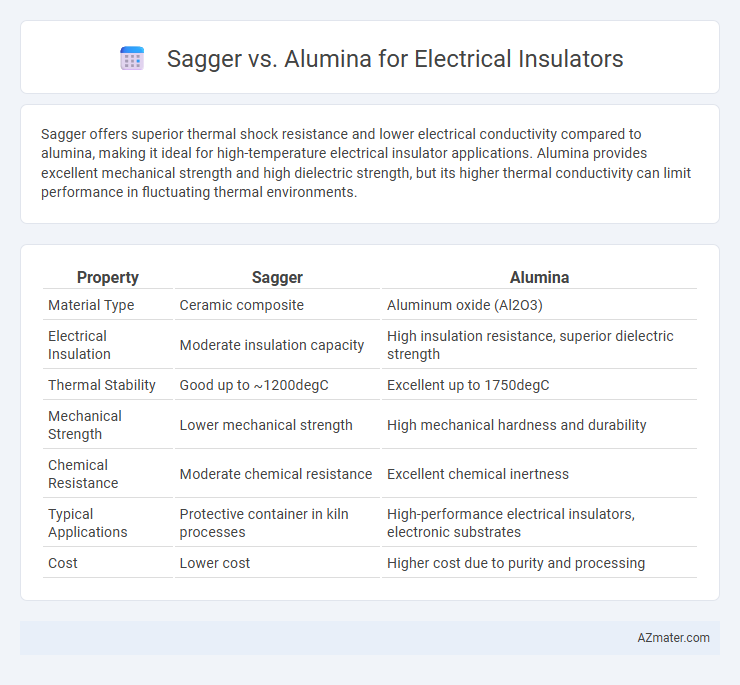
Sagger offers superior thermal shock resistance and lower electrical conductivity compared to alumina, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical insulator applications. Alumina provides excellent mechanical strength and high dielectric strength, but its higher thermal conductivity can limit performance in fluctuating thermal environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic composite | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Electrical Insulation | Moderate insulation capacity | High insulation resistance, superior dielectric strength |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to ~1200degC | Excellent up to 1750degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower mechanical strength | High mechanical hardness and durability |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate chemical resistance | Excellent chemical inertness |
| Typical Applications | Protective container in kiln processes | High-performance electrical insulators, electronic substrates |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to purity and processing |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are critical materials designed to prevent the unwanted flow of electric current, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems. Sagger, a ceramic material primarily used in kiln processes, offers moderate electrical insulation properties but lacks the high dielectric strength and thermal stability found in alumina (Al2O3). Alumina is preferred for electrical insulators due to its excellent electrical resistance, high mechanical strength, and superior thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-voltage applications and harsh operating environments.
Overview of Sagger Materials
Sagger materials, primarily composed of high-purity alumina, are crucial for protecting ceramics and electronic components during high-temperature firing processes. These materials offer excellent thermal stability, chemical inertness, and electrical insulation properties, making them ideal for use in electrical insulators. The superior purity and controlled grain size of sagger alumina enhance mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock compared to conventional alumina insulators.
Overview of Alumina Materials
Alumina is a widely used ceramic material renowned for its excellent electrical insulation properties, high thermal conductivity, and superior mechanical strength. It offers high dielectric strength and resistance to electrical breakdown, making it ideal for insulating applications in electrical devices. Compared to sagger materials, alumina provides better chemical stability and durability under high-temperature conditions, enhancing the reliability of electrical insulators.
Physical Properties Comparison
Sagger and alumina exhibit distinct physical properties that influence their effectiveness as electrical insulators; alumina typically offers higher thermal conductivity, greater mechanical strength, and superior dielectric strength compared to sagger. Alumina's melting point exceeds 2000degC, ensuring excellent stability at high temperatures, whereas sagger, primarily composed of refractory clay, has a lower melting point and reduced thermal resistance. Furthermore, alumina's low dielectric loss and high resistivity contribute to its widespread use in high-performance electrical insulation applications, surpassing the capabilities of sagger materials.
Electrical Performance Analysis
Sagger and alumina exhibit distinct electrical performance characteristics critical for insulator applications, with alumina offering superior dielectric strength and lower electrical conductivity compared to sagger materials. Alumina's high purity and density contribute to enhanced insulation resistance and reduced dielectric losses, making it preferable for high-voltage environments. Electrical performance analysis reveals that alumina maintains stability under thermal stress, while sagger materials may exhibit increased leakage currents and reduced breakdown voltage.
Thermal Resistance Evaluation
Sagger exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to alumina, making it highly effective for electrical insulators operating under high-temperature conditions. The thermal conductivity of sagger is notably lower, reducing heat transfer and enhancing insulation performance during thermal cycling. Evaluations show sagger maintains structural integrity and dielectric strength at elevated temperatures better than alumina, ensuring reliability in harsh electrical environments.
Durability and Lifespan
Sagger materials generally offer sufficient thermal resistance but tend to have lower durability compared to alumina-based electrical insulators, which exhibit superior mechanical strength and longer lifespan under high-temperature conditions. Alumina insulators resist cracking and wear due to their robust ceramic composition, resulting in extended operational reliability in harsh electrical environments. The enhanced durability and prolonged service life of alumina make it the preferred choice for critical insulator applications requiring consistent performance over time.
Cost-effectiveness and Availability
Sagger and alumina differ significantly in cost-effectiveness and availability as electrical insulators, with alumina offering superior performance but at a higher price due to its advanced manufacturing process. Sagger, typically made from refractory clay, is more readily available and cost-effective, making it suitable for applications where budget constraints outweigh the need for high electrical resistance. The choice hinges on project requirements, balancing alumina's reliability and durability against sagger's affordability and accessibility in industrial settings.
Typical Applications in Industry
Sagger and alumina serve distinct functions in electrical insulation across various industries, with sagger primarily used as protective containers for ceramic components during high-temperature firing processes. Alumina, known for its excellent dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance, is extensively applied in electrical insulators for power transmission, electronics, and high-voltage equipment. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing rely on alumina-based insulators for robust performance in harsh environments, while saggers are essential in ceramics and electronic component fabrication to ensure material purity and shape stability.
Choosing the Right Material for Electrical Insulators
Choosing between sagger and alumina for electrical insulators depends on their thermal stability, dielectric strength, and mechanical durability. Alumina offers superior electrical insulation properties, high thermal conductivity, and excellent resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Saggers primarily serve as protective containers in firing processes and lack the inherent electrical insulating properties required for efficient insulator performance.
Infographic: Sagger vs Alumina for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com