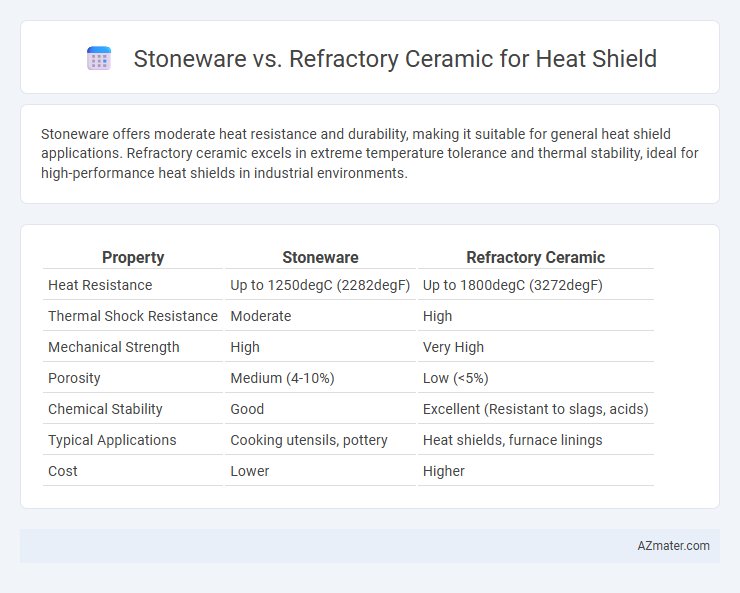
Stoneware offers moderate heat resistance and durability, making it suitable for general heat shield applications. Refractory ceramic excels in extreme temperature tolerance and thermal stability, ideal for high-performance heat shields in industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Stoneware | Refractory Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1250degC (2282degF) | Up to 1800degC (3272degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Very High |
| Porosity | Medium (4-10%) | Low (<5%) |
| Chemical Stability | Good | Excellent (Resistant to slags, acids) |
| Typical Applications | Cooking utensils, pottery | Heat shields, furnace linings |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction: Comparing Stoneware and Refractory Ceramic Heat Shields
Stoneware heat shields offer moderate thermal resistance and durability, commonly used in less extreme temperature environments due to their dense, vitrified structure. Refractory ceramic heat shields provide superior thermal insulation and withstand extreme temperatures up to 1700degC, making them ideal for industrial applications such as furnaces and aerospace components. The key difference lies in refractory ceramics' ability to maintain structural integrity under prolonged high heat exposure, unlike stoneware which may crack or degrade.
Material Composition and Properties
Stoneware heat shields primarily consist of dense clay combined with fluxes, fired at high temperatures to achieve strong thermal resistance and mechanical durability. Refractory ceramics contain specialized alumina, silica, and other oxides engineered to withstand extreme temperatures exceeding 1500degC while maintaining structural integrity and low thermal conductivity. The superior chemical stability and thermal shock resistance of refractory ceramics make them more suitable than stoneware for prolonged exposure in high-heat shielding applications.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Conductivity
Stoneware exhibits moderate heat resistance withstanding temperatures up to approximately 1200degC, while refractory ceramics endure much higher temperatures, often exceeding 1600degC, making them superior for extreme heat shields. Thermal conductivity in stoneware is relatively low, providing good insulation but less efficiency compared to refractory ceramics that combine low thermal conductivity with enhanced heat durability. Refractory ceramics are engineered for thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, positioning them as the preferred material for advanced heat shield applications requiring prolonged exposure to extreme heat.
Durability and Lifespan
Stoneware exhibits high durability and moderate heat resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring thermal insulation but less effective under extreme temperatures compared to refractory ceramics. Refractory ceramics are engineered to withstand thermal shock, high temperatures exceeding 1500degC, and corrosive environments, resulting in a significantly longer lifespan in heat shield applications. The superior chemical stability and mechanical strength of refractory ceramics ensure optimal performance and durability in industrial and aerospace heat shield uses.
Performance Under Extreme Temperatures
Stoneware exhibits moderate thermal resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 1200degC, making it suitable for general high-heat applications but limited in extreme environments. Refractory ceramics, engineered for superior thermal stability, endure temperatures exceeding 1600degC without significant deformation or thermal shock, ensuring reliable performance in advanced heat shield applications. Their microstructure and composition enhance insulating properties and resistance to thermal fatigue, critical for protecting sensitive components in aerospace and industrial settings.
Practical Applications in Heat Shields
Stoneware offers high durability and moderate thermal resistance, making it suitable for heat shields in low- to medium-temperature applications such as cooking appliances and industrial ovens. Refractory ceramics exhibit superior thermal insulation and can withstand extreme temperatures exceeding 1,700degC, ideal for aerospace, automotive, and furnace linings. Practical applications favor refractory ceramics for high-heat environments due to their resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, while stoneware is cost-effective for less demanding heat shield requirements.
Weight and Structural Considerations
Stoneware offers moderate weight and durability, making it suitable for heat shields where balanced thermal insulation and structural integrity are necessary. Refractory ceramic, significantly lighter and engineered for high thermal resistance, provides enhanced strength under extreme temperatures with minimal thermal expansion. Weight savings from refractory ceramics improve overall system performance, while stoneware's robustness supports structural stability in heat shield applications.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Stoneware offers a cost-effective solution for heat shields due to its widespread availability and lower manufacturing expenses compared to refractory ceramics. Refractory ceramics provide superior thermal resistance and durability but come at a higher cost and limited accessibility due to specialized production processes. Choosing between them depends on balancing budget constraints with the desired performance in high-temperature applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Stoneware heat shields, made from natural clay with minimal processing, generally have a lower environmental impact due to reduced energy consumption and lower emissions during production. Refractory ceramics involve high-temperature sintering of specialized materials, resulting in greater energy use and higher carbon footprint but offer enhanced durability and longer lifespan, which can justify their sustainability in long-term applications. Both materials can be recycled or repurposed, but stoneware's biodegradability and natural composition make it more eco-friendly for disposal or reuse.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Material for Your Heat Shield
Stoneware offers excellent thermal shock resistance and durability, making it suitable for moderate heat shield applications requiring strength and affordability. Refractory ceramics, with superior high-temperature tolerance and minimal thermal expansion, are ideal for extreme heat environments demanding long-term stability and insulation. Selecting the right material depends on the heat shield's operating temperature, mechanical stress, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Stoneware vs Refractory Ceramic for Heat Shield
 azmater.com
azmater.com