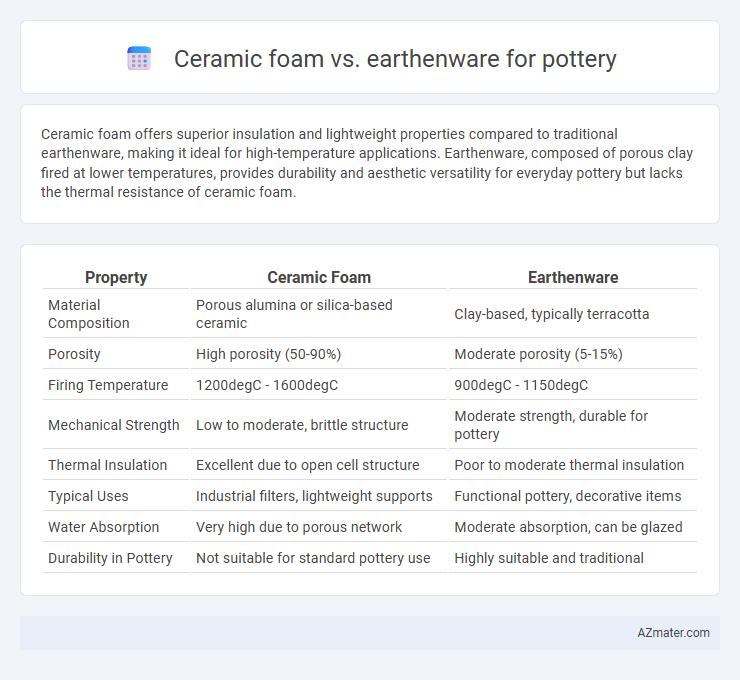
Ceramic foam offers superior insulation and lightweight properties compared to traditional earthenware, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Earthenware, composed of porous clay fired at lower temperatures, provides durability and aesthetic versatility for everyday pottery but lacks the thermal resistance of ceramic foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Foam | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Porous alumina or silica-based ceramic | Clay-based, typically terracotta |
| Porosity | High porosity (50-90%) | Moderate porosity (5-15%) |
| Firing Temperature | 1200degC - 1600degC | 900degC - 1150degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate, brittle structure | Moderate strength, durable for pottery |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent due to open cell structure | Poor to moderate thermal insulation |
| Typical Uses | Industrial filters, lightweight supports | Functional pottery, decorative items |
| Water Absorption | Very high due to porous network | Moderate absorption, can be glazed |
| Durability in Pottery | Not suitable for standard pottery use | Highly suitable and traditional |
Understanding Ceramic Foam and Earthenware: An Overview
Ceramic foam, characterized by its porous, lightweight structure, offers excellent thermal insulation and durability in pottery applications, contrasting with earthenware, which is a traditional clay-based material fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a more porous and less durable finish. Earthenware's lower firing temperature makes it more absorbent and less resistant to cracks, whereas ceramic foam retains structural integrity under higher thermal stress. Selecting between ceramic foam and earthenware depends on desired properties such as insulation, strength, and aesthetics in pottery creations.
Key Material Properties: Porosity, Strength, and Texture
Ceramic foam exhibits high porosity, providing excellent insulation and lightweight properties but lower mechanical strength compared to earthenware. Earthenware features moderate porosity, offering better durability and strength suited for functional pottery, with a denser and smoother texture. The choice between ceramic foam and earthenware depends on the required balance of insulation, strength, and surface finish in pottery applications.
Thermal Resistance: How Each Material Handles Heat
Ceramic foam exhibits superior thermal resistance due to its porous structure, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes and high heat without cracking, making it ideal for kiln furniture and thermal insulation applications. Earthenware, being more porous and less dense, has lower thermal resistance, leading to potential cracking or deformation under high heat or sudden temperature changes during firing. The difference in thermal expansion rates between ceramic foam and earthenware significantly influences their durability and suitability for various pottery uses involving heat exposure.
Applications in Pottery: Traditional vs. Modern Techniques
Ceramic foam, known for its lightweight structure and high porosity, is increasingly used in modern pottery for creating intricate textures and improving thermal insulation during firing processes. Earthenware, a traditional pottery material, remains popular for its natural, rustic appearance and ease of shaping, typically glazed for durability in functional ceramics like bowls and pots. Modern techniques leverage ceramic foam to enhance design complexity and firing efficiency, while earthenware continues to be favored in artisanal and cultural pottery practices.
Workability: Molding, Shaping, and Finishing Differences
Ceramic foam offers superior workability in molding and shaping due to its lightweight structure and high porosity, allowing for intricate and delicate designs. Earthenware, with its denser and coarser texture, requires more effort during shaping and is less forgiving for fine detailing but provides a sturdier feel. Finishing ceramic foam pieces enables smoother surfaces with less cracking, while earthenware often needs additional sanding and sealing to achieve a refined finish.
Firing Temperatures and Methods for Ceramic Foam and Earthenware
Ceramic foam typically requires high firing temperatures ranging from 1200degC to 1400degC, achieved through techniques like kiln firing in oxidizing or reducing atmospheres to enhance its porous structure. Earthenware, conversely, is fired at lower temperatures between 1000degC and 1150degC, often in an oxidizing atmosphere, producing a more porous and less vitrified product suitable for decorative and functional pottery. The distinct firing temperature ranges and methods directly influence the material properties, durability, and applications of ceramic foam and earthenware in pottery.
Durability and Longevity in Finished Pottery Pieces
Ceramic foam pottery offers enhanced durability due to its lightweight, porous structure that resists thermal shock and mechanical stress better than traditional earthenware. Earthenware, while more affordable, tends to be more fragile and prone to chipping over time because of its lower firing temperature and higher porosity. Finished pieces made from ceramic foam generally exhibit greater longevity, maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal in demanding environments.
Glazing Compatibility: Surface Treatments and Decoration
Ceramic foam and earthenware differ significantly in glazing compatibility, with ceramic foam offering a highly porous surface that enhances glaze adhesion and creates unique textured finishes ideal for specialized surface treatments. Earthenware's relatively smooth, less porous body requires specific glaze formulations to prevent defects like crazing or peeling and supports traditional decorative techniques such as slip trailing or sgraffito. Surface treatments on ceramic foam often emphasize the interplay between open pore structures and glaze, while earthenware focuses on smoothness and color retention in decorative glazing.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact Considerations
Ceramic foam pottery offers improved sustainability due to its lightweight structure, reducing raw material usage and energy consumption during firing compared to traditional earthenware. Earthenware, composed of natural clay, is biodegradable but often requires higher firing temperatures, leading to greater carbon emissions. Choosing ceramic foam can enhance eco-friendly production by minimizing resource waste and lowering the overall environmental footprint of pottery manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Material: Pros and Cons for Potters
Ceramic foam offers superior insulation and lightweight properties, making it ideal for kiln furniture and heat-resistant pottery applications, while earthenware provides a traditional, porous finish favored for decorative and functional items. Potters benefit from ceramic foam's durability and thermal shock resistance but must weigh its higher cost and limited aesthetic versatility. Earthenware's affordability and ease of shaping contrast with its lower strength and susceptibility to chipping, influencing material choice based on project requirements.
Infographic: Ceramic foam vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com