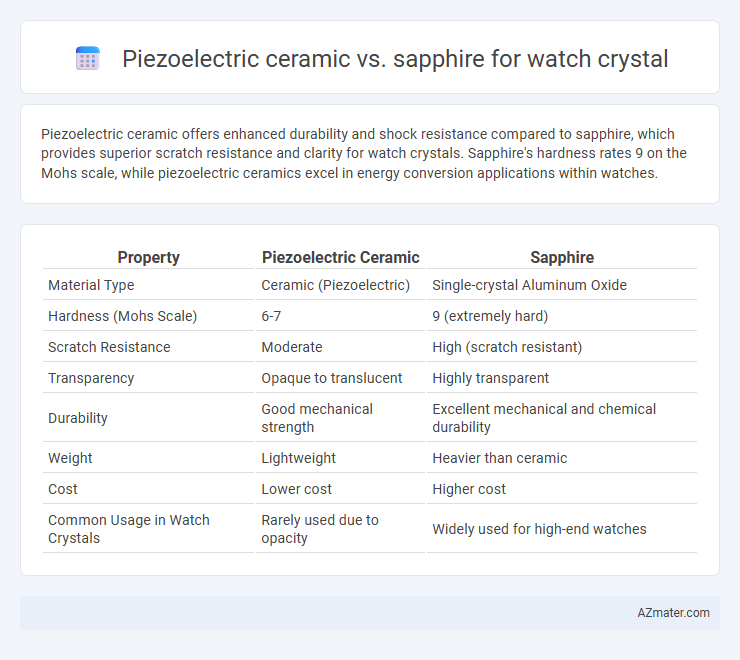
Piezoelectric ceramic offers enhanced durability and shock resistance compared to sapphire, which provides superior scratch resistance and clarity for watch crystals. Sapphire's hardness rates 9 on the Mohs scale, while piezoelectric ceramics excel in energy conversion applications within watches.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Piezoelectric Ceramic | Sapphire |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ceramic (Piezoelectric) | Single-crystal Aluminum Oxide |
| Hardness (Mohs Scale) | 6-7 | 9 (extremely hard) |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | High (scratch resistant) |
| Transparency | Opaque to translucent | Highly transparent |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength | Excellent mechanical and chemical durability |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than ceramic |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Usage in Watch Crystals | Rarely used due to opacity | Widely used for high-end watches |
Introduction to Watch Crystal Materials
Piezoelectric ceramics offer durability and scratch resistance through their crystalline structure, making them a cost-effective option for watch crystals. Sapphire, renowned for its exceptional hardness ranking 9 on the Mohs scale, provides superior scratch resistance and clarity, often used in high-end watches. The choice between piezoelectric ceramic and sapphire depends on balancing factors like hardness, transparency, cost, and resistance to everyday wear.
Overview of Piezoelectric Ceramic Crystals
Piezoelectric ceramic crystals in watch crystals offer excellent sensitivity and durability due to their ability to generate an electric charge under mechanical stress, enhancing timekeeping accuracy. These ceramics provide superior shock resistance compared to sapphire, which is known for its hardness but brittleness. Their unique electro-mechanical properties improve the precision of quartz movements and contribute to the longevity of the watch crystal under various conditions.
Properties of Sapphire Crystals
Sapphire crystals exhibit exceptional hardness, ranking 9 on the Mohs scale, which provides superior scratch resistance compared to piezoelectric ceramic materials commonly used in watch crystals. The optical clarity of sapphire ensures high transparency and minimal distortion, enhancing the readability of watch dials under various lighting conditions. Additionally, sapphire's excellent chemical inertness and thermal stability make it highly durable, maintaining its structural integrity and appearance over prolonged exposure to environmental stress.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Piezoelectric ceramic watch crystals offer high durability due to their impact resistance and flexibility, making them less prone to shattering compared to sapphire. Sapphire crystals excel in scratch resistance with a hardness rating of 9 on the Mohs scale, significantly outperforming most ceramics which typically have lower hardness. While sapphire provides superior scratch protection, piezoelectric ceramics deliver enhanced durability against drops and impact, balancing toughness and performance in watch crystal applications.
Optical Clarity and Transparency
Piezoelectric ceramic watch crystals offer decent optical clarity but generally fall short in transparency compared to sapphire, which is renowned for its exceptional clarity and near-perfect transparency. Sapphire crystals exhibit superior scratch resistance and minimal light distortion, delivering unparalleled visibility and durability in watch faces. This makes sapphire the preferred choice for luxury watches seeking optimal optical performance and long-lasting transparency.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Piezoelectric ceramic watch crystals are significantly lighter than sapphire, enhancing overall wrist comfort during extended wear. Their reduced density contributes to a less bulky feel, making them ideal for sporty or daily-use watches. In contrast, sapphire crystals, while heavier, provide unmatched scratch resistance but may add noticeable weight that affects comfort, especially in larger timepieces.
Cost Differences Between Piezoelectric Ceramic and Sapphire
Piezoelectric ceramic watch crystals typically cost less than sapphire counterparts due to lower material and manufacturing expenses, making them a budget-friendly option for timepieces. Sapphire crystals offer superior scratch resistance and durability but require more complex processing, which significantly raises their price. The cost differential often influences consumer choice, balancing affordability with performance and longevity.
Impact Resistance and Longevity
Piezoelectric ceramic watch crystals offer superior impact resistance due to their ability to absorb and dissipate mechanical shocks effectively, making them less prone to cracking under sudden impacts compared to sapphire. Sapphire crystals provide exceptional scratch resistance and hardness, enhancing longevity in terms of surface durability but are more brittle and susceptible to shattering upon hard impacts. The choice between piezoelectric ceramic and sapphire hinges on prioritizing either impact resilience or long-term surface integrity in watch crystal applications.
Application Suitability in Different Watch Types
Piezoelectric ceramic offers excellent shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for sports and dive watches requiring high impact tolerance. Sapphire crystal excels in scratch resistance and clarity, preferred in luxury and dress watches where aesthetic longevity is crucial. Both materials suit different watch types by balancing robustness and optical quality according to usage conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Watch Crystal Material
Piezoelectric ceramic offers excellent durability and scratch resistance, making it a reliable choice for active lifestyles and sports watches. Sapphire crystals provide superior clarity and exceptional hardness, delivering premium scratch resistance and a clearer view of the dial, ideal for luxury and high-end timepieces. Selecting the best watch crystal material depends on whether durability and cost-effectiveness or optical clarity and luxury appeal are the top priorities.
Infographic: Piezoelectric ceramic vs Sapphire for Watch crystal
 azmater.com
azmater.com