware is a porous, low-fired pottery made primarily from natural clay mixed with minerals like quartz and feldspar, typically fired between 1,000degC and 1,150degC. Its coarse texture and relatively low vitrification result in a more absorbent and less durable material compared to stoneware or porcelain. Earthenware's distinctive porous surface necessitates glazing or coating to enhance water resistance and durability, making ceramic coatings essential for functional pottery.
What is Ceramic Coating in Pottery?
Ceramic coating in pottery refers to a glass-like layer applied to earthenware or other pottery surfaces to enhance durability, water resistance, and aesthetic appeal. This coating, often made from silica, alumina, and other minerals, fuses to the pottery during firing at high temperatures, creating a smooth, non-porous finish. Unlike the porous nature of earthenware, ceramic coatings improve the strength of the piece and protect it from stains and scratches.
Visual and Textural Differences Between Earthenware and Ceramic Coating
Earthenware pottery typically features a porous, matte surface with visible textures and natural imperfections that highlight its handmade quality. Ceramic coatings provide a smooth, glossy finish that enhances color vibrancy and offers a uniform texture, creating a more polished and refined appearance. The difference in surface treatment results in earthenware having a rustic, tactile feel, while ceramic-coated pieces exhibit durability and sleekness ideal for decorative use.
Durability: Which Lasts Longer—Earthenware or Ceramic Coating?
Earthenware pottery, made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, is more prone to chipping and water absorption, reducing its durability compared to ceramic coatings. Ceramic coatings, typically composed of high-temperature fired glazes or advanced ceramic materials, create a hard, non-porous surface that significantly enhances resistance to scratches, stains, and temperature fluctuations. The longevity of pottery with ceramic coatings generally surpasses that of uncoated earthenware, making ceramic coatings the preferred choice for durable and long-lasting pottery finishes.
Heat Resistance: Earthenware vs Ceramic-Coated Pottery
Earthenware pottery typically withstands lower temperatures, usually around 1,000 to 1,150degC (1,832 to 2,102degF), making it more prone to thermal shock and less suitable for high-heat applications. Ceramic coatings on pottery enhance heat resistance significantly, allowing the vessel to endure temperatures above 1,200degC (2,192degF) while providing a durable, heat-retentive surface. This increased heat tolerance makes ceramic-coated pottery ideal for cooking and serving hot dishes compared to traditional earthenware.
Safety and Non-Toxicity: Foodware Considerations
Earthenware pottery, often porous and fired at lower temperatures, requires lead-free, food-safe glazes to ensure non-toxicity and avoid harmful leaching when used for foodware. Ceramic coatings, typically applied on stoneware or porcelain, undergo higher-temperature firings that vitrify the surface, creating a durable, non-porous, and inherently safer barrier against contaminants. Prioritizing FDA-approved glazes and coatings is essential to maintain food safety standards and prevent exposure to toxins in functional pottery.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Earthenware pottery requires gentle cleaning with mild soap and water to prevent damage due to its porous surface, often needing sealing to enhance durability. Ceramic coatings provide a non-porous, smooth finish that resists stains and simplifies maintenance, allowing for easier cleaning with just a damp cloth. Regular care for ceramic-coated pottery includes avoiding abrasive cleaners to maintain the coating's integrity and extend its lifespan.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color, Finish, and Design Options
Earthenware offers warm, rustic tones with matte or slightly textured finishes, emphasizing traditional and handcrafted aesthetics ideal for decorative pottery. Ceramic coatings provide a broader spectrum of vibrant colors and glossy or satin finishes, allowing for intricate designs and modern, sleek appearances. The choice between earthenware and ceramic coatings significantly impacts the visual appeal, with earthenware favoring natural, earthy charm and ceramics enabling diverse, polished creative expressions.
Cost Comparison: Budgeting for Earthenware and Ceramic-Coated Pottery
Earthenware pottery is generally more affordable due to lower material costs and simpler firing processes, making it ideal for budget-conscious buyers. Ceramic coatings add a protective, durable layer that increases the overall expense because of advanced materials and multi-step application techniques. Budgeting for ceramic-coated pottery requires accounting for higher initial investment balanced against longer-lasting, more resilient finishes.
Which to Choose: Key Factors for Selecting the Right Pottery
Earthenware pottery offers a rustic, porous finish ideal for decorative pieces, while ceramic coatings provide a durable, non-porous surface suited for functional ware like dishes and cookware. Key factors for selecting the right pottery include intended use, durability requirements, and glaze safety, with ceramic coatings generally preferred for food use due to their resistance to stains and water. Cost and firing temperature are also crucial, as earthenware requires lower kiln temperatures, making it more budget-friendly but less durable than high-fired ceramic coatings.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Ceramic coating for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com