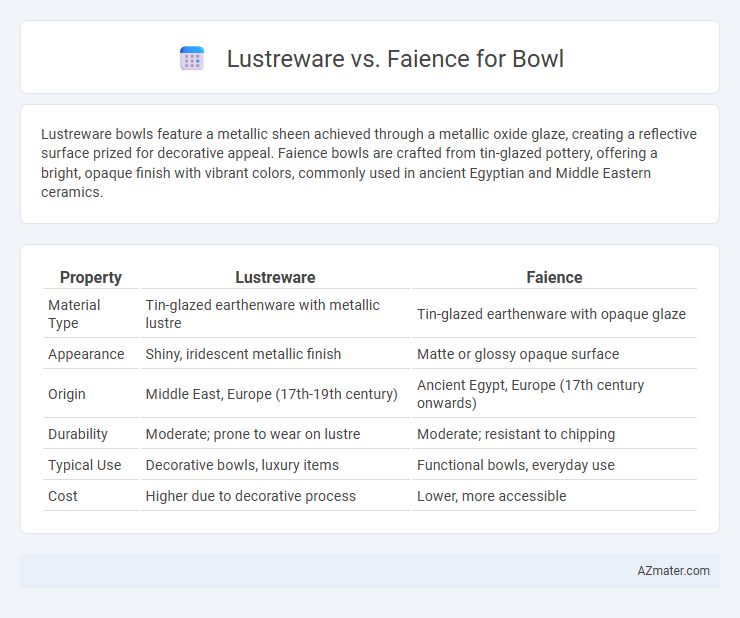
Lustreware bowls feature a metallic sheen achieved through a metallic oxide glaze, creating a reflective surface prized for decorative appeal. Faience bowls are crafted from tin-glazed pottery, offering a bright, opaque finish with vibrant colors, commonly used in ancient Egyptian and Middle Eastern ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lustreware | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Tin-glazed earthenware with metallic lustre | Tin-glazed earthenware with opaque glaze |
| Appearance | Shiny, iridescent metallic finish | Matte or glossy opaque surface |
| Origin | Middle East, Europe (17th-19th century) | Ancient Egypt, Europe (17th century onwards) |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to wear on lustre | Moderate; resistant to chipping |
| Typical Use | Decorative bowls, luxury items | Functional bowls, everyday use |
| Cost | Higher due to decorative process | Lower, more accessible |
Introduction to Lustreware and Faience
Lustreware is a type of pottery characterized by its metallic, iridescent glaze achieved through a complex firing process involving metallic salts, popular in Middle Eastern and European ceramics since the 9th century. Faience is a tin-glazed, opaque earthenware known for its bright, glossy surface and was historically produced in ancient Egypt and later in Renaissance Europe. Both Lustreware and Faience offer unique aesthetic qualities suitable for decorative bowls, with Lustreware prized for its shimmering surface and Faience valued for its vibrant, vividly colored glaze.
Historical Origins of Lustreware and Faience
Lustreware originated in the Islamic world during the 9th century, characterized by its iridescent metallic glaze created through a complex reduction firing technique that imparts a shimmering surface. Faience, with roots tracing back to ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, involves tin-glazed pottery that produces a bright, opaque white surface often decorated with vibrant colors, widely popularized in Renaissance Italy. Both techniques reflect significant cultural exchanges, with lustreware emphasizing metallic sheen and faience focusing on vivid, opaque finishes in ceramic bowls.
Materials and Techniques Used
Lustreware bowls are crafted using a delicate metallic glaze technique that involves applying silver or copper compounds to create an iridescent sheen, while faience bowls are produced from a tin-glazed earthenware clay that yields a bright, opaque white surface ideal for painted decoration. Lustreware's complex firing process in a reduced oxygen kiln brings out its distinctive shimmering colors, contrasting with faience's single firing that solidifies the glossy glaze without metallic reflections. The primary materials for lustreware include fine clay coated with a copper or silver-based lustrous glaze, whereas faience relies on a lead or tin glaze applied to porous clay for a smooth, opaline finish.
Differences in Glazing Methods
Lustreware bowls feature a metallic glaze created by applying a thin layer of metal oxides that reflect iridescent light, achieved through a secondary firing process in a reduction kiln. Faience bowls utilize an opaque, tin-based glaze that provides a bright, glossy, and smooth surface, typically fired in an oxidizing atmosphere, resulting in vibrant colors and a matte finish. The key difference in glazing methods lies in lustreware's chemically reduced metallic sheen versus faience's tin-opacified, vividly colored glaze.
Color Palette and Surface Design
Lustreware bowls exhibit an iridescent, metallic sheen achieved through a thin layer of metallic oxides, creating a rich color palette dominated by golds, silvers, and rainbow-like hues. Faience bowls feature opaque, tin-glazed surfaces with vibrant and opaque color palettes, often including blues, greens, yellows, and whites, emphasizing bold and intricate floral or geometric patterns. Surface design on lustreware emphasizes smooth, reflective textures with subtle shimmer, while faience relies on matte or glossy finishes highlighting detailed hand-painted motifs.
Durability and Practicality of Each Style
Lustreware bowls feature a metallic glaze that offers a striking iridescent finish but can be more delicate and prone to scratching or wear over time compared to faience. Faience bowls, typically made of tin-glazed earthenware, provide a harder surface that resists chipping and is better suited for everyday use, making them more durable and practical for frequent handling. The choice between lustreware and faience depends on the balance between decorative appeal and long-term functionality in kitchen or dining settings.
Regional Variations and Influences
Lustreware bowls, characterized by their metallic sheen, are predominantly associated with Middle Eastern and Spanish regions, where techniques like copper and silver luster were refined during the Islamic Golden Age. Faience bowls, featuring tin-glazed, opaque surfaces, are commonly linked to Egyptian and North African pottery traditions, reflecting Phoenician and Islamic artistic influences. Regional variations in Lustreware and Faience reflect differing raw materials, firing methods, and cultural aesthetics shaped by trade routes and religious practices across the Mediterranean basin.
Collectibility and Market Value
Lustreware bowls, prized for their iridescent glaze and vibrant colors, often command higher prices in the collector's market due to their intricate craftsmanship and rarity. Faience bowls, characterized by their tin-glazed, opaque white surface and traditional motifs, hold significant cultural value but generally have lower market value compared to lustreware. Collectors prioritize lustreware for its unique visual appeal and limited production, driving stronger demand and elevated auction results.
Aesthetic Appeal for Modern Bowls
Lustreware bowls captivate with their iridescent glaze that reflects light in a spectrum of shimmering hues, offering a dynamic and luxurious aesthetic ideal for modern decor. Faience bowls present a matte, opaque surface often decorated with vibrant, intricate patterns inspired by ancient Egyptian artistry, appealing to those seeking a bold yet rustic charm. The choice between lustreware and faience for contemporary bowls hinges on the desired visual impact, whether it's the glossy, radiant allure or the textured, colorful authenticity.
Choosing the Right Bowl: Lustreware or Faience?
Lustreware bowls feature a shimmering metallic glaze achieved through a complex firing process, offering vibrant iridescence and a distinct decorative appeal, while faience bowls are made from tin-glazed earthenware known for their bright, opaque colors and smooth, glassy finish. When choosing the right bowl, consider lustreware for decorative display and artistic value, and faience for functional use with a sturdy, colorful surface ideal for everyday dining. The decision hinges on desired aesthetic impact, durability, and intended use in both contemporary and traditional settings.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Faience for Bowl
 azmater.com
azmater.com