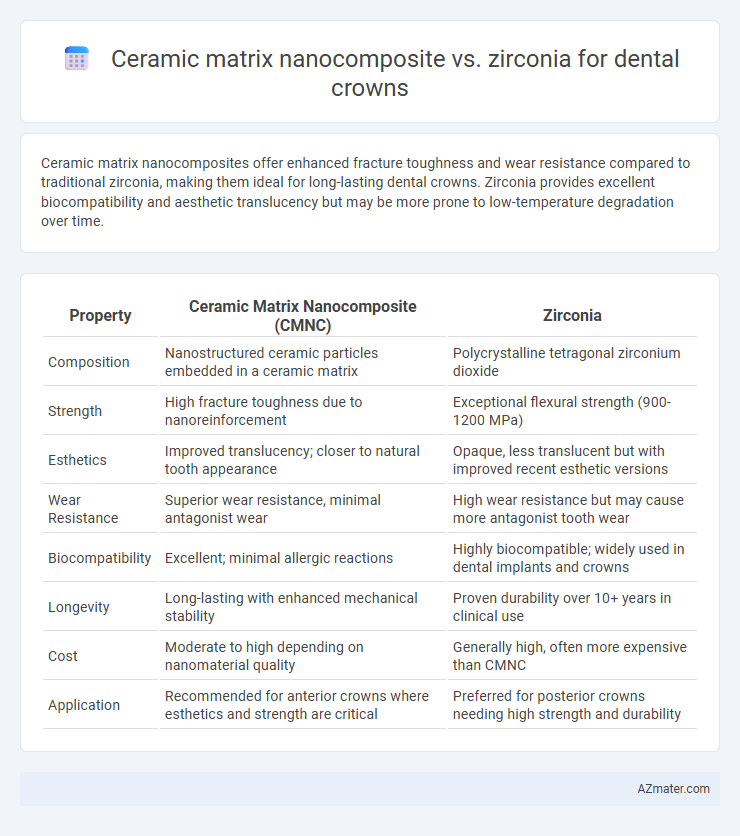
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites offer enhanced fracture toughness and wear resistance compared to traditional zirconia, making them ideal for long-lasting dental crowns. Zirconia provides excellent biocompatibility and aesthetic translucency but may be more prone to low-temperature degradation over time.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Matrix Nanocomposite (CMNC) | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Nanostructured ceramic particles embedded in a ceramic matrix | Polycrystalline tetragonal zirconium dioxide |
| Strength | High fracture toughness due to nanoreinforcement | Exceptional flexural strength (900-1200 MPa) |
| Esthetics | Improved translucency; closer to natural tooth appearance | Opaque, less translucent but with improved recent esthetic versions |
| Wear Resistance | Superior wear resistance, minimal antagonist wear | High wear resistance but may cause more antagonist tooth wear |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent; minimal allergic reactions | Highly biocompatible; widely used in dental implants and crowns |
| Longevity | Long-lasting with enhanced mechanical stability | Proven durability over 10+ years in clinical use |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on nanomaterial quality | Generally high, often more expensive than CMNC |
| Application | Recommended for anterior crowns where esthetics and strength are critical | Preferred for posterior crowns needing high strength and durability |
Introduction to Dental Crown Materials
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites offer enhanced mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to traditional zirconia crowns, making them suitable for high-stress dental applications. Zirconia remains a popular choice due to its excellent biocompatibility, translucency, and ability to withstand occlusal forces. Both materials play critical roles in dental crown fabrication, balancing aesthetic demands with functional durability for long-term oral health.
Overview of Ceramic Matrix Nanocomposites
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites (CMNCs) for dental crowns combine nanoscale reinforcements such as silicon carbide or alumina nanoparticles within a ceramic matrix, significantly enhancing mechanical properties like fracture toughness and wear resistance compared to traditional zirconia. Their nano-engineered microstructure provides superior bond strength to dental adhesives, reducing the risk of crown debonding and improving long-term durability in oral environments. Studies show CMNCs exhibit improved esthetics and translucency over conventional zirconia, making them favorable for posterior and anterior crown restorations.
Properties of Zirconia for Dental Applications
Zirconia exhibits outstanding mechanical properties such as high fracture toughness (9-10 MPa*m^0.5) and flexural strength (900-1,200 MPa), making it highly suitable for dental crowns exposed to substantial masticatory forces. Its excellent biocompatibility and low plaque affinity promote gum health and reduce inflammation risk around the restoration. The material's inherent esthetic qualities include translucency and color stability, closely mimicking natural tooth enamel for superior cosmetic outcomes in dental applications.
Strength and Fracture Resistance Comparison
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites exhibit enhanced strength and fracture resistance compared to traditional zirconia, due to the incorporation of nanoscale reinforcements that improve toughness and crack deflection. Zirconia, known for its high flexural strength around 900-1200 MPa, remains a strong candidate but can be more brittle under tensile stress than composite alternatives. Nanocomposites typically demonstrate improved damage tolerance and fatigue resistance, making them increasingly preferred for durable dental crowns subjected to chewing forces.
Aesthetic Performance: Natural Look and Color Stability
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites offer superior aesthetic performance for dental crowns due to their enhanced translucency and ability to mimic the natural enamel's optical properties. Zirconia provides high strength but tends to exhibit less translucency and may show slight color changes over time, impacting long-term aesthetic stability. The advanced nanostructure in ceramic matrix nanocomposites ensures better color retention and a more lifelike appearance, making them preferable for visible anterior restorations.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to zirconia due to their reduced ion release and enhanced cellular response, minimizing allergic reactions and inflammation. Zirconia crowns, while durable, can sometimes provoke localized tissue irritation or sensitivity due to surface roughness and phase transformation under stress. Patient safety is enhanced with ceramic matrix nanocomposites through improved integration with oral tissues and lower risks of hypersensitivity or long-term cytotoxicity.
Wear Resistance and Longevity of Dental Crowns
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites exhibit superior wear resistance compared to traditional zirconia crowns due to their enhanced microstructure incorporating nanoscale fillers, which improve hardness and reduce surface roughness. Zirconia crowns, while highly durable and biocompatible, may experience low-temperature degradation leading to compromised longevity under oral conditions. The increased wear resistance and structural stability of ceramic matrix nanocomposites contribute to extended lifespan and consistent performance in dental crown applications.
Ease of Fabrication and Clinical Handling
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites offer enhanced machinability and faster fabrication times compared to zirconia, facilitating efficient dental crown production. Their improved toughness and crack resistance allow for easier intraoral adjustments and reduced risk of chipping during clinical handling. Zirconia, while highly durable, often requires more precise milling and sintering processes, making its fabrication more complex and handling less forgiving in chairside procedures.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites offer enhanced durability and resistance to wear, making them a cost-effective option for dental crowns due to their extended lifespan and reduced need for replacements. Zirconia crowns are widely accessible and popular for their high strength and aesthetic appeal, but their higher initial cost may limit affordability for some patients. The choice between these materials depends on balancing upfront expenses with long-term benefits, where ceramic matrix nanocomposites provide a promising alternative for budget-sensitive dental care.
Recommendations for Clinical Selection
Ceramic matrix nanocomposites offer enhanced fracture toughness and wear resistance compared to traditional zirconia, making them suitable for patients with high occlusal loads and bruxism. Zirconia remains preferred for its superior translucency and biocompatibility, especially in anterior crowns where esthetics are paramount. Clinical selection should consider patient-specific factors such as bite force, esthetic demands, and potential allergic reactions to optimize long-term crown performance.
Infographic: Ceramic matrix nanocomposite vs Zirconia for Dental crown
 azmater.com
azmater.com