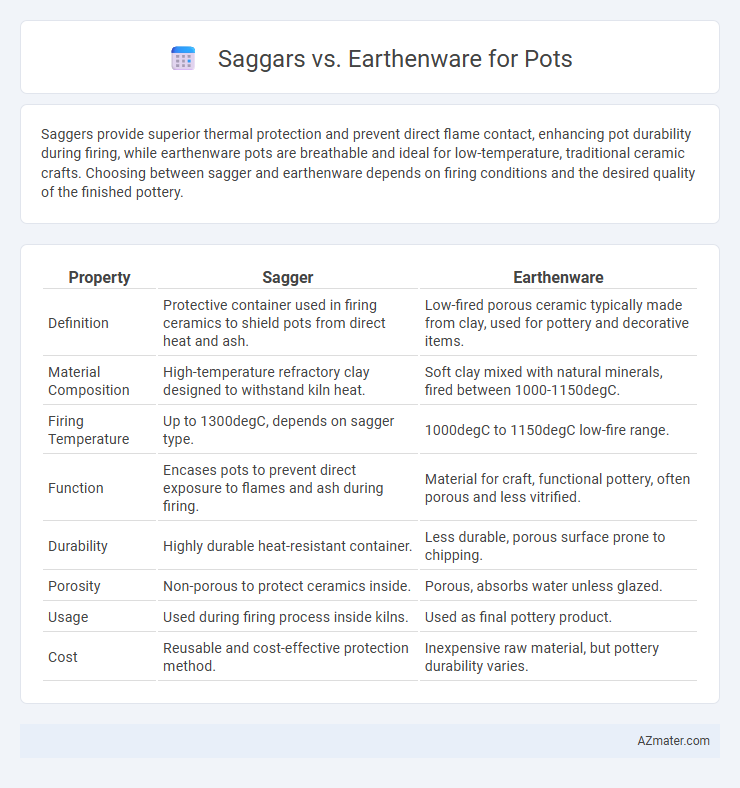
Saggers provide superior thermal protection and prevent direct flame contact, enhancing pot durability during firing, while earthenware pots are breathable and ideal for low-temperature, traditional ceramic crafts. Choosing between sagger and earthenware depends on firing conditions and the desired quality of the finished pottery.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sagger | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protective container used in firing ceramics to shield pots from direct heat and ash. | Low-fired porous ceramic typically made from clay, used for pottery and decorative items. |
| Material Composition | High-temperature refractory clay designed to withstand kiln heat. | Soft clay mixed with natural minerals, fired between 1000-1150degC. |
| Firing Temperature | Up to 1300degC, depends on sagger type. | 1000degC to 1150degC low-fire range. |
| Function | Encases pots to prevent direct exposure to flames and ash during firing. | Material for craft, functional pottery, often porous and less vitrified. |
| Durability | Highly durable heat-resistant container. | Less durable, porous surface prone to chipping. |
| Porosity | Non-porous to protect ceramics inside. | Porous, absorbs water unless glazed. |
| Usage | Used during firing process inside kilns. | Used as final pottery product. |
| Cost | Reusable and cost-effective protection method. | Inexpensive raw material, but pottery durability varies. |
Understanding Sagger and Earthenware: An Overview
Sagger is a protective container used in high-temperature kilns to shield ceramics, particularly earthenware, from direct flame and ash, ensuring uniform firing and preventing damage. Earthenware is a porous, low-fired pottery made from natural clay, known for its rustic texture and ability to hold water, but less durable than stoneware or porcelain. Understanding the difference highlights that saggers serve as a functional tool for enhancing the quality of earthenware during the firing process.
Historical Origins of Sagger and Earthenware Techniques
Sagger, originating in ancient pottery practices, functioned as a protective container to shield ceramics from direct kiln flames, enabling refined firing techniques that enhanced durability and texture. Earthenware dates back to prehistoric times, characterized by porous clay materials fired at lower temperatures, widely used for utilitarian vessels and decorative objects across diverse ancient civilizations. These methods reflect distinct historical advancements in pottery craftsmanship, where sagger technology enabled higher-quality ceramic finishes and earthenware embodied foundational pottery traditions.
