Ceramic foam offers superior insulation and lightweight properties compared to terracotta, making it ideal for advanced pottery applications requiring thermal efficiency. Terracotta provides traditional aesthetics and durability, favored for rustic pottery but lacks the thermal resistance and pore structure of ceramic foam.
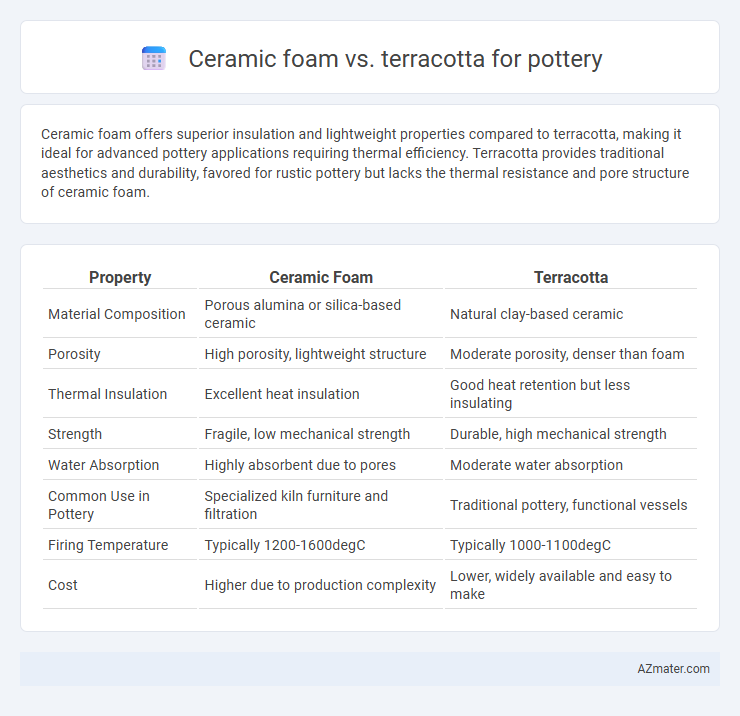
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Foam | Terracotta |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Porous alumina or silica-based ceramic | Natural clay-based ceramic |
| Porosity | High porosity, lightweight structure | Moderate porosity, denser than foam |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent heat insulation | Good heat retention but less insulating |
| Strength | Fragile, low mechanical strength | Durable, high mechanical strength |
| Water Absorption | Highly absorbent due to pores | Moderate water absorption |
| Common Use in Pottery | Specialized kiln furniture and filtration | Traditional pottery, functional vessels |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1200-1600degC | Typically 1000-1100degC |
| Cost | Higher due to production complexity | Lower, widely available and easy to make |
Introduction to Ceramic Foam and Terracotta
Ceramic foam is a lightweight, porous material made from ceramics that offers exceptional thermal insulation and durability, making it ideal for advanced pottery techniques and sculptural art. Terracotta, a traditional clay-based material, is renowned for its natural reddish-brown color, breathability, and ease of shaping, widely used in classic pottery and earthenware. Both materials differ significantly in texture, firing temperatures, and functional properties, influencing their suitability for various pottery applications.
Material Composition and Properties
Ceramic foam consists of a porous structure made from alumina, silica, or zirconia, offering lightweight properties and high thermal insulation ideal for kiln furniture. Terracotta is a clay-based material rich in iron oxide, known for its reddish-brown color, durability, and moderate porosity, providing excellent breathability and moisture absorption for pottery. The porous nature of ceramic foam enhances heat resistance and mechanical support, while terracotta's natural composition contributes to its strength and aesthetic appeal in traditional pottery.
Historical Context and Popularity
Ceramic foam, known for its lightweight and porous structure, has gained popularity in modern pottery due to its enhanced insulation properties and innovative texture possibilities. Terracotta, with its rich history dating back to ancient civilizations like the Greeks and Romans, remains a staple in traditional pottery for its natural reddish-brown hue and earthy aesthetic. The enduring cultural significance of terracotta contrasts with the emerging industrial uses of ceramic foam, reflecting evolving artistic and functional preferences in pottery.
Thermal Performance and Insulation
Ceramic foam exhibits superior thermal insulation owing to its highly porous structure, which traps air and reduces heat transfer more effectively than terracotta. Terracotta, while providing moderate insulation, tends to conduct heat faster due to its denser composition, making it less efficient for thermal performance in pottery applications. The enhanced thermal resistance of ceramic foam makes it ideal for pottery that requires prolonged heat retention or protection against thermal shock.
Porosity and Breathability
Ceramic foam exhibits higher porosity compared to traditional terracotta, allowing for superior breathability and moisture regulation in pottery applications. The interconnected pore structure of ceramic foam enhances air and vapor permeability, making it ideal for plants and humid environments. Terracotta, while breathable due to its natural clay composition, has a denser structure with lower porosity, limiting airflow and drying speed relative to ceramic foam.
Strength, Durability, and Longevity
Ceramic foam offers superior strength and durability compared to traditional terracotta due to its porous, lightweight structure that resists cracking under thermal stress. Terracotta, while aesthetically appealing and cost-effective, is more prone to chipping and erosion over time when exposed to environmental factors. The longevity of ceramic foam pottery exceeds terracotta, making it ideal for functional and decorative pieces requiring enhanced resilience.
Artistic Flexibility and Design Potential
Ceramic foam offers enhanced artistic flexibility due to its lightweight structure and porous texture, allowing artists to experiment with sculptural forms and intricate details that terracotta's denser, more rigid composition cannot easily support. Terracotta provides a traditional, warm aesthetic favored for rustic and earthy designs, but its limitations in fine detail and fragility restrict complex or delicate artistry. The choice between ceramic foam and terracotta fundamentally impacts design potential, with ceramic foam enabling innovative textures and shapes while terracotta emphasizes classical, durable craftsmanship.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Ceramic foam is generally more expensive than terracotta due to its advanced manufacturing process and specialized properties, while terracotta remains affordable and widely accessible because of traditional production methods and abundant raw materials. Availability of ceramic foam is limited to specialized suppliers and industrial markets, contrasting with terracotta's widespread availability in local pottery stores and craft markets. Cost efficiency and easy access make terracotta the preferred choice for hobbyists and small-scale potters, whereas ceramic foam suits professionals seeking enhanced insulation and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic foam offers superior environmental benefits over traditional terracotta, as its production requires lower energy consumption and generates less CO2 emissions due to more efficient firing processes. Terracotta, while biodegradable and natural, often involves higher water usage and extensive clay mining, contributing to soil degradation and habitat disruption. The lightweight nature and durability of ceramic foam enhance sustainability by reducing transportation emissions and extending the lifecycle of pottery products.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Pottery Project
Ceramic foam offers high porosity and thermal insulation, making it ideal for pottery requiring efficient heat distribution and faster firing times. Terracotta provides a traditional aesthetic with natural iron content, offering durability and breathability suitable for rustic or functional pieces. Selecting between ceramic foam and terracotta depends on your project's thermal requirements, desired finish, and firing conditions.
Infographic: Ceramic foam vs Terracotta for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com