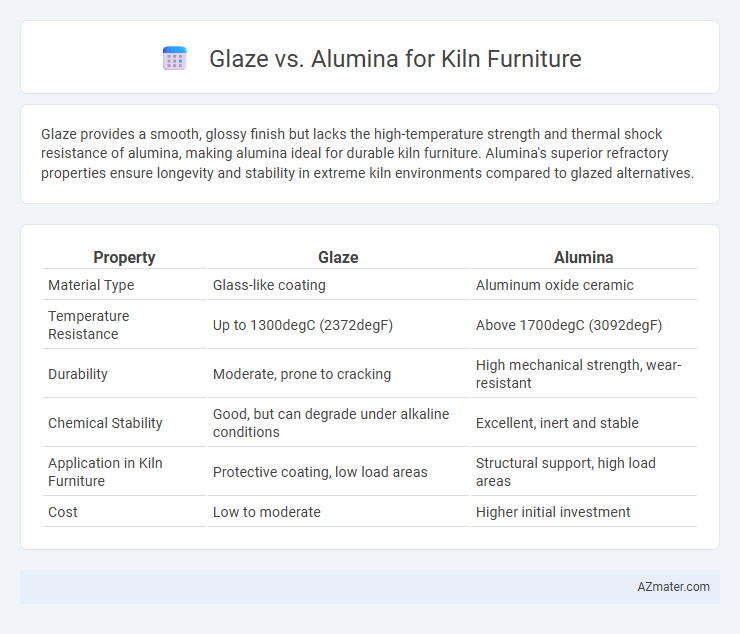
Glaze provides a smooth, glossy finish but lacks the high-temperature strength and thermal shock resistance of alumina, making alumina ideal for durable kiln furniture. Alumina's superior refractory properties ensure longevity and stability in extreme kiln environments compared to glazed alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glaze | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass-like coating | Aluminum oxide ceramic |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1300degC (2372degF) | Above 1700degC (3092degF) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High mechanical strength, wear-resistant |
| Chemical Stability | Good, but can degrade under alkaline conditions | Excellent, inert and stable |
| Application in Kiln Furniture | Protective coating, low load areas | Structural support, high load areas |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Higher initial investment |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Kiln furniture materials, such as glaze and alumina, play a crucial role in ceramics and glass firing processes by providing support and thermal stability at high temperatures. Alumina, known for its high melting point above 2072degC and excellent mechanical strength, is preferred for heavy-duty kiln shelves and setters due to its resistance to thermal shock and chemical attack. Glaze coatings on kiln furniture enhance surface durability, reduce sticking of ceramic ware, and increase the lifespan by forming a protective barrier against molten materials and glaze runs during firing cycles.
What is Glaze in Kiln Furniture?
Glaze in kiln furniture refers to a glassy coating applied to ceramic materials to create a smooth, non-porous surface that resists slag and glaze adherence during firing. This protective layer enhances the durability and longevity of kiln shelves by preventing sticking and contamination from molten glass or glaze drips. Unlike alumina, which provides high thermal strength and resistance, glaze primarily serves as a surface barrier to improve the performance and maintenance of kiln furniture.
Understanding Alumina for Kiln Furniture
Alumina, a high-purity oxide ceramic, offers exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical attack, making it ideal for kiln furniture in high-temperature environments. Its superior mechanical strength and low thermal expansion prevent warping and degradation during repeated firing cycles. This ensures durability and consistent performance, outperforming glaze-coated materials that can crack or deteriorate under extreme kiln conditions.
Key Differences Between Glaze and Alumina
Glaze and alumina serve distinct roles in kiln furniture, with glaze acting as a glassy coating that provides a smooth, non-stick surface to protect ceramic pieces, while alumina is a high-temperature refractory material offering structural strength and thermal stability. Glaze melts and fuses onto surfaces during firing, enhancing aesthetics and preventing adhesion, whereas alumina withstands extreme heat without melting, maintaining the integrity of kiln supports and shelves. The key difference lies in glaze's function as a surface treatment and alumina's role as a durable structural component in high-temperature environments.
Thermal Performance: Glaze vs Alumina
Glaze coatings on kiln furniture provide a smooth, protective barrier that enhances thermal shock resistance but may degrade at extremely high temperatures, typically above 1200degC. Alumina-based kiln furniture offers superior thermal stability and higher melting points, often exceeding 1700degC, making it ideal for prolonged exposure to intense heat. The higher alumina content ensures better thermal conductivity and resistance to wear, crucial for maintaining structural integrity during repeated firing cycles.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Glaze-coated kiln furniture offers enhanced chemical resistance and surface smoothness, reducing wear from molten materials and extending lifespan in glass and ceramic firing processes. Alumina kiln furniture exhibits superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, providing excellent durability under high temperatures and thermal shock conditions. Comparing durability, alumina typically outlasts glazed materials due to its intrinsic hardness and resistance to cracking, making it ideal for long-term kiln operations requiring heavy-duty performance.
Cost Efficiency: Glaze vs Alumina
Alumina kiln furniture offers higher durability and thermal resistance compared to glazed alternatives, resulting in longer service life and reduced replacement costs. Though glaze kiln furniture may have a lower initial price, frequent maintenance and replacement can increase overall expenses over time. Cost efficiency favors alumina for high-temperature, heavy-use scenarios due to its superior strength and minimal degradation.
Application Suitability in Various Firings
Glaze and alumina serve distinct roles in kiln furniture applications, with alumina offering superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength ideal for high-temperature firings above 1300degC, such as porcelain and stoneware production. Glaze coatings enhance surface protection and reduce sticking in lower temperature firings up to 1100degC, commonly used in earthenware and decorative ceramics. Selecting between glaze and alumina depends on firing temperature, chemical interaction with ceramic bodies, and the need for durability under repeated thermal cycling.
Maintenance and Cleaning Considerations
Glaze coatings on kiln furniture require careful maintenance to prevent cracking and peeling, which can compromise thermal insulation and lead to contamination. Alumina kiln furniture offers superior durability with minimal surface degradation, reducing cleaning frequency and enabling straightforward removal of residue using mild abrasives or chemical cleaners. Selecting alumina enhances longevity and lowers maintenance costs compared to glazed alternatives, making it preferable for high-temperature industrial applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Kiln Furniture
Glaze and alumina offer distinct advantages for kiln furniture, with glaze providing a smooth, protective surface that reduces sticking and contamination, while alumina excels in thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures above 1700degC. Choosing the best material depends on your firing temperature, with alumina preferred for ultra-high-temperature firings in ceramics and glass, and glazed kiln furniture suitable for lower to mid-range temperatures to maintain surface integrity and ease of cleaning. Consider durability, thermal expansion, and interaction with your specific kiln atmosphere to optimize performance and longevity of your kiln furniture components.
Infographic: Glaze vs Alumina for Kiln Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com