Cubic zirconia offers superior clarity, brilliance, and durability compared to steatite, making it a popular choice for high-quality jewelry. Steatite is softer and more porous, often used for carved or decorative pieces but less suitable for everyday wear.
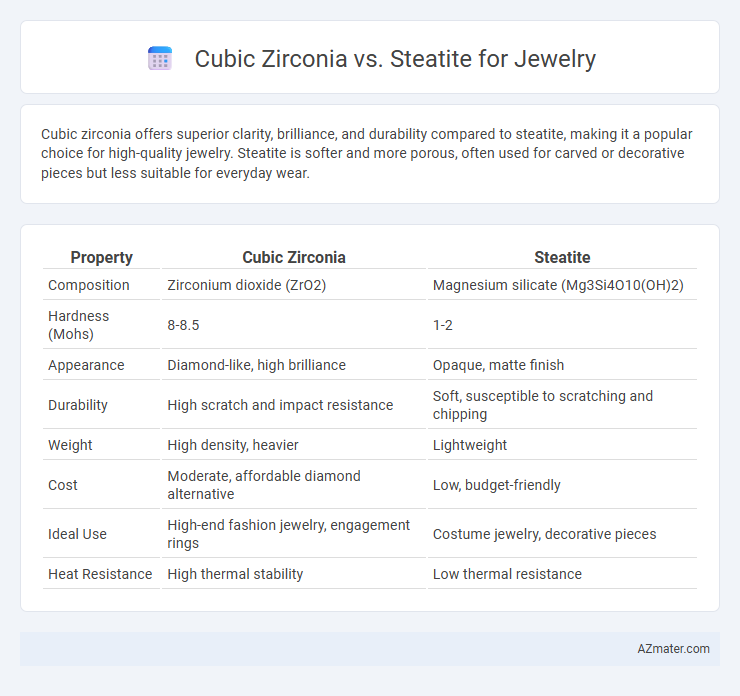
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cubic Zirconia | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) | Magnesium silicate (Mg3Si4O10(OH)2) |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 8-8.5 | 1-2 |
| Appearance | Diamond-like, high brilliance | Opaque, matte finish |
| Durability | High scratch and impact resistance | Soft, susceptible to scratching and chipping |
| Weight | High density, heavier | Lightweight |
| Cost | Moderate, affordable diamond alternative | Low, budget-friendly |
| Ideal Use | High-end fashion jewelry, engagement rings | Costume jewelry, decorative pieces |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal stability | Low thermal resistance |
Introduction to Cubic Zirconia and Steatite
Cubic zirconia, a synthetic gemstone known for its diamond-like brilliance and affordability, is widely used in jewelry for its high refractive index and durability. Steatite, also called soapstone, is a soft mineral primarily composed of talc, valued for its carvability and matte finish but less common in fine jewelry due to its lower hardness. Understanding the physical properties and aesthetic qualities of cubic zirconia and steatite helps in selecting the ideal material for jewelry pieces based on desired durability and appearance.
Origin and Formation of Each Gemstone
Cubic zirconia is a synthetic gemstone created through a high-temperature melt process using zirconium dioxide, primarily produced in laboratories to mimic the appearance of diamonds with high clarity and brilliance. Steatite, also known as soapstone, is a natural metamorphic rock composed mainly of talc formed through the alteration of ultramafic rocks under low-grade metamorphic conditions, often found in regions with geothermal activity. The distinct origins of cubic zirconia as a man-made crystal and steatite as a naturally occurring mineral influence their physical properties and suitability for different types of jewelry.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetic Qualities
Cubic zirconia offers a brilliant, diamond-like sparkle with high clarity and a flawless finish, making it a popular choice for jewelry that demands brilliance and shine. Steatite, also known as soapstone, has a matte, smooth texture with muted, earthy tones that provide a distinct, natural aesthetic but lacks the reflective qualities of gemstones. The vibrant luster of cubic zirconia contrasts sharply with the subdued, soft appearance of steatite, catering to different style preferences in jewelry design.
Hardness and Durability Comparison
Cubic zirconia boasts a high hardness rating of 8 to 8.5 on the Mohs scale, making it highly resistant to scratches and ideal for everyday jewelry. In contrast, steatite, also known as soapstone, is much softer with a Mohs hardness of 1 to 2, rendering it prone to scratches and less durable for frequent wear. The superior hardness of cubic zirconia ensures long-lasting brilliance and structural integrity in jewelry applications compared to the fragile nature of steatite.
Cost and Affordability for Consumers
Cubic zirconia offers a highly affordable alternative to diamonds, with prices typically ranging from $10 to $30 per carat, making it accessible for budget-conscious jewelry buyers seeking brilliance and clarity. Steatite, or soapstone, is even more cost-effective, often priced under $5 per carat, but it lacks the hardness and sparkle that make cubic zirconia desirable in fine jewelry. Consumers prioritizing cost and appearance will find cubic zirconia provides the best balance between affordability and aesthetic appeal compared to steatite's lower price but limited use in traditional jewelry settings.
Popularity and Usage in Jewelry Design
Cubic zirconia is widely favored in jewelry design for its diamond-like brilliance and affordability, making it a popular choice for rings, earrings, and pendants. Steatite, though less common, is valued for its smooth texture and is often used in carved or artisan jewelry pieces, especially in cultural or vintage designs. The popularity of cubic zirconia surpasses steatite due to its versatility and sparkling appearance, aligning with mainstream fashion trends.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Cubic zirconia jewelry requires regular cleaning with mild soap and water to maintain its brilliance and prevent dullness caused by oils and dirt. Steatite, being a soft and porous mineral, demands gentle handling and avoidance of water exposure to prevent surface degradation and discoloration. Proper storage in a soft pouch or lined box is essential for both materials to avoid scratches and extend their lifespan.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Cubic zirconia, a synthetic gemstone, is preferred in jewelry for its low environmental impact compared to mined materials, requiring less water and energy during production. Steatite, a naturally occurring mineral often used in carvings and beads, involves environmentally disruptive mining practices that can lead to habitat loss and soil degradation. Ethical considerations favor cubic zirconia due to its lab-created origin, minimizing concerns about worker exploitation and conflict minerals commonly associated with natural stone extraction.
Market Availability and Sourcing
Cubic zirconia dominates the jewelry market due to its wide availability, consistent quality, and affordable synthetic production from zirconium dioxide. In contrast, steatite, a naturally occurring talc mineral, is less common in jewelry, often limited to artisanal or niche markets because of its softness and variability in sourcing from regional talc deposits. The reliable global supply chains for cubic zirconia make it the preferred choice for mass-market jewelry, while steatite remains a specialty material with limited commercial distribution.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Jewelry Needs
Cubic zirconia offers exceptional brilliance and durability, making it an ideal choice for sparkling, affordable jewelry that mimics the look of diamonds. Steatite, known for its softness and unique matte finish, is best suited for ornamental pieces or designs requiring easy carving rather than daily wear. Selecting between cubic zirconia and steatite hinges on your priorities for durability, appearance, and maintenance in your jewelry collection.
Infographic: Cubic zirconia vs Steatite for Jewelry
 azmater.com
azmater.com