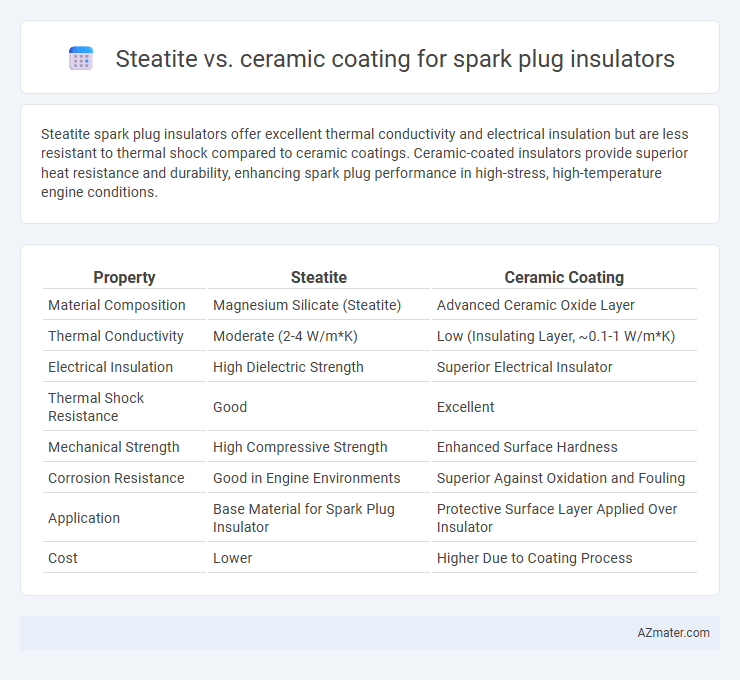
Steatite spark plug insulators offer excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation but are less resistant to thermal shock compared to ceramic coatings. Ceramic-coated insulators provide superior heat resistance and durability, enhancing spark plug performance in high-stress, high-temperature engine conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Steatite | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Magnesium Silicate (Steatite) | Advanced Ceramic Oxide Layer |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate (2-4 W/m*K) | Low (Insulating Layer, ~0.1-1 W/m*K) |
| Electrical Insulation | High Dielectric Strength | Superior Electrical Insulator |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | High Compressive Strength | Enhanced Surface Hardness |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good in Engine Environments | Superior Against Oxidation and Fouling |
| Application | Base Material for Spark Plug Insulator | Protective Surface Layer Applied Over Insulator |
| Cost | Lower | Higher Due to Coating Process |
Introduction to Spark Plug Insulators
Spark plug insulators are critical components that prevent electrical shorts and withstand high temperatures within the engine cylinder. Steatite insulators, composed of magnesium silicate ceramics, offer excellent thermal shock resistance and electrical insulation but may have lower mechanical strength compared to advanced ceramic coatings. Ceramic coatings, often derived from alumina or zirconia, provide superior durability, heat resistance, and dielectric properties, enhancing spark plug longevity and engine performance under extreme operating conditions.
Overview of Steatite Material
Steatite, a dense and hard ceramic composed mainly of magnesium silicate, offers excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, making it ideal for spark plug insulators. Its high resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack ensures durability under the extreme conditions inside combustion engines. Compared to advanced ceramic coatings, steatite provides reliable and cost-effective insulation with proven performance in automotive spark plugs.
Characteristics of Ceramic Coatings
Ceramic coatings on spark plug insulators exhibit superior thermal resistance and electrical insulation compared to steatite, enabling them to withstand higher combustion temperatures without degradation. These coatings provide a hard, wear-resistant surface that minimizes erosion and enhances spark plug longevity under extreme engine conditions. The low thermal conductivity of ceramic materials also helps maintain optimal heat dissipation, improving ignition efficiency and overall engine performance.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Steatite spark plug insulators exhibit excellent thermal conductivity, allowing efficient heat dissipation and reducing the risk of overheating under high-performance engine conditions. Ceramic coatings, however, provide superior thermal insulation, maintaining higher insulator temperatures to prevent fouling and improve combustion efficiency. The choice between steatite and ceramic coatings hinges on balancing heat conduction for stability versus insulation for maintaining optimal combustion temperatures.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Steatite spark plug insulators offer high mechanical strength due to their dense microstructure, making them resistant to cracking under thermal stress. Ceramic coatings enhance durability by providing excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and thermal cycling, which extends spark plug lifespan. Combining steatite insulators with ceramic coatings optimizes both mechanical strength and durability, ensuring reliable performance in demanding engine conditions.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Steatite spark plug insulators exhibit excellent electrical insulation due to their high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity, ensuring reliable spark performance under high voltage conditions. Ceramic coatings enhance the insulator's resistance to electrical breakdown by providing a dense, non-porous surface that minimizes leakage currents and improves thermal stability. The combination of steatite material with advanced ceramic coatings results in superior electrical insulation properties, critical for efficient ignition and engine reliability.
Resistance to Chemical and Thermal Shock
Steatite spark plug insulators exhibit superior resistance to thermal shock due to their high thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical strength, enabling them to withstand rapid temperature fluctuations without cracking. Ceramic coatings on spark plug insulators provide enhanced chemical resistance, protecting against corrosive gases and deposits that degrade performance over time. Combining steatite's thermal shock durability with ceramic's chemical inertness often results in a spark plug insulator that delivers optimal longevity and reliability in harsh combustion environments.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost
Steatite spark plug insulators are produced using a cost-effective, powder-pressing technique followed by sintering at moderate temperatures, resulting in dense, durable parts with good thermal conductivity. Ceramic coatings for spark plug insulators involve advanced deposition methods like plasma spraying or chemical vapor deposition, increasing manufacturing complexity and expense. The higher production costs of ceramic coatings reflect their enhanced performance and protection properties compared to the more economical steatite insulators.
Applications and Suitability
Steatite spark plug insulators offer excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-performance combustion engines and industrial applications where heat resistance and durability are critical. Ceramic coatings enhance insulation properties, providing superior resistance to corrosion and electrical conductivity, which suits applications in harsh environmental conditions and high-voltage ignition systems. Choosing between steatite and ceramic coatings depends on specific requirements for thermal management, electrical insulation, and environmental exposure in automotive, aerospace, or heavy machinery industries.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulator Material
Steatite insulators offer excellent thermal shock resistance and high mechanical strength, making them suitable for high-performance spark plugs in demanding engine conditions. Ceramic coatings provide superior electrical insulation and improved resistance to wear and corrosion, extending the lifespan of the spark plug under extreme temperatures. Selecting the right insulator material depends on balancing thermal durability, electrical insulation properties, and environmental exposure specific to the engine's operational requirements.
Infographic: Steatite vs Ceramic coating for Spark plug insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com