Earthenware bricks are porous and fired at lower temperatures, making them less durable but more affordable. Fireclay bricks are denser, highly heat-resistant, and ideal for high-temperature applications due to their composition of refractory clays.
Table of Comparison
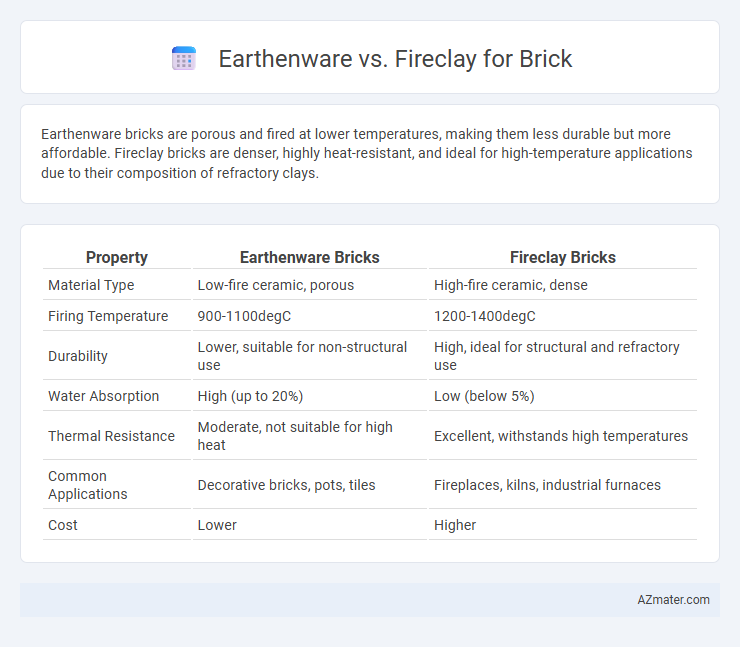
| Property | Earthenware Bricks | Fireclay Bricks |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Low-fire ceramic, porous | High-fire ceramic, dense |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1100degC | 1200-1400degC |
| Durability | Lower, suitable for non-structural use | High, ideal for structural and refractory use |
| Water Absorption | High (up to 20%) | Low (below 5%) |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, not suitable for high heat | Excellent, withstands high temperatures |
| Common Applications | Decorative bricks, pots, tiles | Fireplaces, kilns, industrial furnaces |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Earthenware and Fireclay Bricks
Earthenware bricks are made from natural clay, typically fired at lower temperatures around 1000-1150degC, resulting in a porous and softer structure ideal for decorative or non-load-bearing applications. Fireclay bricks, composed of fire-resistant clay materials, undergo higher firing temperatures above 1250degC, producing a denser, more heat-resistant brick suited for high-temperature environments like kilns and furnaces. The contrasting thermal and mechanical properties of earthenware and fireclay bricks determine their specific structural and industrial uses.
Composition and Raw Materials
Earthenware bricks are primarily composed of natural clay mixed with sand and sometimes other minerals like iron oxide, which impart a reddish hue and moderate firing temperature around 1000degC. Fireclay bricks contain a higher concentration of alumina and silica, derived from refractory clay deposits, enabling them to withstand higher temperatures up to 1600degC with greater thermal shock resistance. The distinct raw material composition in fireclay bricks results in superior durability and heat resistance compared to the more porous and softer earthenware bricks commonly used for decorative or non-structural applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Earthenware bricks are typically manufactured by shaping natural clay mixed with water and then fired at moderate temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a porous and relatively soft material. Fireclay bricks undergo a more intense manufacturing process involving high refractory clays fired at temperatures exceeding 1,400degC, producing bricks with superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength. The distinct firing temperatures and clay compositions significantly influence the durability and heat tolerance properties essential for industrial applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Earthenware bricks exhibit lower compressive strength, typically ranging from 5 to 20 MPa, and higher porosity, making them more susceptible to water absorption and frost damage compared to fireclay bricks. Fireclay bricks demonstrate excellent mechanical properties with compressive strengths exceeding 30 MPa, along with superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion due to their high alumina content and dense microstructure. The physical durability of fireclay bricks, including low porosity and high refractoriness, makes them ideal for high-temperature applications, whereas earthenware bricks are more suitable for general construction with moderate structural demands.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Fireclay bricks exhibit superior strength and durability compared to earthenware bricks due to their higher firing temperatures and denser composition, resulting in enhanced resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress. Earthenware bricks, while more porous and less dense, typically have lower compressive strength and are more susceptible to weathering and erosion over time. In construction applications requiring long-term structural integrity and exposure to high-stress environments, fireclay bricks offer greater longevity and reliability than traditional earthenware options.
Thermal Insulation and Heat Resistance
Earthenware bricks offer moderate thermal insulation due to their porous structure, helping to retain heat and regulate indoor temperatures effectively. Fireclay bricks exhibit superior heat resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as fireplaces and kilns, withstanding temperatures above 1600degC. The combination of earthenware's insulation properties and fireclay's durability provides a strategic choice for construction requiring both energy efficiency and thermal endurance.
Water Absorption and Porosity
Earthenware bricks typically exhibit higher water absorption rates, ranging from 15% to 25%, due to their increased porosity compared to fireclay bricks, which absorb less than 10%. Fireclay bricks are manufactured from refractory clays with a denser microstructure, resulting in lower porosity and enhanced resistance to moisture penetration. Consequently, fireclay bricks are preferred in environments requiring superior durability and minimal water absorption.
Common Applications in Construction
Earthenware bricks, known for their porous nature and affordability, are commonly used in non-load-bearing walls, garden landscaping, and decorative facades where aesthetics and lightweight materials are prioritized. Fireclay bricks, made from refractory clay, provide superior heat resistance and structural strength, making them ideal for high-temperature environments such as fireplaces, kiln linings, and industrial furnaces. Both materials offer unique advantages in construction, with earthenware favored for general masonry and fireclay for specialized thermal applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fireclay bricks demonstrate lower environmental impact compared to earthenware due to their higher durability and heat resistance, resulting in longer lifespans and less frequent replacement. Earthenware typically requires less intensive firing temperatures, reducing energy consumption during production, but its fragility often leads to higher waste. Sustainable brick choices favor fireclay for its recyclability and minimal maintenance, while earthenware's lower embodied energy suits applications prioritizing immediate resource efficiency.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Earthenware bricks generally offer a lower-cost option due to less intensive manufacturing processes and abundant raw materials, making them widely available in regional markets. Fireclay bricks, known for higher durability and resistance to heat, come at a premium price reflecting the specialized extraction and firing techniques required, often limiting availability to industrial suppliers or niche markets. Market demand drives pricing dynamics, with earthenware favored for cost-sensitive construction and fireclay preferred where thermal performance justifies the investment.
Infographic: Earthenware vs Fireclay for Brick
 azmater.com
azmater.com