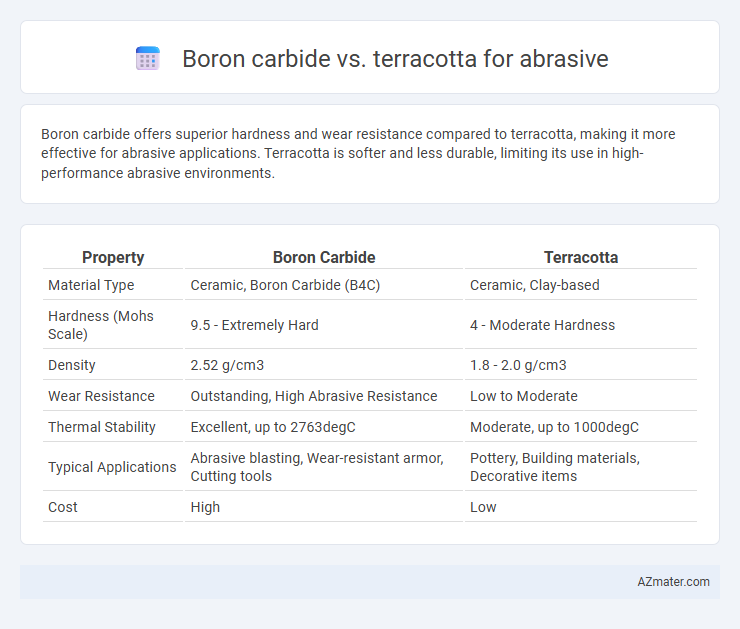
Boron carbide offers superior hardness and wear resistance compared to terracotta, making it more effective for abrasive applications. Terracotta is softer and less durable, limiting its use in high-performance abrasive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Boron Carbide | Terracotta |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic, Boron Carbide (B4C) | Ceramic, Clay-based |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 9.5 - Extremely Hard | 4 - Moderate Hardness |
| Density | 2.52 g/cm3 | 1.8 - 2.0 g/cm3 |
| Wear Resistance | Outstanding, High Abrasive Resistance | Low to Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, up to 2763degC | Moderate, up to 1000degC |
| Typical Applications | Abrasive blasting, Wear-resistant armor, Cutting tools | Pottery, Building materials, Decorative items |
| Cost | High | Low |
Understanding Boron Carbide: Composition and Properties
Boron carbide, composed primarily of boron and carbon atoms arranged in a complex icosahedral structure, exhibits exceptional hardness and thermal stability, making it one of the hardest known materials after diamond and cubic boron nitride. Its high melting point around 2763degC and low density (about 2.52 g/cm3) contribute to its efficiency as a lightweight yet durable abrasive material suitable for industrial applications such as grinding, lapping, and polishing. In comparison, terracotta, a clay-based ceramic, lacks the extreme hardness and thermal resistance of boron carbide, limiting its effectiveness as an abrasive and confining its use mainly to artistic and structural purposes.
What is Terracotta? Material Breakdown
Terracotta is a porous, reddish-brown clay-based ceramic commonly used for pottery, tiles, and sculptures, composed mainly of natural clay minerals such as kaolinite, illite, and montmorillonite. Unlike boron carbide, which is an extremely hard and dense ceramic compound used for abrasive applications due to its high hardness (above 9.5 Mohs) and wear resistance, terracotta has low hardness and abrasive properties. Terracotta's microstructure features a network of fine, interconnected pores that reduce its durability and make it unsuitable for abrasive uses compared to the ultra-hard, crystalline nature of boron carbide.
Comparing Abrasive Strength: Boron Carbide vs Terracotta
Boron carbide exhibits superior abrasive strength with a Mohs hardness of about 9.5, making it one of the hardest materials used for industrial abrasives, ideal for cutting, grinding, and sandblasting applications. Terracotta, primarily composed of fired clay, has a significantly lower hardness and abrasive capability, rendering it less effective and more prone to wear in high-friction scenarios. The high thermal stability and chemical inertness of boron carbide further enhance its performance in abrasive processes compared to the brittle and porous nature of terracotta.
Durability and Wear Resistance Analysis
Boron carbide exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to terracotta due to its high hardness rating of approximately 9.5 on the Mohs scale, making it one of the hardest materials used in abrasive applications. Terracotta, being a ceramic material primarily composed of fired clay, has significantly lower abrasion resistance and is more prone to chipping and wear under heavy or repeated mechanical stress. The dense crystal structure of boron carbide ensures longer lifespan and consistent performance in industrial grinding and cutting, whereas terracotta is typically limited to low-impact, decorative, or light abrasive uses.
Application Suitability: Boron Carbide vs Terracotta in Industry
Boron carbide, known for its exceptional hardness and chemical stability, is widely used in abrasive applications requiring high wear resistance, such as cutting tools, sandblasting, and grinding media in industries like aerospace and defense. Terracotta, while durable and heat-resistant, finds limited use in abrasive contexts primarily for traditional pottery and decorative applications rather than industrial wear processes. The superior hardness and fracture toughness of boron carbide make it the preferred choice for high-performance abrasive applications compared to the softer, more porous terracotta.
Cost Efficiency and Availability Considerations
Boron carbide is a highly durable abrasive with a higher cost but offers superior performance and longer lifespan compared to terracotta, making it cost-efficient for heavy-duty applications. Terracotta, being more readily available and inexpensive, suits low-budget projects with less demanding abrasive requirements but may wear out faster and require frequent replacement. Evaluating the balance between upfront cost and operational longevity is crucial for selecting the optimal abrasive material based on project scale and frequency of use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Boron carbide offers high hardness and durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste generation in abrasive applications. Terracotta, being a natural clay material, is biodegradable and has a lower carbon footprint but wears out faster, leading to increased consumption and waste. The sustainability of boron carbide depends on energy-intensive manufacturing, whereas terracotta's environmental impact is mitigated by its renewable sourcing and easier end-of-life disposal.
Efficiency in Abrasive Performance
Boron carbide exhibits superior abrasive efficiency compared to terracotta due to its extreme hardness, ranking just below diamond, which enables faster material removal and longer tool life. Terracotta, being a ceramic material with lower hardness and fracture toughness, wears down quicker and is less effective on tougher materials. In industrial applications requiring high-impact and precision grinding, boron carbide delivers more consistent performance and reduced downtime.
Maintenance and Longevity Comparison
Boron carbide exhibits exceptional hardness and chemical stability, resulting in superior wear resistance and extended lifespan compared to terracotta when used as an abrasive material. Terracotta, being more porous and softer, demands frequent maintenance and replacement due to its susceptibility to chipping and erosion under abrasive conditions. The durability of boron carbide significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs, making it a more efficient and cost-effective choice for industrial abrasive applications.
Choosing the Right Abrasive: Boron Carbide or Terracotta?
Boron carbide, known for its exceptional hardness and high wear resistance, is ideal for abrasive applications requiring durability and precision, such as grinding and sandblasting. Terracotta, while softer and more porous, offers a cost-effective and eco-friendly option suitable for gentle polishing and cleaning tasks. Choosing between boron carbide and terracotta depends on the specific abrasive needs, balancing factors like hardness, longevity, environmental impact, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Boron carbide vs Terracotta for Abrasive
 azmater.com
azmater.com