Material Composition: Sagger vs Earthenware
Sagger is a protective container made from refractory materials such as fireclay or kaolin, designed to encase pottery during high-temperature firing, preventing direct exposure to flames and ash. Earthenware consists primarily of porous clay fired at lower temperatures (typically between 1,000degC and 1,150degC), resulting in a more absorbent and less durable material compared to stoneware or porcelain. The key distinction lies in sagger's composition engineered for thermal resistance and insulation, whereas earthenware's clay composition offers malleability but retains porosity after firing.
Firing Process Differences in Sagger and Earthenware Pots
The firing process for sagger pots involves placing the pottery inside a protective container called a sagger, which shields it from direct flame and reduces contamination, allowing for controlled atmosphere effects and intricate surface finishes. In contrast, earthenware pots are fired directly in the kiln without a protective barrier, exposing them to open flame and ash, which can affect the surface texture and color. Sagger firing typically reaches temperatures between 1200-1300degC, enabling more refined results, while earthenware firing occurs at lower temperatures around 1000-1150degC, resulting in a more porous and less vitrified pottery body.
Durability and Strength: Which is Better?
Sagger pots are known for their enhanced durability due to the protective firing technique inside a sagger container, which reduces exposure to direct flame and thermal shock. Earthenware pots, while aesthetically pleasing and porous, tend to be more fragile and prone to cracking under high heat or impact. For strength and long-term resilience, sagger-fired ceramics typically outperform traditional earthenware in withstanding mechanical stress and temperature fluctuations.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finishes Compared
Sagger pottery often features rustic, wood-fired surface finishes with rich, varied textures and natural ash glazes that create unique, earthy aesthetics ideal for artisanal designs. Earthenware pots typically boast smooth, uniform surfaces with glossy or matte glazes available in a broad color palette, emphasizing refined craftsmanship and decorative appeal. The aesthetic qualities of sagger pottery highlight organic, unpredictable patterns, while earthenware focuses on controlled, consistent finishes suited for both functional and ornamental uses.
Functional Uses: Sagger vs Earthenware in Everyday Life
Sagger ceramics are primarily designed as protective containers used in kiln firing to shield pottery from direct flame and ash, enhancing the durability of the final ware. Earthenware pots, made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, excel in everyday cooking and storage due to their heat retention and breathability. While saggers serve a specialized function in pottery production, earthenware offers practical utility in kitchens and households around the world.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Sagger pots, typically used for high-temperature firing, are often made from refractory clay that can withstand repeated use, reducing waste and enhancing sustainability through durability. Earthenware pots, composed of natural clay, generally require lower firing temperatures, consuming less energy but tend to be more fragile and porous, which may limit their lifespan and contribute to higher material usage over time. Considering environmental impact, saggers offer long-term reuse benefits, while earthenware provides lower initial energy consumption but may generate more frequent replacement waste.
Cost Effectiveness for Potters and Buyers
Sagger offers potters enhanced durability and protection during firing, reducing breakage and lowering long-term costs, but often comes with a higher upfront investment compared to earthenware. Earthenware pots are generally more affordable for buyers due to lower production costs and materials, making them cost-effective for everyday use but less durable and prone to chipping. Potters must balance sagger's protective benefits against earthenware's affordability when targeting different market segments.
Choosing the Right Option: Sagger or Earthenware Pot?
Choosing between sagger and earthenware pots depends on the intended use and firing requirements. Sagger pots are primarily used as protective containers inside kiln firings to shield ceramics from direct flame and ash, enhancing finish quality during high-temperature firings, while earthenware pots serve as functional pottery vessels made from porous clay fired at lower temperatures, ideal for decorative and everyday use. Opting for sagger is best for ceramic artists focusing on refining glaze effects in high-heat environments, whereas earthenware is suitable for those needing durable, breathable dinnerware or storage containers.
Infographic: Sagger vs Earthenware for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com