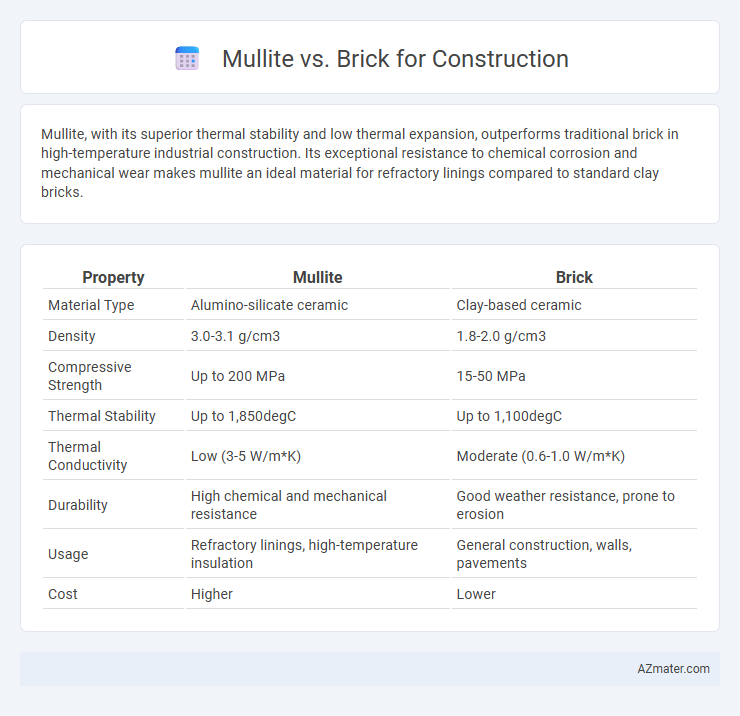
Mullite, with its superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, outperforms traditional brick in high-temperature industrial construction. Its exceptional resistance to chemical corrosion and mechanical wear makes mullite an ideal material for refractory linings compared to standard clay bricks.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mullite | Brick |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alumino-silicate ceramic | Clay-based ceramic |
| Density | 3.0-3.1 g/cm3 | 1.8-2.0 g/cm3 |
| Compressive Strength | Up to 200 MPa | 15-50 MPa |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1,850degC | Up to 1,100degC |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (3-5 W/m*K) | Moderate (0.6-1.0 W/m*K) |
| Durability | High chemical and mechanical resistance | Good weather resistance, prone to erosion |
| Usage | Refractory linings, high-temperature insulation | General construction, walls, pavements |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Mullite and Brick in Construction
Mullite, a silicate mineral known for its high-temperature resistance and thermal stability, is increasingly utilized in refractory applications for industrial furnaces and kilns. Brick, a traditional building material composed primarily of clay or shale, offers durability and thermal insulation in both structural and decorative construction. Comparing their properties highlights mullite's superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, while brick remains favored for conventional construction due to cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacture.
Composition and Material Differences
Mullite, primarily composed of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, contains high alumina content and forms through the heat treatment of kaolin, offering excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion. Bricks, typically made from clay rich in silica and alumina but with variable impurities, lack the precise alumina-silica ratio found in mullite, resulting in lower refractory and mechanical properties. Mullite's crystalline structure provides superior resistance to thermal shock and corrosion, making it ideal for high-temperature construction applications compared to conventional bricks.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Mullite exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to traditional brick, owing to its low thermal conductivity and high melting point of about 1840degC, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Its dense crystal structure reduces heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency in construction. Bricks, while cost-effective, have higher thermal conductivity and lower thermal resistance, limiting their effectiveness in extreme temperature environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Mullite exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to traditional brick, with compressive strength often exceeding 150 MPa versus brick's typical range of 10-40 MPa. Its superior fracture toughness and thermal stability make mullite an ideal choice for high-stress construction applications, including refractory linings and structural components in harsh environments. Conversely, bricks are more prone to cracking under heavy loads and thermal cycling, limiting their use in high-strength or high-temperature scenarios.
Durability and Longevity
Mullite offers superior durability and longevity compared to traditional bricks due to its high melting point of around 1840degC and excellent thermal stability, making it resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Bricks, typically composed of clay with lower firing temperatures, tend to degrade faster under extreme weather conditions and mechanical stress. The enhanced structural integrity of mullite ensures longer-lasting construction materials ideal for high-temperature and refractory applications.
Fire Resistance and Thermal Stability
Mullite exhibits superior fire resistance compared to traditional bricks, withstanding temperatures above 1800degC due to its excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion coefficient. This mineral's crystalline structure ensures minimal deformation and enhanced durability under continuous high heat exposure, making it ideal for refractory linings in industrial furnaces and kilns. In contrast, conventional fired clay bricks typically degrade or crack at temperatures exceeding 1000degC, limiting their effectiveness in high-temperature construction applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mullite bricks exhibit superior environmental benefits due to their high thermal efficiency and durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering resource consumption. Unlike traditional clay bricks, mullite is composed mainly of alumina and silica, materials that contribute to lower carbon emissions during production. Sustainable construction projects favor mullite bricks as they enhance energy conservation and produce fewer pollutants, supporting eco-friendly building practices.
Cost and Availability
Mullite offers superior thermal resistance and durability but comes at a higher cost compared to traditional bricks, which are more affordable and widely available. Bricks benefit from extensive manufacturing and distribution networks, ensuring easy access and lower initial expenses in construction projects. However, mullite's specialized production limits availability, impacting its use primarily to high-performance or refractory applications where cost sensitivity is lower.
Common Applications in Construction
Mullite is widely used in high-temperature applications such as refractory linings, kiln furniture, and thermal insulation due to its exceptional thermal stability and low thermal expansion. Bricks are commonly employed in structural walls, pavements, and exterior facades, offering durability, fire resistance, and ease of installation. While mullite excels in specialized industrial environments, bricks remain a versatile choice for conventional building construction.
Choosing the Right Material: Mullite vs. Brick
Mullite offers exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications, while traditional bricks excel in affordability and ease of use for general construction. Its superior mechanical strength and low thermal expansion make mullite preferable for environments requiring durability against thermal shock. For residential or standard commercial buildings, bricks remain a cost-effective option with well-established structural reliability and wide availability.
Infographic: Mullite vs Brick for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com