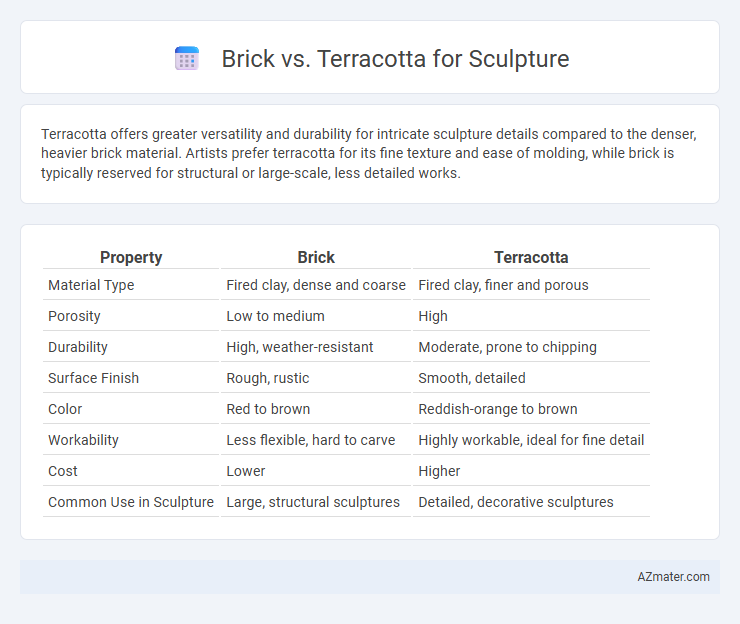
Terracotta offers greater versatility and durability for intricate sculpture details compared to the denser, heavier brick material. Artists prefer terracotta for its fine texture and ease of molding, while brick is typically reserved for structural or large-scale, less detailed works.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Brick | Terracotta |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Fired clay, dense and coarse | Fired clay, finer and porous |
| Porosity | Low to medium | High |
| Durability | High, weather-resistant | Moderate, prone to chipping |
| Surface Finish | Rough, rustic | Smooth, detailed |
| Color | Red to brown | Reddish-orange to brown |
| Workability | Less flexible, hard to carve | Highly workable, ideal for fine detail |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Use in Sculpture | Large, structural sculptures | Detailed, decorative sculptures |
Introduction to Brick and Terracotta in Sculpture
Brick and terracotta are both traditional materials used in sculpture, valued for their durability and versatility. Brick, typically fired clay shaped into rectangular blocks, offers a robust structure ideal for large-scale or architectural sculptures. Terracotta, a variant of fired clay, is prized for its fine-grained texture and warm, reddish-brown hue, allowing for detailed and expressive sculptural works.
Historical Use of Brick and Terracotta in Art
Brick and terracotta have been integral in sculpture since ancient civilizations, with brick widely used in Mesopotamian and Indus Valley architecture for reliefs and monumental forms, showcasing durability and structural versatility. Terracotta, favored in Greek, Etruscan, and Chinese art, allowed for intricate detailing and mass production of decorative and religious figures due to its malleability and kiln-fired hardness. Both materials represent distinct artistic traditions, with brick emphasizing architectural grandeur and terracotta highlighting fine craftsmanship and accessibility.
Material Composition and Properties
Brick sculptures are primarily made from clay mixed with sand and fired at high temperatures, resulting in a dense, durable material with moderate porosity and a reddish-brown hue. Terracotta, composed mainly of fine-grained clay fired at lower temperatures than brick, offers a smoother texture, greater plasticity, and enhanced porosity, which allows for detailed modeling and natural thermal regulation. The choice between brick and terracotta depends on the desired aesthetic finish, durability requirements, and environmental exposure, with terracotta favored for intricate designs and brick preferred for structural robustness.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Terracotta sculptures exhibit superior durability in moist environments compared to bricks, as terracotta is fired at higher temperatures, making it more resistant to weathering and erosion. Brick sculptures, often made from clay with added materials, can be more porous and susceptible to cracking over time when exposed to freeze-thaw cycles. Both materials benefit from proper sealing, but terracotta's dense composition ensures greater longevity for outdoor sculptures.
Aesthetic Qualities and Finishing Options
Brick sculptures exhibit a rustic, earthy aesthetic with natural color variations and a coarse texture that enhances architectural integration, while terracotta offers a smoother, finer surface conducive to intricate detailing and vibrant glazes. Terracotta's malleability allows for delicate finishes and ornamental designs, making it ideal for expressive, lifelike forms, whereas brick's robust composition emphasizes solidity and traditional craftsmanship. Finishing options for terracotta include polishing, glazing, and painting to enrich color and shine, whereas brick sculptures often retain their raw, matte finish or may be sealed to protect against weathering without altering the natural texture.
Suitability for Different Sculpture Types
Brick offers durability and structural support suitable for large-scale outdoor sculptures and architectural elements, withstands weathering, and provides a rough texture ideal for abstract or geometric forms. Terracotta, composed of refined clay fired at lower temperatures, excels in detailed, intricate sculptures, allowing for fine lines and delicate features, making it preferred for figurative and ornamental works. Both materials suit different artistic intents: brick supports monumental and rugged styles, while terracotta caters to detailed, smaller-scale sculptures requiring precision and subtlety.
Cost and Accessibility Analysis
Brick sculptures generally offer lower costs due to abundant raw materials and straightforward manufacturing processes, making them accessible for large-scale or budget-conscious projects. Terracotta, while also molded from clay, involves higher expenses because of specialized firing techniques and quality control required for artistic detail and durability. Accessibility to terracotta may be limited by regional kiln availability and artisan expertise, whereas bricks are widely produced and distributed globally.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Terracotta sculptures, made from natural clay, offer a biodegradable and energy-efficient alternative compared to fired bricks, which require higher kilning temperatures, resulting in greater carbon emissions. Bricks often involve intensive mining processes that can degrade ecosystems, whereas terracotta sourcing typically has a lower environmental footprint due to its raw material abundance and lower processing energy. Choosing terracotta enhances sustainability by supporting materials with minimal chemical additives and promoting eco-friendly manufacturing practices, reducing long-term environmental harm.
Maintenance and Restoration Needs
Brick sculptures demand regular sealing to prevent water absorption and cracking, with repairs often requiring mortar replacement and color matching to maintain integrity. Terracotta sculptures need careful handling due to their porous nature, necessitating periodic cleaning and crack stabilization, often restored using specialized adhesives to preserve the original texture and color. Both materials require climate-controlled environments to minimize deterioration but terracotta generally demands more delicate restoration techniques due to its brittleness.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Sculpture
Choosing between brick and terracotta for sculpture depends on factors like durability, texture, and aesthetic goals. Brick offers robust structural strength and weather resistance, ideal for large outdoor installations, while terracotta provides finer detail and a warm, natural finish suited for intricate, indoor works. Consider the sculpture's environment, desired detail level, and longevity to select the material that best aligns with your artistic vision and practical needs.
Infographic: Brick vs Terracotta for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com