Refractory materials offer superior thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for high-temperature electrical insulators, while porcelain provides excellent dielectric properties and moisture resistance, enhancing insulation performance in humid conditions. Choosing between refractory and porcelain insulators depends on the specific electrical load, temperature requirements, and environmental exposure of the application.
Table of Comparison
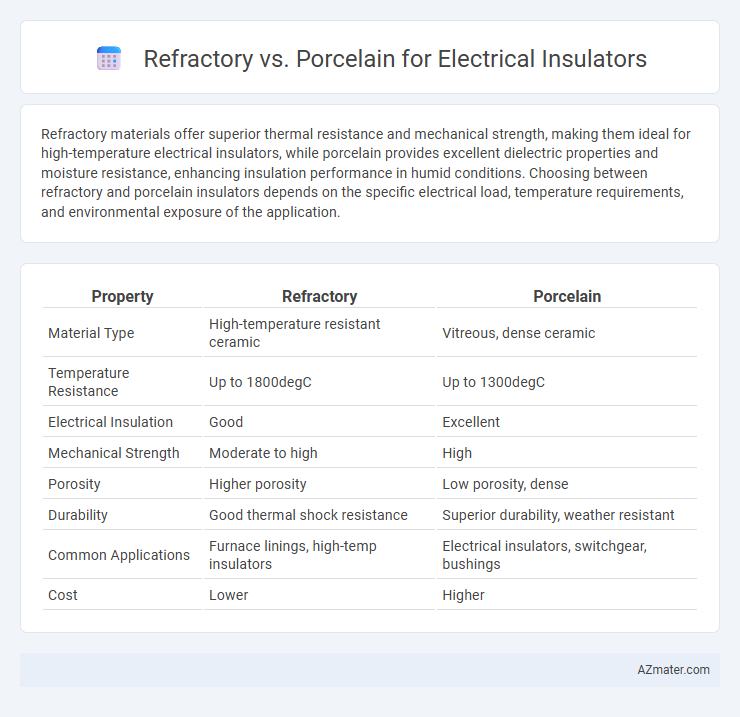
| Property | Refractory | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-temperature resistant ceramic | Vitreous, dense ceramic |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1800degC | Up to 1300degC |
| Electrical Insulation | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate to high | High |
| Porosity | Higher porosity | Low porosity, dense |
| Durability | Good thermal shock resistance | Superior durability, weather resistant |
| Common Applications | Furnace linings, high-temp insulators | Electrical insulators, switchgear, bushings |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are critical components in power transmission and distribution systems, designed to prevent the flow of electric current to unwanted areas, thereby ensuring safety and system reliability. Refractory materials and porcelain are both widely used insulator materials, with porcelain offering excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and moisture resistance, while refractory insulators are favored for their high-temperature endurance and resistance to thermal shock. Understanding the distinct properties of refractory versus porcelain insulators guides engineers in selecting the appropriate material based on environmental conditions and electrical stress requirements.
What Are Refractory Insulators?
Refractory insulators are materials designed to withstand extremely high temperatures while maintaining electrical insulation properties, commonly used in industrial furnaces and high-temperature electrical equipment. These insulators are typically composed of ceramic substances such as alumina or silica, known for their exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength. Unlike porcelain insulators, refractory insulators excel in environments where heat resistance is critical, providing reliable insulation under harsh thermal conditions.
What Are Porcelain Insulators?
Porcelain insulators are ceramic materials primarily composed of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, known for their high mechanical strength and excellent electrical insulation properties. Commonly used in high-voltage power lines and electrical equipment, porcelain insulators resist heat, moisture, and chemical corrosion, ensuring reliability in harsh environmental conditions. Their smooth, non-porous surface minimizes contamination and leakage currents, making them a preferred choice for outdoor electrical insulation applications.
Material Composition: Refractory vs Porcelain
Refractory electrical insulators are primarily composed of high-temperature resistant materials such as alumina, silica, and magnesia, designed to withstand extreme thermal conditions without degradation. Porcelain insulators consist mainly of kaolin clay, feldspar, and quartz, offering excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength but with lower thermal resistance compared to refractory materials. The material composition directly influences the applications, where refractory insulators suit high-heat environments, while porcelain is preferred for standard electrical insulation needs.
Electrical Properties Comparison
Refractory materials offer superior thermal resistance but generally have lower dielectric strength compared to porcelain insulators, which provide excellent electrical insulation and high dielectric strength suitable for high-voltage applications. Porcelain insulators exhibit low electrical conductivity and high withstand voltage, making them ideal for preventing current leakage and ensuring safety in electrical systems. The choice between refractory and porcelain depends on specific electrical performance requirements, with porcelain preferred for its stable insulating properties and refractory materials favored in high-temperature environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Refractory materials used in electrical insulators exhibit high mechanical strength due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. Porcelain insulators offer excellent mechanical durability with superior resistance to mechanical stress, impact, and environmental factors such as moisture and pollution. Comparing both, porcelain provides enhanced long-term performance in outdoor electrical systems, while refractory materials excel in high-temperature environments requiring robust thermal stability.
Thermal Performance Differences
Refractory materials exhibit superior thermal resistance compared to porcelain, making them suitable for high-temperature electrical insulator applications. Porcelain offers excellent dielectric properties but has lower thermal conductivity, limiting its performance under rapid temperature fluctuations. The thermal expansion coefficient of refractory insulators is typically lower than porcelain, reducing thermal stress and enhancing durability in extreme thermal environments.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Refractory materials generally offer a cost advantage over porcelain for electrical insulators due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making them a budget-friendly option for high-temperature applications. Porcelain insulators, while typically more expensive, provide superior electrical insulation properties and greater availability through well-established supply chains and standardized production. Cost analysis should weigh initial expenditure against long-term performance and availability factors, as refractory options may require more frequent replacement compared to durable porcelain insulators.
Typical Applications in Power Systems
Refractory materials are commonly used in high-temperature environments such as furnace linings and industrial heating equipment within power systems, where they provide excellent thermal insulation and resistance to thermal shock. Porcelain insulators dominate applications in overhead power lines, substations, and transformers due to their superior mechanical strength, electrical insulation properties, and weather resistance. The choice between refractory and porcelain depends on operational temperature ranges, mechanical load requirements, and environmental exposure in electrical power infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Insulator: Key Considerations
Choosing the right electrical insulator between refractory and porcelain depends on factors like thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and application environment. Porcelain insulators offer excellent dielectric strength and weather resistance, making them ideal for high-voltage outdoor use, while refractory insulators excel in extreme heat conditions due to their superior thermal stability. Evaluating the specific operational demands, such as temperature range, load requirements, and environmental exposure, ensures optimal performance and longevity of the electrical insulation system.
Infographic: Refractory vs Porcelain for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com