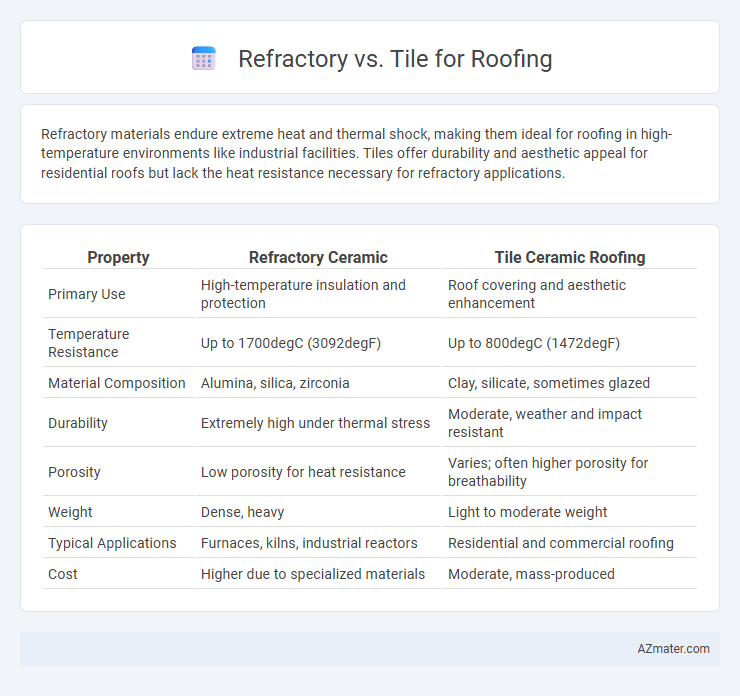
Refractory materials endure extreme heat and thermal shock, making them ideal for roofing in high-temperature environments like industrial facilities. Tiles offer durability and aesthetic appeal for residential roofs but lack the heat resistance necessary for refractory applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Refractory Ceramic | Tile Ceramic Roofing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-temperature insulation and protection | Roof covering and aesthetic enhancement |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1700degC (3092degF) | Up to 800degC (1472degF) |
| Material Composition | Alumina, silica, zirconia | Clay, silicate, sometimes glazed |
| Durability | Extremely high under thermal stress | Moderate, weather and impact resistant |
| Porosity | Low porosity for heat resistance | Varies; often higher porosity for breathability |
| Weight | Dense, heavy | Light to moderate weight |
| Typical Applications | Furnaces, kilns, industrial reactors | Residential and commercial roofing |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials | Moderate, mass-produced |
Introduction to Roofing Materials: Refractory vs Tile
Refractory materials and tiles are prominent choices in roofing, each offering distinct thermal resistance and durability characteristics. Refractory roofing excels in high-temperature environments due to its heat-resistant properties, making it ideal for industrial applications and harsh climates. Tile roofing, often made from clay or concrete, provides robust weather protection and aesthetic appeal while maintaining moderate thermal insulation suitable for residential and commercial buildings.
What Are Refractory Roofing Materials?
Refractory roofing materials are designed to withstand extremely high temperatures, making them ideal for industrial applications such as kilns, furnaces, and power plants. These materials include fire bricks, ceramic fibers, and castables that provide thermal insulation and resistance to thermal shock, abrasion, and chemical corrosion. Unlike traditional tile roofing, refractory materials offer superior durability in environments exposed to intense heat and harsh conditions.
Understanding Traditional Tile Roofing
Traditional tile roofing, made from clay or concrete, offers exceptional durability and natural insulation, making it a popular choice for residential homes in Mediterranean and Spanish-style architecture. Unlike refractory materials, which are designed to withstand extremely high temperatures in industrial settings, tile roofing focuses on weather resistance, longevity, and aesthetic appeal, often lasting over 50 years with minimal maintenance. The weight and installation method of tile roofs require sturdy roof framing and professional expertise to ensure proper alignment and waterproofing.
Comparative Durability: Refractory vs Tile Roofs
Refractory roofs typically offer superior durability compared to tile roofs due to their resistance to extreme temperatures, chemical corrosion, and mechanical wear. Tile roofs, while durable, are more prone to cracking and chipping under heavy impact or drastic temperature fluctuations. The long-term lifespan of refractory materials often surpasses traditional roofing tiles, making them ideal for industrial and high-heat environments.
Energy Efficiency: Insulation and Heat Resistance
Refractory roofing materials offer superior heat resistance and insulation properties, effectively reducing heat transfer and maintaining cooler interior temperatures in extreme weather. Tile roofing, especially clay and concrete tiles, provides excellent thermal mass, which helps regulate indoor temperature by absorbing and slowly releasing heat. Both materials enhance energy efficiency by minimizing reliance on artificial cooling and heating systems, but refractory materials typically outperform tiles in high-temperature environments due to their advanced heat resistance capabilities.
Cost Analysis: Refractory vs Tile Roof Installation
Refractory roofing systems typically incur higher upfront costs due to specialized materials and labor compared to traditional tile roofing, which offers a more cost-effective installation with widely available components. Tile roofs provide long-term value with lower maintenance expenses and increased durability, helping offset their initial installation cost. Analyzing total life cycle costs shows tile roofing as a financially preferable option in most residential and commercial roofing projects.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Refractory roofing materials offer superior heat resistance and durability, requiring minimal maintenance due to their robust composition, often lasting over 50 years under proper conditions. Tile roofing, especially clay or concrete tiles, demands regular inspections for cracks or displacement but provides excellent longevity, typically exceeding 40 years with timely upkeep. Both materials benefit from periodic cleaning and sealing to maintain structural integrity and weather resistance, though refractory roofs generally have lower maintenance frequency compared to tile roofs.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Refractory roofing materials offer a rustic, natural aesthetic with their rough texture and earthy tones, ideal for traditional and Mediterranean-style homes, while tiles provide a sleek, uniform appearance that suits modern and contemporary designs. Tile roofs come in a wide array of colors, shapes, and finishes, allowing for extensive design customization and the ability to create complex patterns and styles. Refractory materials typically lack the variety seen in tiles, limiting design flexibility but contributing unique character and thermal mass benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Refractory roofing materials, often made from fire-resistant ceramics or metals, boast high durability and energy efficiency by reflecting heat and reducing cooling costs, which lowers carbon emissions over their lifespan. Tile roofing, typically composed of clay or concrete, offers natural thermal insulation, promotes sustainable sourcing, and is fully recyclable, minimizing landfill waste and environmental degradation. Both options support sustainable building practices through longevity and reduced resource consumption, but tile roofing's biodegradability and lower embodied energy give it a greener edge in environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Roofing Material: Key Factors
Choosing between refractory and tile roofing materials depends on factors such as durability, thermal resistance, and cost. Refractory roofing excels in high-temperature environments due to its heat-resistant properties, making it ideal for industrial settings, while tile roofing offers aesthetic appeal and excellent weather resistance suited for residential buildings. Consider the building's exposure to heat, climate conditions, and budget constraints to ensure the selected material aligns with the roofing performance requirements.
Infographic: Refractory vs Tile for Roofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com