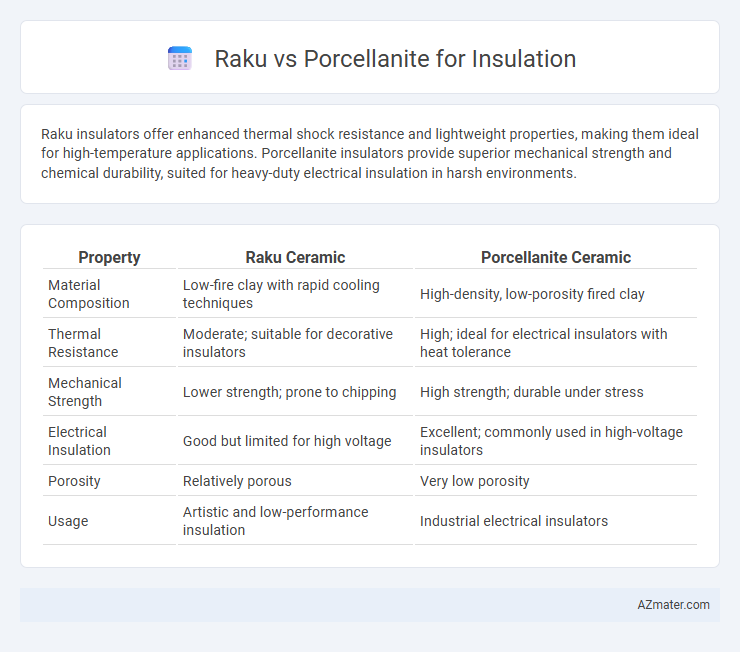
Raku insulators offer enhanced thermal shock resistance and lightweight properties, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. Porcellanite insulators provide superior mechanical strength and chemical durability, suited for heavy-duty electrical insulation in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Raku Ceramic | Porcellanite Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Low-fire clay with rapid cooling techniques | High-density, low-porosity fired clay |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate; suitable for decorative insulators | High; ideal for electrical insulators with heat tolerance |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower strength; prone to chipping | High strength; durable under stress |
| Electrical Insulation | Good but limited for high voltage | Excellent; commonly used in high-voltage insulators |
| Porosity | Relatively porous | Very low porosity |
| Usage | Artistic and low-performance insulation | Industrial electrical insulators |
Introduction to Raku and Porcellanite Insulators
Raku insulators are handcrafted ceramic components known for their unique glazing techniques and thermal shock resistance, making them suitable for specialized electrical applications. Porcellanite insulators, derived from a dense, fine-grained sedimentary rock, offer superior mechanical strength and high dielectric properties commonly utilized in high-voltage power lines. Both materials provide insulation solutions, but Porcellanite excels in durability and electrical insulation performance, while Raku is valued for its artistic and thermal characteristics.
Material Composition: Raku vs Porcellanite
Raku insulators are primarily made from low-firing clays combined with natural fluxes, resulting in a porous, lightweight ceramic with a distinctive crackled glaze. Porcellanite insulators consist of high-firing kaolin clay mixed with feldspar and quartz, creating a dense, vitrified ceramic noted for high mechanical strength and excellent dielectric properties. The material composition differences directly influence Raku's thermal shock resistance and aesthetic qualities versus Porcellanite's superior electrical insulation and durability in high-voltage applications.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Raku insulators are crafted through a rapid firing process followed by immediate cooling, which induces thermal shock and creates unique ceramic textures ideal for high thermal shock resistance. Porcellanite insulators undergo a prolonged high-temperature firing in a controlled kiln environment, resulting in dense, vitrified ceramics with superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance. While Raku's rapid technique favors artistic variability and thermal properties, Porcellanite manufacturing emphasizes durability and consistent electrical insulation performance.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Raku and Porcellanite insulators differ significantly in thermal resistance and performance, with Porcellanite exhibiting superior heat tolerance and thermal stability up to 1300degC, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Raku, often used in artistic ceramics, shows moderate thermal resistance but can crack under rapid temperature changes due to its porous structure. Porcellanite's dense, vitrified composition ensures better insulation performance and durability in industrial settings where thermal shock resistance is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Porcellanite insulators exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to Raku, with higher resistance to cracking under stress and greater load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for high-tension electrical systems. Durability-wise, Porcellanite provides enhanced longevity due to its dense, non-porous structure that resists weathering, chemical attack, and thermal cycling better than the more porous and brittle Raku material. The combined mechanical robustness and environmental resilience of Porcellanite insulators ensure stable performance in demanding outdoor electrical infrastructure applications.
Electrical Insulation Properties
Raku and porcellanite differ significantly in electrical insulation properties, with porcellanite exhibiting superior dielectric strength and lower electrical conductivity, making it more suitable for high-voltage insulator applications. Porcellanite's dense, vitrified structure provides excellent resistance to electrical breakdown and environmental degradation, enhancing insulator performance and longevity. Raku, typically used in artistic ceramics, has more porous and thermally variable characteristics, resulting in lower and less consistent electrical insulation capabilities.
Cost Analysis: Raku vs Porcellanite
Raku insulators generally exhibit lower initial costs due to simpler manufacturing processes and readily available materials, making them a budget-friendly option for small-scale or artisanal projects. Porcellanite insulators, however, offer enhanced durability and longevity, which can result in lower long-term expenses despite higher upfront costs, especially in industrial or high-stress applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including maintenance frequency and replacement rates, is crucial when choosing between Raku and Porcellanite insulators.
Applications in Electrical and Industrial Fields
Raku ceramic exhibits superior thermal shock resistance and electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical insulators in industrial furnaces and power generation equipment. Porcellanite offers excellent mechanical strength and dielectric stability, suited for insulating components in high-voltage electrical systems and heavy machinery. Both materials are critical in electrical and industrial fields, with Raku preferred for extreme thermal environments and Porcellanite favored for robust, high-stress insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Raku insulators, made from low-fired ceramics, typically require less energy during production compared to Porcellanite, which is fired at higher temperatures and therefore has a larger carbon footprint. Porcellanite insulators offer superior durability and resistance to environmental degradation, translating to a longer service life and reduced waste generation over time. Choosing Raku insulators benefits from lower initial environmental impact, while Porcellanite supports sustainability through longevity and reduced replacement frequency.
Selecting the Right Insulator Material
Selecting the right insulator material requires evaluating the thermal durability, dielectric strength, and mechanical robustness of Raku and Porcellanite. Raku pottery offers unique aesthetic appeal but has lower mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to Porcellanite, which is known for its superior dielectric properties and long-term durability in electrical insulation. Porcellanite's fine-grained, dense structure makes it ideal for high-voltage insulators that demand consistent performance under varying environmental conditions.
Infographic: Raku vs Porcellanite for Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com